Antivirus software primarily targets known viruses by scanning files and programs for signature-based threats, while antimalware solutions offer broader protection against a wide range of malicious software, including spyware, ransomware, and Trojans. Modern security suites often integrate both antivirus and antimalware capabilities to enhance detection rates and prevent complex cyberattacks. Effective endpoint security relies on real-time scanning, behavioral analysis, and frequent updates to keep systems safe from evolving threats.
Table of Comparison
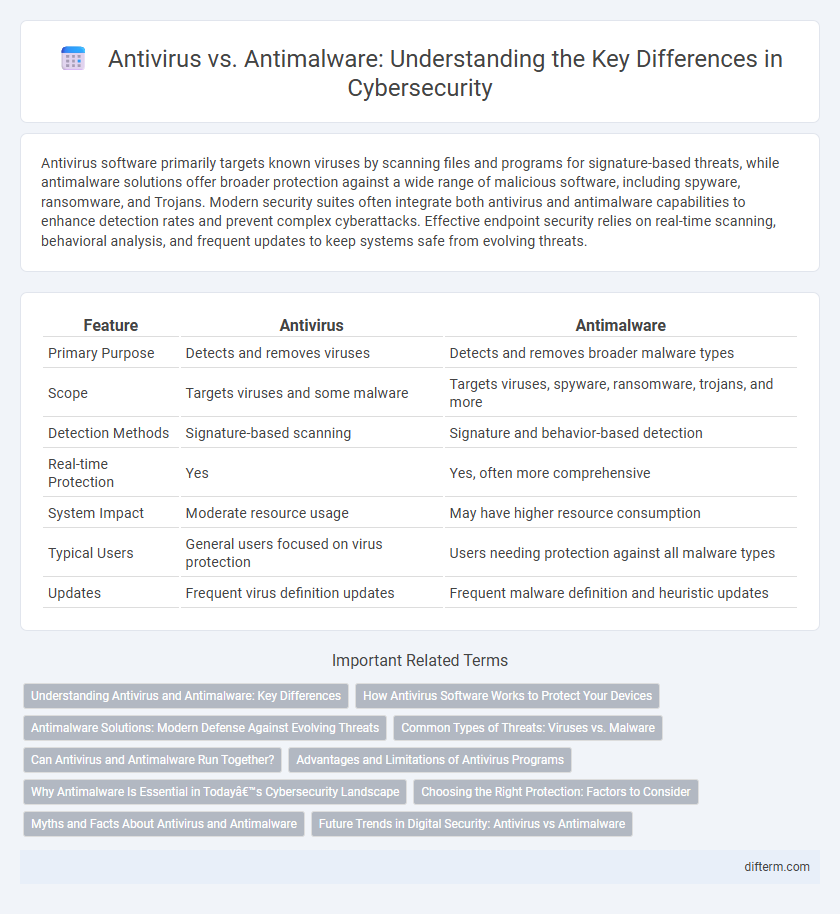
| Feature | Antivirus | Antimalware |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Detects and removes viruses | Detects and removes broader malware types |
| Scope | Targets viruses and some malware | Targets viruses, spyware, ransomware, trojans, and more |
| Detection Methods | Signature-based scanning | Signature and behavior-based detection |
| Real-time Protection | Yes | Yes, often more comprehensive |
| System Impact | Moderate resource usage | May have higher resource consumption |
| Typical Users | General users focused on virus protection | Users needing protection against all malware types |
| Updates | Frequent virus definition updates | Frequent malware definition and heuristic updates |
Understanding Antivirus and Antimalware: Key Differences
Antivirus software specifically targets viruses and known malware signatures to prevent infection and remove threats, while antimalware solutions provide broader protection against various malicious software including ransomware, spyware, and adware. Antivirus programs rely heavily on signature-based detection methods, whereas antimalware tools utilize heuristic analysis and real-time behavior monitoring for identifying emerging threats. Understanding these distinctions helps users select comprehensive security solutions that address evolving cyber threats effectively.
How Antivirus Software Works to Protect Your Devices
Antivirus software protects your devices by continuously scanning files and programs for known signatures of malicious code, utilizing heuristic analysis to detect unknown threats. It monitors system behavior and quarantines suspicious files to prevent infection and spread. Regular updates to virus definitions ensure protection against the latest malware variants and cyber threats.
Antimalware Solutions: Modern Defense Against Evolving Threats
Antimalware solutions offer comprehensive protection by detecting and neutralizing a wide range of threats, including viruses, ransomware, spyware, and zero-day exploits, using advanced heuristics and behavior-based analysis. Unlike traditional antivirus software that primarily targets known virus signatures, antimalware tools continuously update their databases and employ machine learning algorithms to identify emerging and polymorphic malware variants. Incorporating antimalware solutions within enterprise security architectures enhances real-time threat detection, reduces false positives, and improves incident response capabilities against sophisticated cyber attacks.
Common Types of Threats: Viruses vs. Malware
Viruses are a specific type of malware designed to replicate and spread by attaching to legitimate files, often causing system disruptions and damage. Malware encompasses a broader range of threats including viruses, ransomware, spyware, trojans, and worms, each targeting different vulnerabilities to steal data, disrupt operations, or gain unauthorized access. Understanding these distinctions helps in selecting the appropriate security solutions to effectively detect and mitigate diverse cyber threats.
Can Antivirus and Antimalware Run Together?
Antivirus and antimalware programs can run together on the same system, but compatibility depends on their specific features and resource usage. Running both can enhance security by providing layered protection against different types of threats, yet overlapping functions may cause conflicts or performance issues. Choosing complementary software that supports coexistence ensures effective threat detection without degrading system efficiency.
Advantages and Limitations of Antivirus Programs
Antivirus programs excel at detecting and removing known viruses by leveraging signature-based scanning and heuristic analysis, offering robust protection against traditional malware threats. Their limitations include difficulty in identifying zero-day exploits and ransomware variants, as well as potential performance slowdowns during real-time scanning. Integrating behavior-based detection and frequent updates can enhance antivirus effectiveness but may still require complementary antimalware tools for comprehensive cybersecurity coverage.
Why Antimalware Is Essential in Today’s Cybersecurity Landscape
Antimalware solutions provide comprehensive protection against a broader range of threats including ransomware, spyware, and trojans, unlike traditional antivirus which primarily targets known viruses. In today's cybersecurity landscape, sophisticated attacks exploit multiple vulnerabilities, making layered defense essential for detecting and neutralizing emerging threats. Advanced behavior-based detection and real-time analysis in antimalware tools significantly reduce risk by identifying zero-day exploits and polymorphic malware that antivirus may miss.
Choosing the Right Protection: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right security software depends on understanding the differences between antivirus and antimalware tools, as antivirus primarily targets known viruses while antimalware offers broader protection against various threats like ransomware, spyware, and trojans. Evaluating factors such as detection rates, real-time scanning capabilities, system impact, and update frequency ensures comprehensive defense tailored to specific cybersecurity needs. User environment, including device type and typical online activities, influences whether a specialized antimalware solution or a combined antivirus-antimalware suite provides optimal protection.
Myths and Facts About Antivirus and Antimalware
Antivirus software primarily targets traditional viruses, while antimalware tools provide broader protection against various threats including ransomware, spyware, and Trojans. A common myth is that antivirus alone ensures complete security, but modern cybersecurity demands layered defense combining both antivirus and antimalware solutions. Effective protection requires understanding that malware constantly evolves, making reliance on a single tool insufficient for comprehensive threat detection and removal.
Future Trends in Digital Security: Antivirus vs Antimalware
Future trends in digital security emphasize the integration of antivirus and antimalware technologies into unified threat detection platforms leveraging artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance predictive capabilities. Advanced behavioral analysis and cloud-based threat intelligence are increasingly prioritized to combat sophisticated, polymorphic malware and zero-day exploits. Continuous updates and adaptive defenses will shape the evolution of security solutions, ensuring proactive protection against emerging cyber threats.
antivirus vs antimalware Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com