Market neutral strategies aim to minimize market risk by maintaining equal long and short positions, seeking consistent returns regardless of market direction. In contrast, long/short strategies actively adjust the balance between long and short positions to capitalize on anticipated market trends and stock-specific opportunities. Both approaches use hedging techniques, but market neutral prioritizes stability while long/short focuses on exploiting market inefficiencies for higher returns.
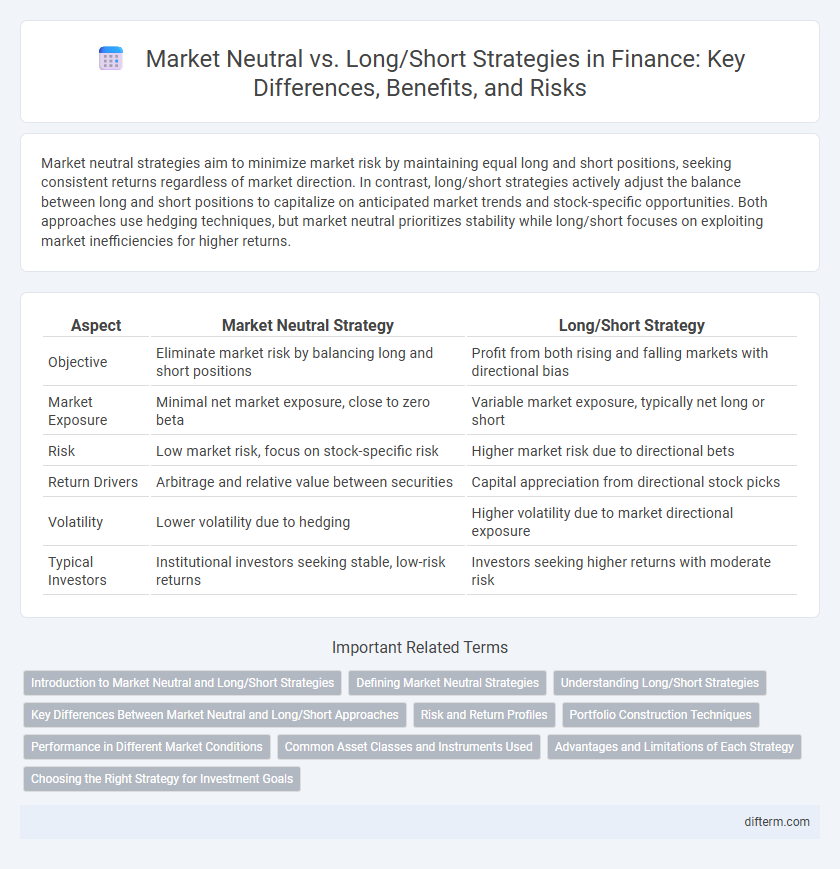
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Market Neutral Strategy | Long/Short Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Objective | Eliminate market risk by balancing long and short positions | Profit from both rising and falling markets with directional bias |
| Market Exposure | Minimal net market exposure, close to zero beta | Variable market exposure, typically net long or short |
| Risk | Low market risk, focus on stock-specific risk | Higher market risk due to directional bets |
| Return Drivers | Arbitrage and relative value between securities | Capital appreciation from directional stock picks |
| Volatility | Lower volatility due to hedging | Higher volatility due to market directional exposure |
| Typical Investors | Institutional investors seeking stable, low-risk returns | Investors seeking higher returns with moderate risk |
Introduction to Market Neutral and Long/Short Strategies
Market neutral strategies seek to eliminate market risk by maintaining equal long and short positions, allowing investors to profit from relative price movements regardless of overall market direction. Long/short strategies involve taking long positions in undervalued assets and short positions in overvalued ones to capitalize on market inefficiencies and generate alpha. Both approaches rely heavily on quantitative analysis and risk management to optimize returns while mitigating exposure to systematic risk.
Defining Market Neutral Strategies
Market neutral strategies aim to eliminate market risk by maintaining balanced long and short positions that offset overall exposure, often targeting zero net beta to the market. These strategies seek consistent returns regardless of market direction by exploiting relative price movements between correlated assets or sectors. Unlike traditional long/short approaches that may take directional bets, market neutral funds prioritize minimizing systematic risk through hedging techniques and precise portfolio construction.
Understanding Long/Short Strategies
Long/short strategies involve taking simultaneous long positions in undervalued stocks while shorting overvalued ones, aiming to generate alpha through asset selection and market timing. This approach leverages market inefficiencies by exploiting price discrepancies, allowing investors to benefit from both rising and falling securities. In contrast, market neutral strategies seek to eliminate market risk by maintaining equal dollar amounts in long and short positions, focusing purely on relative value without exposure to broad market movements.
Key Differences Between Market Neutral and Long/Short Approaches
Market neutral strategies aim to eliminate market risk by balancing long and short positions to achieve zero net exposure, focusing on alpha generation through stock selection. Long/short strategies, on the other hand, maintain net market exposure by taking more substantial long or short positions, seeking to profit from both rising and falling markets. The key difference lies in market exposure management: market neutral prioritizes risk reduction and stable returns, while long/short strategies emphasize directional bets combined with hedging.
Risk and Return Profiles
Market neutral strategies aim to minimize market risk by balancing long and short positions, resulting in lower volatility and more stable returns regardless of market direction. Long/short strategies seek to capitalize on both rising and falling asset prices, offering higher return potential but with increased exposure to market swings. Risk-adjusted returns in market neutral approaches tend to be more consistent, whereas long/short strategies may exhibit greater drawdowns during market downturns.
Portfolio Construction Techniques
Market neutral strategies aim to eliminate market risk by balancing long and short positions to achieve zero net exposure, focusing on extracting alpha regardless of market direction. Long/short strategies actively manage portfolio beta by adjusting net exposure, often combining high-conviction long positions with tactical short sales to capitalize on relative value opportunities. Effective portfolio construction in both approaches requires rigorous risk management, diversification, and factor exposure controls to optimize risk-adjusted returns.
Performance in Different Market Conditions
Market neutral strategies aim to generate consistent returns by hedging market risk, resulting in stable performance across bull and bear markets. Long/short strategies involve taking leveraged positions that can benefit from market trends, often outperforming in trending markets but experiencing higher volatility during sideways or volatile conditions. Empirical data shows market neutral funds typically exhibit lower beta and smoother returns, while long/short funds may deliver higher returns in bullish environments but face greater drawdown risks during market reversals.
Common Asset Classes and Instruments Used
Market neutral strategies typically utilize equity pairs, convertible bonds, and derivatives such as options and futures to exploit price inefficiencies while hedging market risk, aiming for zero beta exposure. Long/short strategies predominantly focus on equities by taking long positions in undervalued stocks and short positions in overvalued stocks to capitalize on market trends and sector rotations. Both strategies often incorporate ETFs, indexes, and credit instruments to diversify exposure across asset classes including equities, fixed income, and commodities.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Strategy
Market neutral strategies offer the advantage of minimizing market risk by balancing long and short positions, leading to reduced volatility and lower correlation with overall market movements, though they may yield limited upside during strong bull markets. Long/short strategies provide greater flexibility to capitalize on market trends by increasing exposure to outperforming assets while shorting underperformers, but this approach involves higher market risk and potential drawdowns during volatile or declining markets. Both strategies require sophisticated risk management and market analysis to effectively harness their respective benefits and mitigate inherent limitations.
Choosing the Right Strategy for Investment Goals
Market neutral and long/short strategies both aim to reduce market risk while capitalizing on asset mispricings, but market neutral strategies focus on maintaining a near-zero net exposure to market movements, ideal for preserving capital in volatile environments. Long/short strategies allow for net exposure by taking larger directional bets, which suits investors seeking higher returns with a balanced risk profile. Selecting the right strategy depends on specific investment goals, risk tolerance, and market outlook, with market neutral preferred for capital preservation and diversification, while long/short is suited for aggressive growth and alpha generation.
Market neutral vs Long/short strategy Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com