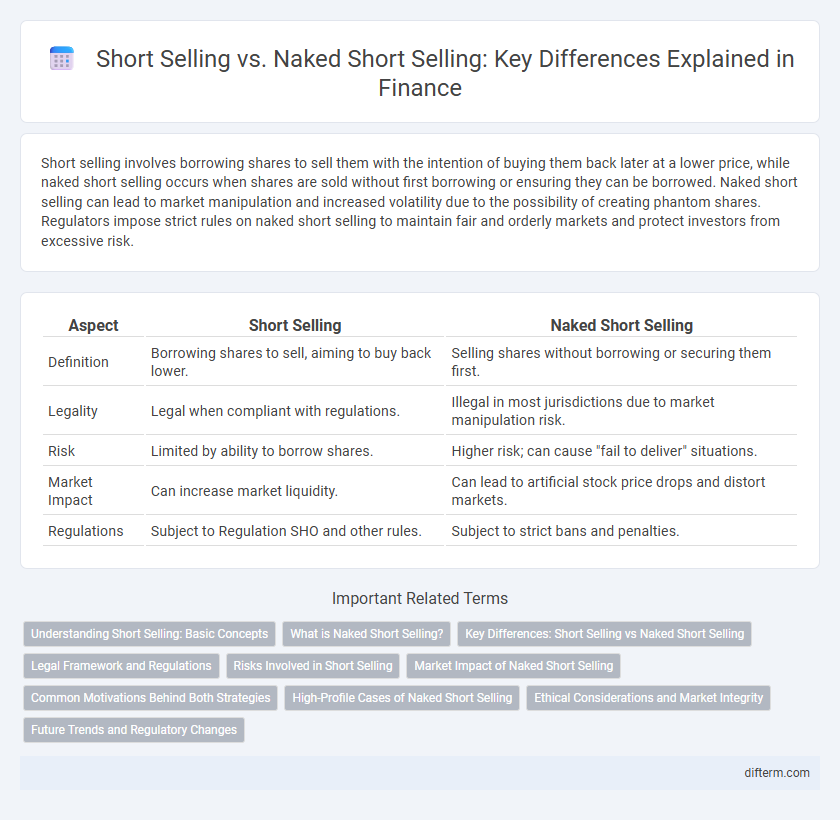
Short selling involves borrowing shares to sell them with the intention of buying them back later at a lower price, while naked short selling occurs when shares are sold without first borrowing or ensuring they can be borrowed. Naked short selling can lead to market manipulation and increased volatility due to the possibility of creating phantom shares. Regulators impose strict rules on naked short selling to maintain fair and orderly markets and protect investors from excessive risk.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Short Selling | Naked Short Selling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Borrowing shares to sell, aiming to buy back lower. | Selling shares without borrowing or securing them first. |
| Legality | Legal when compliant with regulations. | Illegal in most jurisdictions due to market manipulation risk. |
| Risk | Limited by ability to borrow shares. | Higher risk; can cause "fail to deliver" situations. |
| Market Impact | Can increase market liquidity. | Can lead to artificial stock price drops and distort markets. |
| Regulations | Subject to Regulation SHO and other rules. | Subject to strict bans and penalties. |
Understanding Short Selling: Basic Concepts
Short selling involves borrowing shares to sell them with the expectation of buying them back at a lower price for profit, creating a hedge against market declines. Naked short selling differs by selling shares without borrowing them first, potentially causing market distortions and regulatory scrutiny. Understanding the mechanics and risks of both strategies is crucial for investors managing short positions in volatile markets.
What is Naked Short Selling?
Naked short selling involves selling shares without borrowing or ensuring the availability of the stock, creating the potential for delivery failures and market manipulation. Unlike traditional short selling, where the seller borrows shares before selling, naked short selling bypasses this step, increasing systemic risk and regulatory scrutiny. This practice can lead to artificial price declines and regulatory penalties under financial market rules such as Regulation SHO.
Key Differences: Short Selling vs Naked Short Selling
Short selling involves borrowing shares before selling them, ensuring delivery upon settlement, while naked short selling occurs without borrowing or confirming share availability, leading to potential settlement failures. Regulatory agencies impose strict rules on naked short selling to prevent market manipulation and excessive volatility, unlike traditional short selling which is a common hedging strategy. The key difference lies in share borrowing and delivery obligations, impacting market integrity and risk exposure for investors.
Legal Framework and Regulations
Short selling involves borrowing shares to sell them with the obligation to repurchase and return them, adhering to strict legal frameworks such as Regulation SHO in the U.S., which mandates locate and close-out requirements. Naked short selling, the practice of selling shares without ensuring availability for borrowing, is heavily regulated and often banned due to its potential for market manipulation and failure to deliver, with enforcement actions by the SEC targeting violations. Compliance with these regulatory measures ensures market integrity and protects investors from risks associated with excessive short selling practices.
Risks Involved in Short Selling
Short selling involves borrowing shares to sell them with the intention of buying them back at a lower price, exposing investors to unlimited loss if the stock price rises instead of falls. Naked short selling increases these risks significantly by selling shares without borrowing them first, potentially causing market distortions and regulatory scrutiny due to settlement failures. Both practices carry the risk of margin calls and amplify financial losses, making risk management and regulatory compliance critical for traders.
Market Impact of Naked Short Selling
Naked short selling significantly disrupts market stability by enabling the sale of shares that have not been confirmed for borrowing, leading to artificial downward pressure on stock prices and increased volatility. This practice can exacerbate liquidity shortages, impair price discovery, and increase the risk of market manipulation. Regulatory bodies, such as the SEC, have imposed strict rules to curb naked short selling due to its potential to undermine investor confidence and distort fair market operations.
Common Motivations Behind Both Strategies
Short selling and naked short selling are driven by the motivation to profit from anticipated declines in asset prices, often during bearish market conditions. Investors engage in short selling to hedge portfolio risk or exploit overvalued stocks, while naked short selling can be motivated by the desire to capitalize faster on price drops despite regulatory restrictions. Both strategies reflect market skepticism and aim to enhance returns through positions that benefit from downward price movements.
High-Profile Cases of Naked Short Selling
High-profile cases of naked short selling have drawn significant regulatory scrutiny due to their potential to manipulate stock prices and create artificial market pressure. Notable scandals, such as the Overstock.com case involving SEC enforcement actions, highlight how naked short selling can lead to significant financial harm and distort fair trading practices. These incidents underscore the necessity for stringent oversight and transparent market operations to prevent market abuse.
Ethical Considerations and Market Integrity
Short selling involves borrowing shares before selling them, ensuring the position can be covered, which maintains market integrity by reducing manipulative risks. Naked short selling, where shares are sold without confirming borrow availability, raises ethical concerns due to potential market manipulation and increased volatility. Regulatory bodies like the SEC enforce strict rules against naked short selling to uphold transparency and fairness in financial markets.
Future Trends and Regulatory Changes
Short selling involves borrowing shares to sell with the intention of buying them back at a lower price, while naked short selling bypasses the borrowing process, leading to potential market manipulation and liquidity issues. Future trends indicate increased regulatory scrutiny and tighter enforcement of rules by authorities such as the SEC and FINRA to prevent abuses associated with naked short selling. Enhanced transparency measures and real-time trade reporting requirements are expected to be implemented to safeguard market integrity and protect investors.
Short selling vs Naked short selling Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com