Biometric authentication offers enhanced security by using unique physical traits such as fingerprints or facial recognition, reducing the risk of credential theft associated with password authentication. Passwords can be vulnerable to hacking, phishing, and brute-force attacks, whereas biometrics provide a more reliable and convenient method for user verification. Integrating biometric systems enhances overall security posture by minimizing reliance on easily compromised password credentials.
Table of Comparison
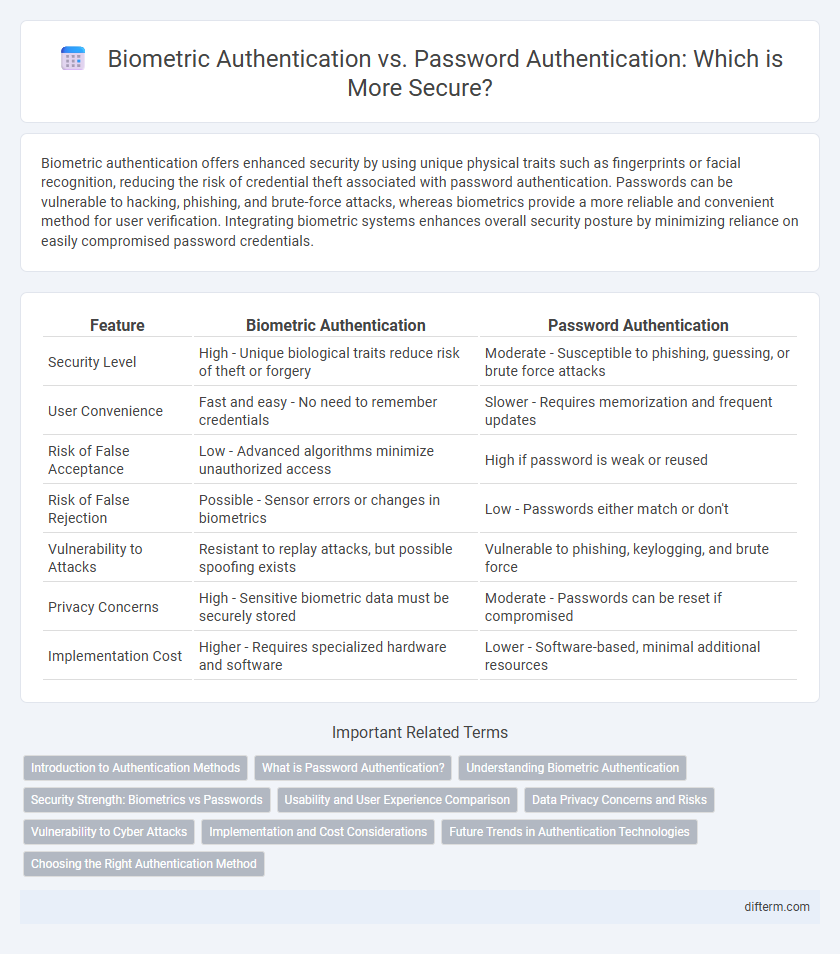
| Feature | Biometric Authentication | Password Authentication |
|---|---|---|
| Security Level | High - Unique biological traits reduce risk of theft or forgery | Moderate - Susceptible to phishing, guessing, or brute force attacks |
| User Convenience | Fast and easy - No need to remember credentials | Slower - Requires memorization and frequent updates |
| Risk of False Acceptance | Low - Advanced algorithms minimize unauthorized access | High if password is weak or reused |
| Risk of False Rejection | Possible - Sensor errors or changes in biometrics | Low - Passwords either match or don't |
| Vulnerability to Attacks | Resistant to replay attacks, but possible spoofing exists | Vulnerable to phishing, keylogging, and brute force |
| Privacy Concerns | High - Sensitive biometric data must be securely stored | Moderate - Passwords can be reset if compromised |
| Implementation Cost | Higher - Requires specialized hardware and software | Lower - Software-based, minimal additional resources |
Introduction to Authentication Methods
Biometric authentication leverages unique physical or behavioral traits, such as fingerprints or facial recognition, to verify identity, providing higher security compared to traditional password authentication. Password authentication relies on memorized alphanumeric codes, which are vulnerable to theft, guessing, and phishing attacks. Advances in biometric sensors and machine learning algorithms enhance accuracy and reduce fraud, making biometric methods increasingly preferred in secure access systems.
What is Password Authentication?
Password authentication is a security mechanism that verifies a user's identity by requiring a secret string of characters, such as letters, numbers, and symbols. It relies on the principle of knowledge-based authentication, where access is granted only if the entered password matches the stored credentials in the system. Despite its widespread use, password authentication is vulnerable to risks like brute force attacks, phishing, and password reuse, prompting the need for stronger security measures.
Understanding Biometric Authentication
Biometric authentication leverages unique physiological traits such as fingerprints, facial recognition, and iris scans to verify identity, offering higher security than traditional password authentication. Unlike passwords that can be stolen, forgotten, or guessed, biometric data is inherently tied to the individual, reducing the risk of unauthorized access. Advanced biometric systems use machine learning algorithms to enhance accuracy and prevent spoofing, making biometric authentication a reliable and user-friendly security solution.
Security Strength: Biometrics vs Passwords
Biometric authentication offers superior security strength by relying on unique physiological traits such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris patterns, which are difficult to replicate or steal compared to traditional passwords. Password authentication is vulnerable to common attacks like phishing, brute force, and credential stuffing, making it less reliable in protecting sensitive information. The integration of biometrics with multi-factor authentication significantly enhances security by combining something you are with something you know or have.
Usability and User Experience Comparison
Biometric authentication provides a seamless and faster user experience by leveraging unique physiological traits such as fingerprints or facial recognition, reducing the need to remember complex passwords. Password authentication often results in user frustration due to frequent resets, forgotten credentials, and susceptibility to weak password creation, negatively impacting usability. Combining biometric systems with password alternatives enhances security while maintaining ease of access and improving overall user satisfaction.
Data Privacy Concerns and Risks
Biometric authentication enhances security by using unique physical traits, reducing the risk of password theft and reuse, but it raises significant data privacy concerns due to the sensitive nature of biometric data and the potential for irreversible identity compromise if breached. Password authentication, while susceptible to hacking and phishing attacks, offers users more control over their credentials and the ability to change passwords regularly to mitigate risks. The trade-off between convenience and privacy emphasizes the need for robust encryption and strict data protection policies to safeguard biometric information and minimize unauthorized access.
Vulnerability to Cyber Attacks
Biometric authentication significantly reduces vulnerability to cyber attacks compared to password authentication, as biometric data like fingerprints and facial recognition cannot be easily guessed, stolen, or brute-forced. Password authentication remains highly susceptible to phishing, keylogging, and credential stuffing attacks due to weak or reused passwords. However, biometric systems can face risks through spoofing or sensor hacking, but advanced anti-spoofing technologies and multi-factor authentication enhance overall security robustness.
Implementation and Cost Considerations
Biometric authentication requires specialized hardware such as fingerprint scanners or facial recognition cameras, which increases initial setup costs but enhances security by reducing risks of stolen or guessed credentials. Password authentication systems have lower upfront expenses since they rely on existing input devices but necessitate ongoing costs for password management, policies, and risk mitigation against phishing or brute-force attacks. Implementing biometrics involves integrating software capable of processing biometric data securely, whereas passwords depend on scalable backend infrastructure and regular user education to maintain effectiveness.
Future Trends in Authentication Technologies
Biometric authentication technologies, such as fingerprint scanning, facial recognition, and voice identification, are rapidly advancing with the integration of AI and machine learning algorithms to enhance accuracy and reduce false positives. Password authentication is increasingly being supplemented or replaced by multi-factor authentication methods combining biometrics with token-based or behavioral data to strengthen security frameworks. Future trends indicate a shift toward passwordless environments leveraging continuous authentication and decentralized identity management systems to improve user experience and mitigate cyber threats.
Choosing the Right Authentication Method
Biometric authentication offers enhanced security by utilizing unique physiological traits such as fingerprints or facial recognition, reducing the risk of password theft and unauthorized access. Password authentication remains widely used due to its simplicity and ease of implementation but is vulnerable to phishing, brute force attacks, and user negligence in selecting strong passwords. Organizations must evaluate factors like security requirements, user convenience, deployment cost, and regulatory compliance when choosing between biometric and password authentication methods.
Biometric Authentication vs Password Authentication Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com