Sensitivity analysis measures the impact of changing one variable at a time on financial outcomes, helping to identify critical risk factors in investments or budgets. Scenario analysis evaluates multiple variables simultaneously, creating comprehensive narratives about potential future states to assess complex risks and opportunities. Both methods enhance decision-making by providing insights into uncertainties, but scenario analysis offers a broader, more holistic view compared to the focused approach of sensitivity analysis.
Table of Comparison
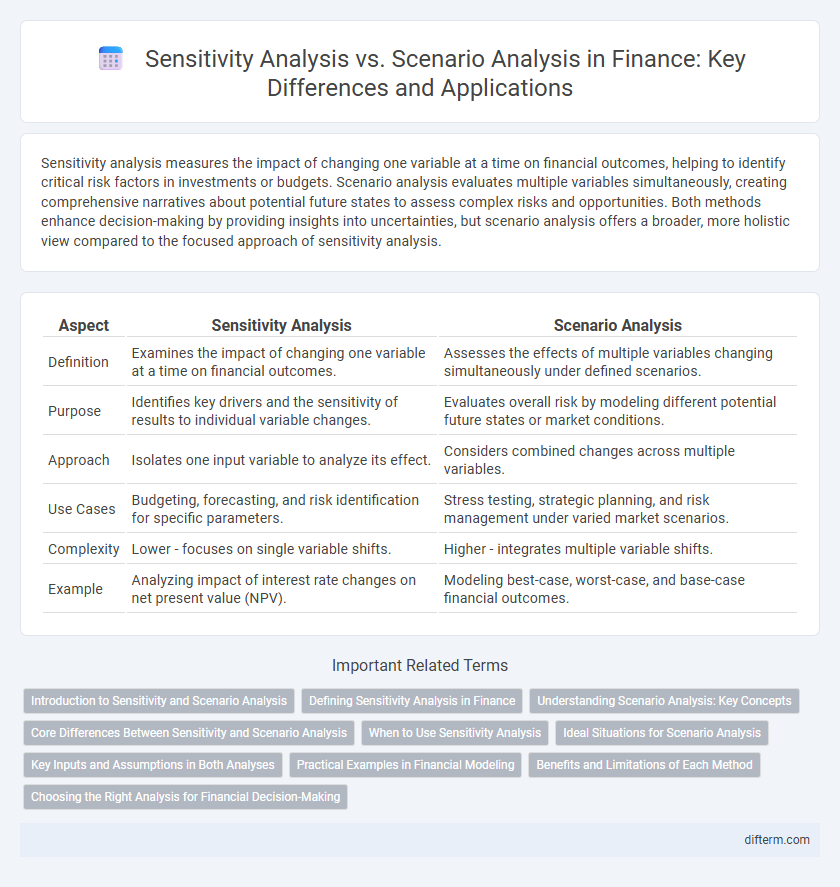
| Aspect | Sensitivity Analysis | Scenario Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Examines the impact of changing one variable at a time on financial outcomes. | Assesses the effects of multiple variables changing simultaneously under defined scenarios. |
| Purpose | Identifies key drivers and the sensitivity of results to individual variable changes. | Evaluates overall risk by modeling different potential future states or market conditions. |
| Approach | Isolates one input variable to analyze its effect. | Considers combined changes across multiple variables. |
| Use Cases | Budgeting, forecasting, and risk identification for specific parameters. | Stress testing, strategic planning, and risk management under varied market scenarios. |
| Complexity | Lower - focuses on single variable shifts. | Higher - integrates multiple variable shifts. |
| Example | Analyzing impact of interest rate changes on net present value (NPV). | Modeling best-case, worst-case, and base-case financial outcomes. |
Introduction to Sensitivity and Scenario Analysis
Sensitivity analysis evaluates how changes in individual financial variables impact an investment or portfolio's performance, providing insight into risk exposure and decision-making under uncertainty. Scenario analysis examines the effects of combined changes in multiple variables within plausible future states, offering a broader perspective on potential outcomes. Both techniques enhance financial modeling by quantifying risks and enabling more robust strategic planning.
Defining Sensitivity Analysis in Finance
Sensitivity analysis in finance evaluates how changes in individual input variables, such as interest rates, discount rates, or cash flow projections, impact the output of financial models like net present value (NPV) or internal rate of return (IRR). This technique isolates the effect of one variable at a time, providing clarity on which factors most significantly influence investment decisions or risk assessments. By quantifying the responsiveness of financial metrics to specific assumptions, sensitivity analysis helps identify key drivers and supports more informed strategic planning.
Understanding Scenario Analysis: Key Concepts
Scenario analysis is a strategic financial planning tool that evaluates potential outcomes by examining different hypothetical future states based on varying assumptions. It helps identify risks, potential impacts on cash flow, and investment returns under multiple conditions, including best-case, worst-case, and most likely scenarios. By modeling these alternative scenarios, businesses improve decision-making, optimize resource allocation, and enhance risk management strategies in uncertain markets.
Core Differences Between Sensitivity and Scenario Analysis
Sensitivity analysis evaluates the impact of varying one key financial variable at a time on a project's outcome, isolating the effect of specific factors like interest rates or sales volume. Scenario analysis examines multiple variables simultaneously by constructing different plausible future states, such as best-case, worst-case, and base-case financial projections. The core difference lies in sensitivity analysis focusing on individual parameter fluctuations, while scenario analysis assesses combined changes for comprehensive strategic planning.
When to Use Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity Analysis is best used when assessing how changes in individual financial variables impact a model's output, providing insight into risk exposure for specific factors such as interest rates or sales volume. It helps prioritize which variables require close monitoring and management in budgeting or investment decisions. This method is particularly useful in environments with variable inputs and uncertainty, enabling more informed decision-making by isolating single-variable effects on portfolio performance or cash flow projections.
Ideal Situations for Scenario Analysis
Scenario analysis is ideal for evaluating the impact of multiple, complex events on financial outcomes, such as shifts in interest rates, market crashes, or regulatory changes. It excels in strategic planning by exploring best-case, worst-case, and base-case scenarios to assess risk and inform decision-making under uncertainty. Financial institutions and investment firms utilize scenario analysis to stress test portfolios and prepare for extreme but plausible market conditions.
Key Inputs and Assumptions in Both Analyses
Sensitivity analysis examines the impact of varying one key input or assumption at a time, such as interest rates or sales volume, to measure its effect on financial outcomes. Scenario analysis evaluates multiple combined assumptions simultaneously, like changes in market conditions and regulatory policies, to assess potential risks and returns under different future states. Both methods rely heavily on accurate identification and quantification of critical variables to enhance decision-making in financial planning and risk management.
Practical Examples in Financial Modeling
Sensitivity analysis in financial modeling examines how changes in one variable, such as interest rates or sales volume, impact key outputs like net present value (NPV) or internal rate of return (IRR), helping investors identify critical risk factors. Scenario analysis evaluates the combined effect of multiple variables changing simultaneously, such as a downturn in market demand coupled with rising raw material costs, to assess the range of potential financial outcomes. Practical applications include stress testing investment portfolios and forecasting budget variations under best-case, worst-case, and base-case conditions.
Benefits and Limitations of Each Method
Sensitivity analysis provides targeted insights by isolating the impact of individual variables on financial outcomes, aiding in risk identification and prioritization, but it may oversimplify complex interdependencies in financial models. Scenario analysis evaluates the combined effects of multiple variables under defined economic conditions, offering a holistic view of potential risks and opportunities, though it requires extensive data and can be resource-intensive. Both methods enhance decision-making by revealing vulnerabilities and uncertainties, yet sensitivity analysis excels in variable isolation while scenario analysis better captures real-world complexity.
Choosing the Right Analysis for Financial Decision-Making
Sensitivity analysis quantifies the impact of individual variable changes on financial outcomes, providing granular insight into risk exposure. Scenario analysis evaluates multiple variables simultaneously under different hypothetical conditions, delivering a comprehensive view of potential future states. Selecting the right analysis depends on whether the decision requires detailed variable impact assessment or broad evaluation of diverse economic scenarios.
Sensitivity Analysis vs Scenario Analysis Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com