Callable stock grants the issuer the right to repurchase shares at a predetermined price before maturity, providing flexibility to manage capital structure and reduce dividend obligations. Puttable stock allows investors to sell shares back to the issuer at a set price, offering downside protection and reducing investment risk. Understanding the distinct features of callable and puttable stocks is essential for investors aiming to optimize portfolio risk and return profiles.
Table of Comparison
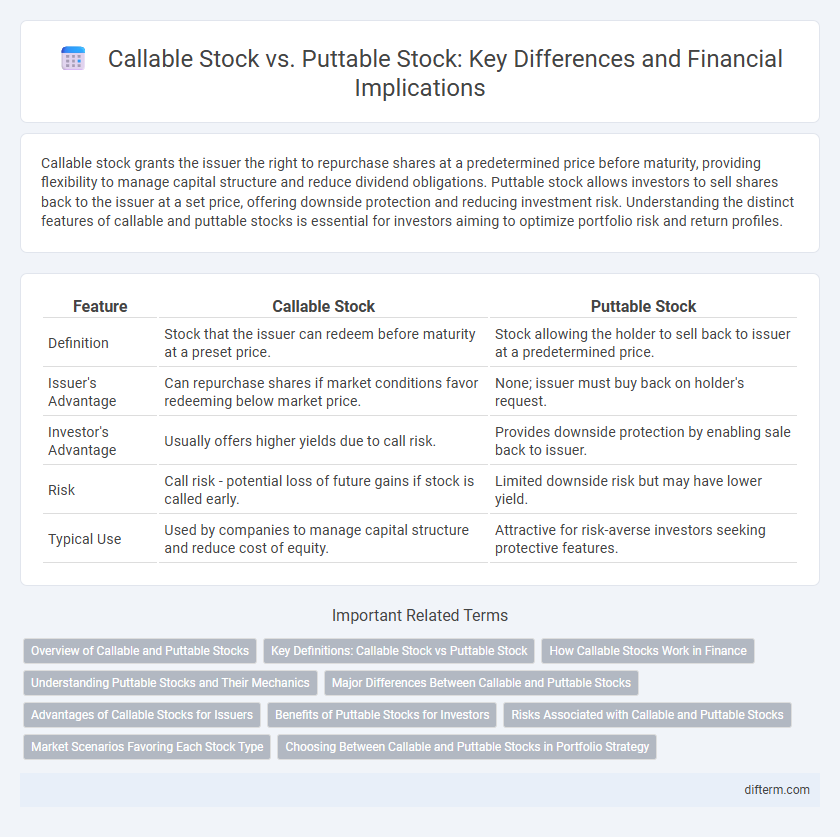
| Feature | Callable Stock | Puttable Stock |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Stock that the issuer can redeem before maturity at a preset price. | Stock allowing the holder to sell back to issuer at a predetermined price. |
| Issuer's Advantage | Can repurchase shares if market conditions favor redeeming below market price. | None; issuer must buy back on holder's request. |
| Investor's Advantage | Usually offers higher yields due to call risk. | Provides downside protection by enabling sale back to issuer. |
| Risk | Call risk - potential loss of future gains if stock is called early. | Limited downside risk but may have lower yield. |
| Typical Use | Used by companies to manage capital structure and reduce cost of equity. | Attractive for risk-averse investors seeking protective features. |
Overview of Callable and Puttable Stocks
Callable stocks grant the issuer the right to repurchase shares at a predetermined price before maturity, providing flexibility to manage capital structure and respond to market conditions. Puttable stocks offer investors the option to sell shares back to the issuer at a specified price, enhancing downside protection and reducing investment risk. Both securities balance issuer and investor interests, impacting valuation, yield, and market behavior in the equity finance landscape.
Key Definitions: Callable Stock vs Puttable Stock
Callable stock grants the issuing company the right to repurchase shares from shareholders at a predetermined price after a specified date, providing flexibility to manage equity and reduce dilution. Puttable stock gives shareholders the option to sell their shares back to the issuer at a set price within a defined timeframe, offering downside protection and liquidity. Both instruments impact corporate financing strategies and investor risk profiles by altering control over share redemption.
How Callable Stocks Work in Finance
Callable stocks allow the issuing company to repurchase shares at a predetermined price after a specified date, providing flexibility to manage capital structure and reduce dividend obligations. This feature can limit upside potential for investors, as the company may call shares when the stock price rises significantly above the call price. Callable stocks are often used in preferred equity to optimize financing costs and protect issuers against declining interest rates or changes in market conditions.
Understanding Puttable Stocks and Their Mechanics
Puttable stocks grant shareholders the right to sell the stock back to the issuer at a predetermined price before maturity, providing downside protection against price declines. These securities often feature a specified put date, enhancing investor confidence by limiting potential losses and increasing flexibility. Companies may issue puttable stocks to attract risk-averse investors by offering a safety net, impacting the stock's valuation and dividend policies.
Major Differences Between Callable and Puttable Stocks
Callable stocks grant the issuer the right to repurchase shares at a predetermined price before maturity, providing the company flexibility to manage equity and reduce cost of capital. Puttable stocks empower investors with the option to sell shares back to the issuer at a specified price, offering downside protection in volatile markets. The primary distinction lies in control: callable stock favors issuers by limiting investor gains, while puttable stock favors investors by limiting losses.
Advantages of Callable Stocks for Issuers
Callable stocks offer issuers the advantage of repurchasing shares at predetermined prices, enabling effective management of equity capital and reduction of dividend obligations during favorable market conditions. This flexibility allows companies to strategically time stock redemption, lowering financing costs and potentially improving earnings per share metrics. Issuers gain enhanced control over capital structure, facilitating responsiveness to changing financial environments without immediate dilution concerns.
Benefits of Puttable Stocks for Investors
Puttable stocks provide investors with the option to sell shares back to the issuer at a predetermined price, offering downside protection in volatile markets. This feature reduces investment risk by limiting potential losses, particularly during price declines or financial instability. The enhanced security and flexibility of puttable stocks make them an attractive choice for risk-averse investors seeking steady returns.
Risks Associated with Callable and Puttable Stocks
Callable stocks carry the risk of forced redemption by the issuer at a predetermined price, potentially resulting in investors missing out on future price appreciation. Puttable stocks expose investors to the risk of early sale pressure, as the holder may exercise the put option during unfavorable market conditions, leading to liquidity challenges. Both securities involve uncertainty regarding timing and price, impacting portfolio stability and expected returns.
Market Scenarios Favoring Each Stock Type
Callable stock tends to be favored in declining interest rate environments or when the issuer's creditworthiness improves, allowing the company to repurchase shares at predetermined prices and reduce dividend costs. Puttable stock gains appeal during market volatility or rising interest rates, as investors have the right to sell shares back to the issuer, providing downside protection and liquidity options. Each stock type aligns with different risk profiles and market expectations, influencing investor preferences in varying economic conditions.
Choosing Between Callable and Puttable Stocks in Portfolio Strategy
Choosing between callable and puttable stocks in portfolio strategy depends on risk tolerance and market outlook; callable stocks offer issuers the right to repurchase shares, potentially limiting upside for investors, while puttable stocks grant investors the option to sell shares back to the issuer, providing a safety net in declining markets. Investors seeking income with moderate risk may favor callable stocks for higher yields, whereas risk-averse investors prioritize puttable stocks for downside protection and capital preservation. Effective portfolio construction balances these features to optimize returns and manage volatility in varying economic conditions.
Callable Stock vs Puttable Stock Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com