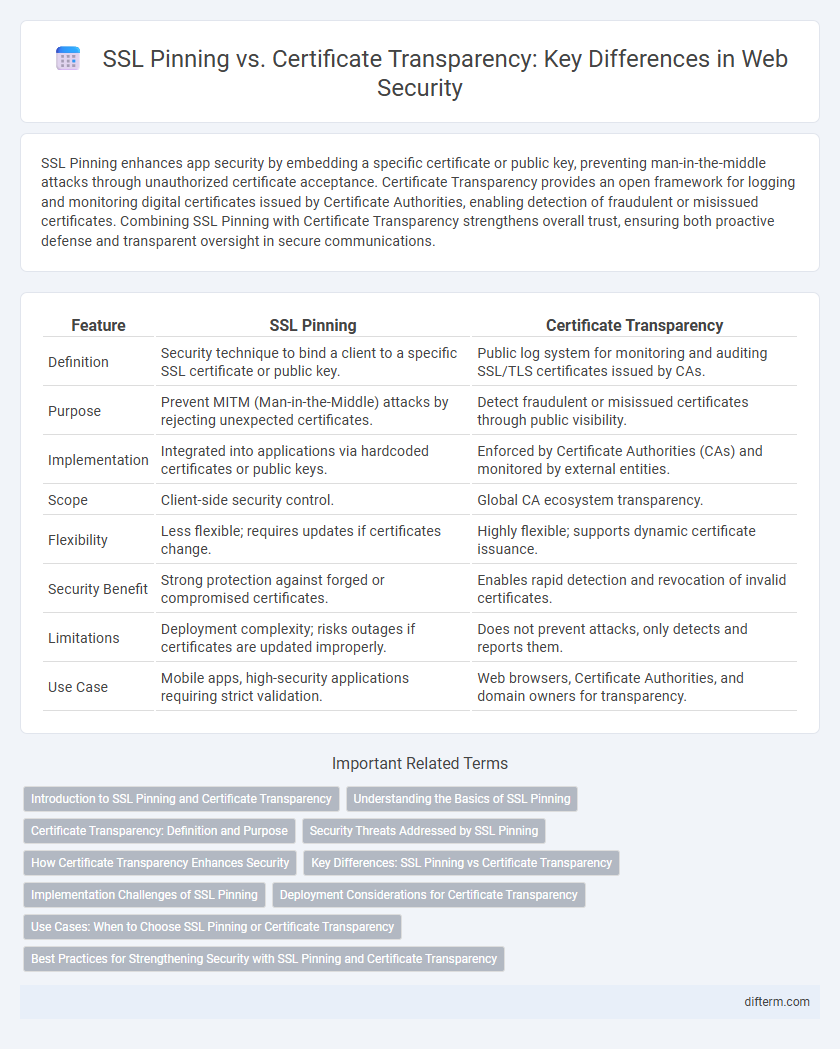
SSL Pinning enhances app security by embedding a specific certificate or public key, preventing man-in-the-middle attacks through unauthorized certificate acceptance. Certificate Transparency provides an open framework for logging and monitoring digital certificates issued by Certificate Authorities, enabling detection of fraudulent or misissued certificates. Combining SSL Pinning with Certificate Transparency strengthens overall trust, ensuring both proactive defense and transparent oversight in secure communications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | SSL Pinning | Certificate Transparency |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Security technique to bind a client to a specific SSL certificate or public key. | Public log system for monitoring and auditing SSL/TLS certificates issued by CAs. |
| Purpose | Prevent MITM (Man-in-the-Middle) attacks by rejecting unexpected certificates. | Detect fraudulent or misissued certificates through public visibility. |
| Implementation | Integrated into applications via hardcoded certificates or public keys. | Enforced by Certificate Authorities (CAs) and monitored by external entities. |
| Scope | Client-side security control. | Global CA ecosystem transparency. |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; requires updates if certificates change. | Highly flexible; supports dynamic certificate issuance. |
| Security Benefit | Strong protection against forged or compromised certificates. | Enables rapid detection and revocation of invalid certificates. |
| Limitations | Deployment complexity; risks outages if certificates are updated improperly. | Does not prevent attacks, only detects and reports them. |
| Use Case | Mobile apps, high-security applications requiring strict validation. | Web browsers, Certificate Authorities, and domain owners for transparency. |
Introduction to SSL Pinning and Certificate Transparency
SSL Pinning is a security technique that associates a host with their expected X.509 certificate or public key to prevent man-in-the-middle attacks during HTTPS connections. Certificate Transparency is a framework that provides an open, publicly auditable log of SSL/TLS certificates issued by Certificate Authorities to detect misissued or malicious certificates. Implementing SSL Pinning enhances app security by verifying certificates locally, while Certificate Transparency enables monitoring and auditing of certificate issuance across the internet.
Understanding the Basics of SSL Pinning
SSL Pinning enhances security by binding a client's trusted certificate or public key to a server, preventing man-in-the-middle attacks even if a certificate authority is compromised. This technique ensures that mobile apps or browsers accept only a predefined certificate, minimizing risks from fraudulent certificates. Understanding SSL Pinning is crucial for developers aiming to protect sensitive data transmissions in mobile and web applications.
Certificate Transparency: Definition and Purpose
Certificate Transparency is a security framework designed to monitor and audit SSL/TLS certificates issued by Certificate Authorities (CAs) to prevent fraudulent or misissued certificates from compromising web security. It involves public logging of certificates in append-only, cryptographically assured logs, enabling domain owners and browsers to detect unauthorized certificates quickly. This transparency enhances trust in the SSL/TLS ecosystem by providing verifiable evidence of certificate issuance, reducing the risk of man-in-the-middle attacks and ensuring stronger protection for encrypted communications.
Security Threats Addressed by SSL Pinning
SSL pinning addresses security threats such as man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks by ensuring the client only trusts a specific server certificate or public key. This technique mitigates risks from compromised certificate authorities or fraudulent certificates by validating the pinned certificate regardless of the trusted CA store. Unlike Certificate Transparency, which detects and logs unauthorized certificates after issuance, SSL pinning proactively prevents interception of secure communications.
How Certificate Transparency Enhances Security
Certificate Transparency enhances security by providing a publicly auditable log of all issued SSL/TLS certificates, enabling early detection of unauthorized or malicious certificates. This transparency helps identify misissued certificates and prevents man-in-the-middle attacks by ensuring that certificate authorities are held accountable for certificate issuance. By complementing SSL pinning, Certificate Transparency strengthens trust in the public key infrastructure and reduces the risk of fraudulent certificates compromising secure communications.
Key Differences: SSL Pinning vs Certificate Transparency
SSL Pinning enhances security by binding a client to a specific server certificate or public key, preventing man-in-the-middle attacks during SSL/TLS handshakes. Certificate Transparency provides a public, auditable log of issued SSL/TLS certificates, enabling detection of misissued or rogue certificates by domain owners and browsers. Key differences lie in SSL Pinning's proactive client-side validation versus Certificate Transparency's reactive monitoring and accountability mechanism.
Implementation Challenges of SSL Pinning
SSL Pinning implementation faces challenges such as managing certificate updates without disrupting user access, requiring app updates whenever certificates change, and handling certificate revocation efficiently. Developers must balance strict pinning policies with the risk of locking out users if pinned certificates expire or get compromised. The complexity increases in distributed environments where multiple certificates and backend services must be consistently pinned and maintained.
Deployment Considerations for Certificate Transparency
Certificate Transparency deployment requires integration with public log servers to enhance the detection of misissued or rogue certificates, ensuring greater trustworthiness in SSL/TLS ecosystems. Organizations must update their certificate validation processes to verify SCTs (Signed Certificate Timestamps) embedded within certificates or delivered via OCSP stapling, which demands compatibility with current TLS clients and infrastructure. Continuous monitoring of CT logs and alerting mechanisms is essential to promptly identify and respond to suspicious certificate activities, optimizing security posture without significant performance degradation.
Use Cases: When to Choose SSL Pinning or Certificate Transparency
SSL Pinning is ideal for mobile apps and environments requiring strict protection against man-in-the-middle attacks by hardcoding trusted certificates or public keys, ensuring secure communication with specific servers. Certificate Transparency supports broader ecosystem monitoring by providing public logs of issued certificates, helping detect misissuance and improve overall trustworthiness in web and enterprise environments. Choose SSL Pinning for application-level security with limited server endpoints, while Certificate Transparency is preferred for large-scale certificate monitoring and proactive security auditing.
Best Practices for Strengthening Security with SSL Pinning and Certificate Transparency
Implementing SSL pinning ensures that applications only trust specific certificates or public keys, effectively preventing man-in-the-middle attacks by rejecting unauthorized or rogue certificates. Certificate Transparency enhances security by providing a public, auditable log of issued TLS certificates, enabling rapid detection of misissued or malicious certificates and promoting accountability. Combining SSL pinning with Certificate Transparency creates a robust defense strategy, maintaining strict certificate validation while benefiting from real-time monitoring and early detection of certificate anomalies.
SSL Pinning vs Certificate Transparency Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com