A Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB) provides comprehensive visibility and control over cloud service usage, enforcing security policies across multiple cloud platforms to protect sensitive data. A Web Application Firewall (WAF) specifically focuses on monitoring and filtering HTTP traffic to protect web applications from attacks such as SQL injection and cross-site scripting. While CASBs secure overall cloud interactions, WAFs offer targeted protection at the web application layer, making them complementary tools in a robust security strategy.
Table of Comparison
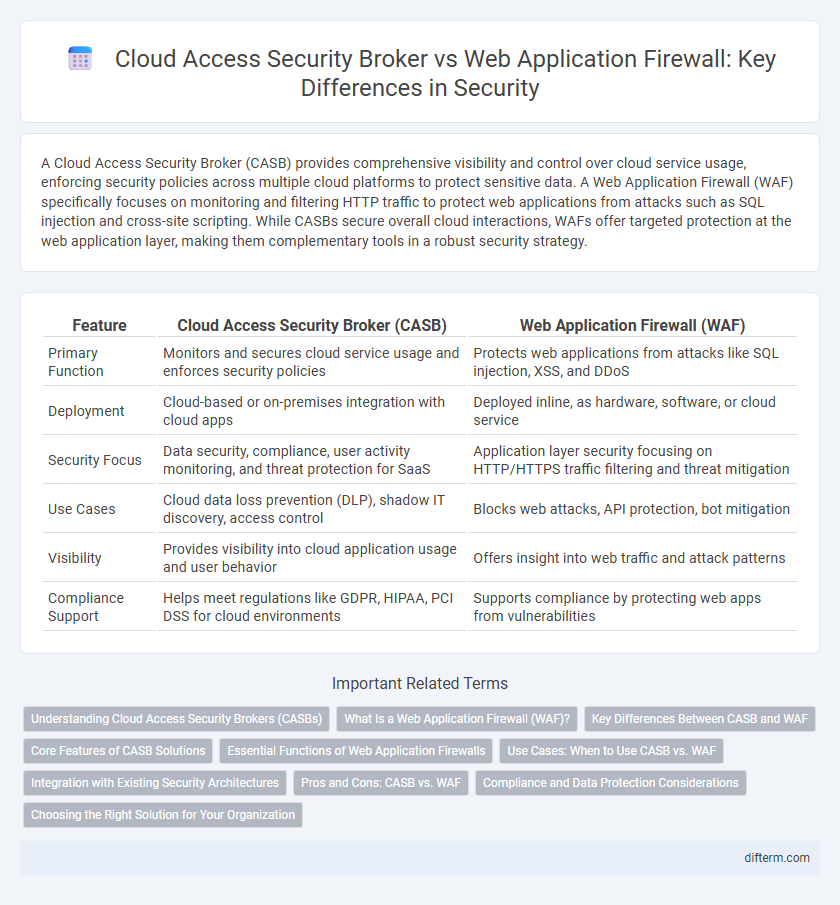
| Feature | Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB) | Web Application Firewall (WAF) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Monitors and secures cloud service usage and enforces security policies | Protects web applications from attacks like SQL injection, XSS, and DDoS |
| Deployment | Cloud-based or on-premises integration with cloud apps | Deployed inline, as hardware, software, or cloud service |
| Security Focus | Data security, compliance, user activity monitoring, and threat protection for SaaS | Application layer security focusing on HTTP/HTTPS traffic filtering and threat mitigation |
| Use Cases | Cloud data loss prevention (DLP), shadow IT discovery, access control | Blocks web attacks, API protection, bot mitigation |
| Visibility | Provides visibility into cloud application usage and user behavior | Offers insight into web traffic and attack patterns |
| Compliance Support | Helps meet regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS for cloud environments | Supports compliance by protecting web apps from vulnerabilities |
Understanding Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs)
Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs) provide visibility and control over data and user activities across multiple cloud services, enforcing security policies and compliance requirements. Unlike Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) that primarily protect web applications from threats such as SQL injection or cross-site scripting, CASBs focus on securing cloud access, including authentication, data loss prevention, and shadow IT discovery. CASBs integrate with cloud platforms via APIs or proxies to monitor and secure data in real time, ensuring comprehensive cloud security beyond traditional perimeter defenses.
What Is a Web Application Firewall (WAF)?
A Web Application Firewall (WAF) is a security solution that monitors, filters, and blocks HTTP traffic to and from a web application to protect against common threats such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and other web attacks. Unlike Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs), which primarily secure cloud service usage and enforce access policies across multiple cloud platforms, WAFs are specifically designed to safeguard web applications by analyzing and filtering incoming traffic at the application layer. WAFs use predefined rule sets and behavioral analysis to detect and mitigate malicious activities in real-time, ensuring application availability and data integrity.
Key Differences Between CASB and WAF
Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASB) provide comprehensive visibility and control over cloud service usage by monitoring user activities, enforcing data security policies, and preventing insider threats, whereas Web Application Firewalls (WAF) primarily protect web applications by filtering and monitoring HTTP traffic to block malicious attacks such as SQL injection and cross-site scripting. CASB operates at the cloud service layer, enabling data loss prevention (DLP), encryption, and compliance management across various SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS environments, while WAF functions at the application layer, focusing on real-time threat detection and mitigation for specific web applications. The key differences lie in their scope, with CASB delivering broad cloud security and governance capabilities, and WAF providing targeted, application-specific protection against external cyber threats.
Core Features of CASB Solutions
Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs) provide core features such as visibility into cloud service usage, data loss prevention (DLP), and threat protection by enforcing security policies across multiple cloud platforms. CASBs offer granular control over user activities, enabling encryption, tokenization, and access management to safeguard sensitive data in real-time. These solutions integrate with identity providers and security information event management (SIEM) systems to enhance compliance and detect anomalous behavior within cloud environments.
Essential Functions of Web Application Firewalls
Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) primarily protect web applications by filtering, monitoring, and blocking malicious HTTP/HTTPS traffic to prevent attacks such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and file inclusion. WAFs enforce security policies at the application layer, providing real-time traffic inspection and anomaly detection to safeguard against zero-day exploits and known vulnerabilities. Unlike Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs), WAFs focus on web application security, ensuring continuous protection and compliance by examining inbound and outbound web traffic for threats.
Use Cases: When to Use CASB vs. WAF
Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs) are essential for enforcing security policies across cloud services, ensuring data protection, compliance, and threat detection in environments with multiple cloud applications. Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) specialize in protecting web applications by filtering and monitoring HTTP traffic to prevent attacks like SQL injection, cross-site scripting, and application-layer DDoS. Use CASBs when managing security and visibility for cloud usage at a user and data level, while WAFs are ideal for defending specific web applications against external application-layer threats.
Integration with Existing Security Architectures
Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs) seamlessly integrate with existing security architectures by bridging gaps between on-premises infrastructure and cloud environments, enabling unified policy enforcement across multiple cloud services. Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) primarily protect web applications at the application layer, integrating through direct deployment in front of web servers or via reverse proxy configurations to filter and monitor HTTP traffic. Organizations often deploy CASBs alongside WAFs for comprehensive protection, leveraging CASBs for broad cloud access control and WAFs for specialized web traffic inspection.
Pros and Cons: CASB vs. WAF
Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs) provide comprehensive visibility and control over user activities across multiple cloud services, addressing data security, compliance, and threat protection with fine-grained policies, but they can be complex to manage and may introduce latency. Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) specialize in protecting web applications from common attacks like SQL injection and cross-site scripting by filtering and monitoring HTTP traffic, offering strong protection against application-layer threats but limited visibility beyond web traffic. CASBs excel in cloud service governance and data loss prevention, while WAFs are essential for real-time application-specific defense, thus organizations often deploy both for a layered security approach.
Compliance and Data Protection Considerations
Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs) provide comprehensive visibility and control over cloud service usage, ensuring compliance with industry regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA by enforcing data loss prevention (DLP) policies and user authentication. Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) specifically protect web applications from attacks like SQL injection and cross-site scripting, helping maintain compliance with standards like PCI DSS by securing sensitive customer data during web transactions. Combining CASB and WAF solutions enhances overall data protection by covering both cloud service access and application-layer threats, ensuring robust compliance management.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Organization
A Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB) provides comprehensive visibility and control over cloud applications, enforcing security policies across multiple cloud services, making it ideal for organizations with extensive cloud adoption. A Web Application Firewall (WAF) specifically protects web applications by filtering and monitoring HTTP traffic to prevent attacks like SQL injection and cross-site scripting, suitable for those focused on safeguarding web-facing assets. Selecting the right solution depends on your organization's security requirements, cloud usage patterns, and the specific threats you aim to mitigate.
cloud access security broker vs web application firewall Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com