Keyloggers capture every keystroke typed on a device, making them effective for stealing passwords and sensitive information. Screen scrapers extract visual data directly from the screen, enabling attackers to bypass encrypted input methods. Both pose significant security threats, but keyloggers primarily target input data while screen scrapers focus on displayed information.
Table of Comparison
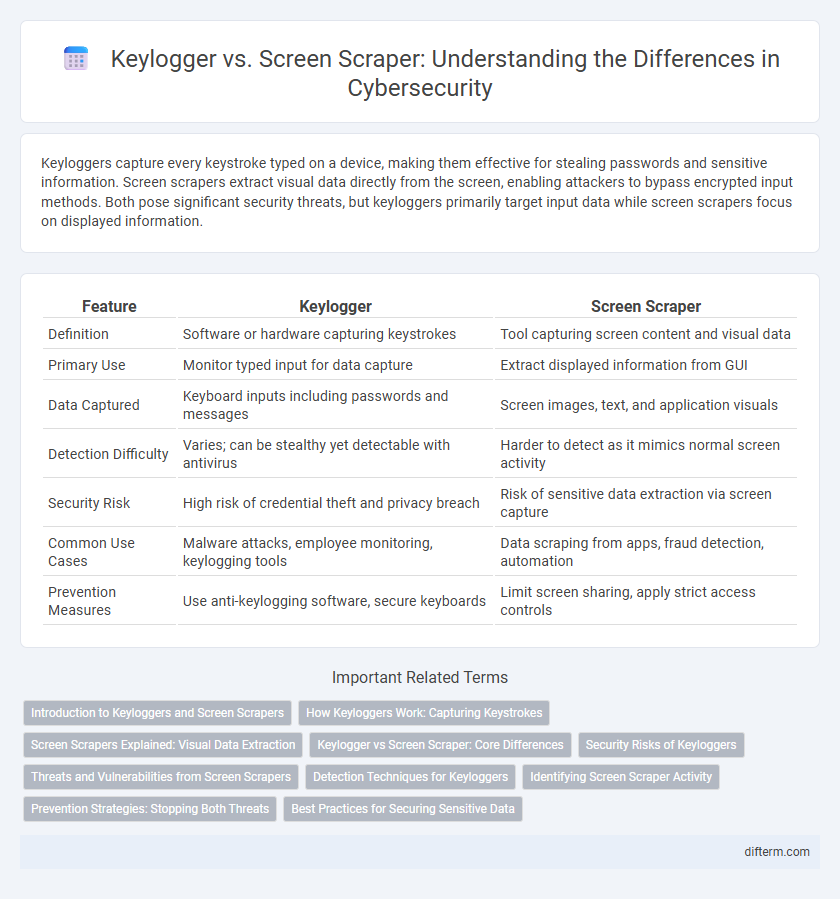
| Feature | Keylogger | Screen Scraper |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Software or hardware capturing keystrokes | Tool capturing screen content and visual data |
| Primary Use | Monitor typed input for data capture | Extract displayed information from GUI |
| Data Captured | Keyboard inputs including passwords and messages | Screen images, text, and application visuals |
| Detection Difficulty | Varies; can be stealthy yet detectable with antivirus | Harder to detect as it mimics normal screen activity |
| Security Risk | High risk of credential theft and privacy breach | Risk of sensitive data extraction via screen capture |
| Common Use Cases | Malware attacks, employee monitoring, keylogging tools | Data scraping from apps, fraud detection, automation |
| Prevention Measures | Use anti-keylogging software, secure keyboards | Limit screen sharing, apply strict access controls |
Introduction to Keyloggers and Screen Scrapers
Keyloggers capture and record every keystroke made on a device, enabling attackers to steal sensitive information such as passwords and credit card numbers. Screen scrapers extract text and graphical data displayed on a user's screen, often targeting confidential information shown during secure transactions or communications. Both tools pose significant cybersecurity risks by covertly harvesting data without user consent, necessitating robust defense mechanisms to detect and prevent their operation.
How Keyloggers Work: Capturing Keystrokes
Keyloggers operate by recording every keystroke typed on a keyboard, capturing sensitive information such as passwords, credit card numbers, and personal messages. These malicious programs can be installed through phishing attacks, malware downloads, or physical access to the device, running silently in the background without detection. Unlike screen scrapers that capture visual data, keyloggers directly intercept input at the device or software level, making them particularly dangerous for stealing confidential digital credentials.
Screen Scrapers Explained: Visual Data Extraction
Screen scrapers capture visual data directly from the display output, extracting information by analyzing screen content pixel by pixel, unlike keyloggers that record keystrokes. This method allows screen scrapers to access data from applications or websites regardless of encryption or input method, posing significant security risks to sensitive visual information. Advanced screen scraping tools often bypass traditional security controls by mimicking user interactions and parsing rendered screen images to steal confidential data.
Keylogger vs Screen Scraper: Core Differences
Keyloggers capture keystrokes to record user input such as passwords and messages, while screen scrapers capture visual data displayed on the screen, effectively recording what the user sees. Keyloggers operate stealthily at the system or hardware level to intercept typed information, whereas screen scrapers rely on screen capture technology or OCR (Optical Character Recognition) to extract content from images or video frames. The core difference lies in the data capture method: keyloggers target input data sources, whereas screen scrapers target output or display data, influencing their respective detection and mitigation strategies.
Security Risks of Keyloggers
Keyloggers pose significant security risks by secretly recording keystrokes, capturing sensitive information such as passwords, credit card numbers, and personal messages. Unlike screen scrapers, which extract visible data from screens, keyloggers operate covertly at the system level, making detection and prevention more challenging. The stealthy nature of keyloggers facilitates unauthorized access, identity theft, and extensive data breaches, emphasizing the critical need for robust anti-malware solutions and system monitoring.
Threats and Vulnerabilities from Screen Scrapers
Screen scrapers pose significant security threats by capturing sensitive information displayed on screens, such as login credentials and personal data, without user consent. Unlike keyloggers that record keystrokes, screen scrapers exploit vulnerabilities in display rendering processes, making it difficult to detect and block their activity. These tools can lead to data breaches, unauthorized access, and exposure of confidential information, especially in environments lacking robust endpoint protection and encryption measures.
Detection Techniques for Keyloggers
Keylogger detection techniques primarily rely on signature-based antivirus scanning, behavioral analysis, and heuristic monitoring to identify abnormal keystroke logging activities. Advanced methods utilize kernel-level monitoring to detect unauthorized hooks or API calls intercepting keyboard inputs. Machine learning models enhance detection accuracy by analyzing patterns of keylogging behavior distinct from legitimate system processes.
Identifying Screen Scraper Activity
Screen scrapers capture visual data displayed on a user's screen by recording pixel information, making their detection challenging compared to keyloggers that track keystrokes. Identifying screen scraper activity involves monitoring unusual GPU and CPU usage, detecting unauthorized access to screen capture APIs, and analyzing process behaviors for suspicious screen recording patterns. Advanced endpoint detection systems leverage behavioral analytics and anomaly detection to flag these covert screen capturing operations effectively.
Prevention Strategies: Stopping Both Threats
Preventing keylogger and screen scraper attacks requires a multi-layered security approach, including the deployment of advanced endpoint protection software and regular system monitoring to detect unusual activities. Implementing strong access controls, using virtual keyboards, and enforcing strict user authentication protocols can significantly reduce the risk of data capture by these malicious tools. Regular software updates and employee cybersecurity training further strengthen defenses against keyloggers and screen scrapers.
Best Practices for Securing Sensitive Data
Keylogger and screen scraper threats require robust encryption protocols and multi-factor authentication to secure sensitive data effectively. Implementing end-to-end encryption alongside real-time monitoring and anomaly detection limits unauthorized access from both keylogging and screen scraping attacks. Regular software updates and user training further enhance defenses by reducing vulnerabilities exploited by these data interception methods.
Keylogger vs Screen Scraper Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com