An order book displays all current buy and sell orders for a financial instrument, reflecting market depth and liquidity in real time. A trade blotter records executed trades, providing a historical log of transactions including price, volume, and time. Understanding the differences enhances trading strategies by combining future order intentions with completed trade data for comprehensive market analysis.
Table of Comparison
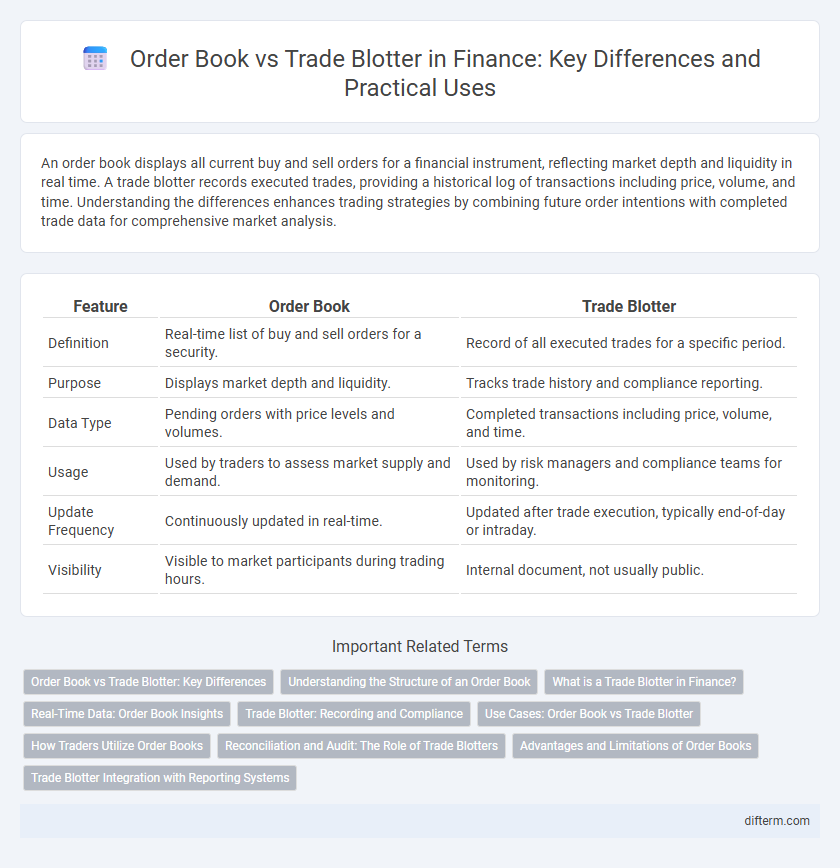
| Feature | Order Book | Trade Blotter |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Real-time list of buy and sell orders for a security. | Record of all executed trades for a specific period. |
| Purpose | Displays market depth and liquidity. | Tracks trade history and compliance reporting. |
| Data Type | Pending orders with price levels and volumes. | Completed transactions including price, volume, and time. |
| Usage | Used by traders to assess market supply and demand. | Used by risk managers and compliance teams for monitoring. |
| Update Frequency | Continuously updated in real-time. | Updated after trade execution, typically end-of-day or intraday. |
| Visibility | Visible to market participants during trading hours. | Internal document, not usually public. |
Order Book vs Trade Blotter: Key Differences
The order book provides a real-time, detailed list of buy and sell orders at various price levels, reflecting market depth and liquidity. The trade blotter, on the other hand, records executed trades with timestamp, price, and volume, serving as a transactional log for trade reconciliation and analysis. Understanding the distinction between order book dynamics and trade blotter records is essential for effective trade execution and market monitoring.
Understanding the Structure of an Order Book
An order book displays real-time buy and sell orders organized by price levels, revealing market depth and liquidity for traders. It provides detailed insights into bid and ask prices, order sizes, and the sequence of trade intentions, enabling market participants to gauge supply and demand dynamics. Unlike a trade blotter, which records executed transactions, the order book captures pending orders, offering a proactive view into market sentiment and potential price movements.
What is a Trade Blotter in Finance?
A trade blotter in finance is a detailed record of all executed trades within a specific time frame, capturing essential data such as trade date, time, price, quantity, and counterparties involved. It serves as a critical tool for compliance, risk management, and trade reconciliation by providing transparency and an audit trail of transaction activities. Unlike an order book, which tracks outstanding buy and sell orders, the trade blotter focuses exclusively on completed transactions.
Real-Time Data: Order Book Insights
The order book provides real-time insights into market depth by displaying current buy and sell orders with price levels and volumes, enabling traders to gauge supply and demand dynamics instantly. Unlike a trade blotter, which records executed transactions after the fact, the order book offers a live snapshot of pending orders that influence price movements and liquidity. Utilizing order book data enhances decision-making by revealing market sentiment and potential price action before trades occur.
Trade Blotter: Recording and Compliance
Trade blotters serve as detailed chronological records of all executed trades, capturing essential data such as trade time, price, quantity, and counterparty information to ensure transparency. They play a critical role in compliance by providing auditors and regulators with verifiable evidence of transaction accuracy and adherence to trading regulations. Maintaining accurate trade blotters helps financial firms manage risk, detect anomalies, and fulfill regulatory reporting requirements efficiently.
Use Cases: Order Book vs Trade Blotter
The order book is primarily utilized for real-time market depth analysis, enabling traders to view live bid and ask prices to inform order placement strategies. In contrast, the trade blotter serves as a comprehensive record of executed trades, providing compliance teams and portfolio managers with detailed transaction histories for auditing and performance review. Both tools are essential in trading operations, with the order book facilitating decision-making before trade execution and the trade blotter ensuring post-trade transparency and regulatory adherence.
How Traders Utilize Order Books
Traders leverage order books to gauge real-time market depth, analyzing bid and ask prices alongside order sizes to identify liquidity and potential price movements. By monitoring changes in order book dynamics, traders can anticipate supply and demand shifts, enabling more informed entry and exit points. This granular insight contrasts with trade blotters, which offer retrospective trade details rather than predictive market structure.
Reconciliation and Audit: The Role of Trade Blotters
Trade blotters play a crucial role in the reconciliation process by providing a detailed chronological record of executed trades, enabling finance teams to verify order book entries and identify discrepancies. Accurate trade blotters ensure audit trails are complete and transparent, supporting regulatory compliance and internal controls. Effective reconciliation between order books and trade blotters reduces operational risk and enhances data integrity across trading platforms.
Advantages and Limitations of Order Books
Order books provide real-time transparency of buy and sell orders, enabling traders to gauge market depth and liquidity effectively. Their limitation lies in displaying only pending orders without revealing executed trade prices or volumes, which are recorded in trade blotters. Thus, order books facilitate strategic order placement while lacking comprehensive post-trade analysis data essential for performance evaluation.
Trade Blotter Integration with Reporting Systems
Trade blotter integration with reporting systems enhances real-time transaction tracking by consolidating executed trades into centralized databases for accurate financial analysis. This integration enables seamless reconciliation and regulatory compliance by automating data flow between trade execution platforms and risk management tools. Leveraging APIs and data normalization protocols ensures consistent trade data quality, facilitating comprehensive portfolio performance reporting and audit readiness.
order book vs trade blotter Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com