Equity crowdfunding involves investors acquiring shares and ownership stakes in startups or businesses, offering potential long-term returns through dividends or capital appreciation. Debt crowdfunding, also known as peer-to-peer lending, requires investors to lend money to businesses or individuals in exchange for fixed interest payments over time without acquiring ownership. Both methods provide alternative financing options, with equity crowdfunding appealing to those seeking growth potential and debt crowdfunding favoring investors looking for predictable income and lower risk.
Table of Comparison
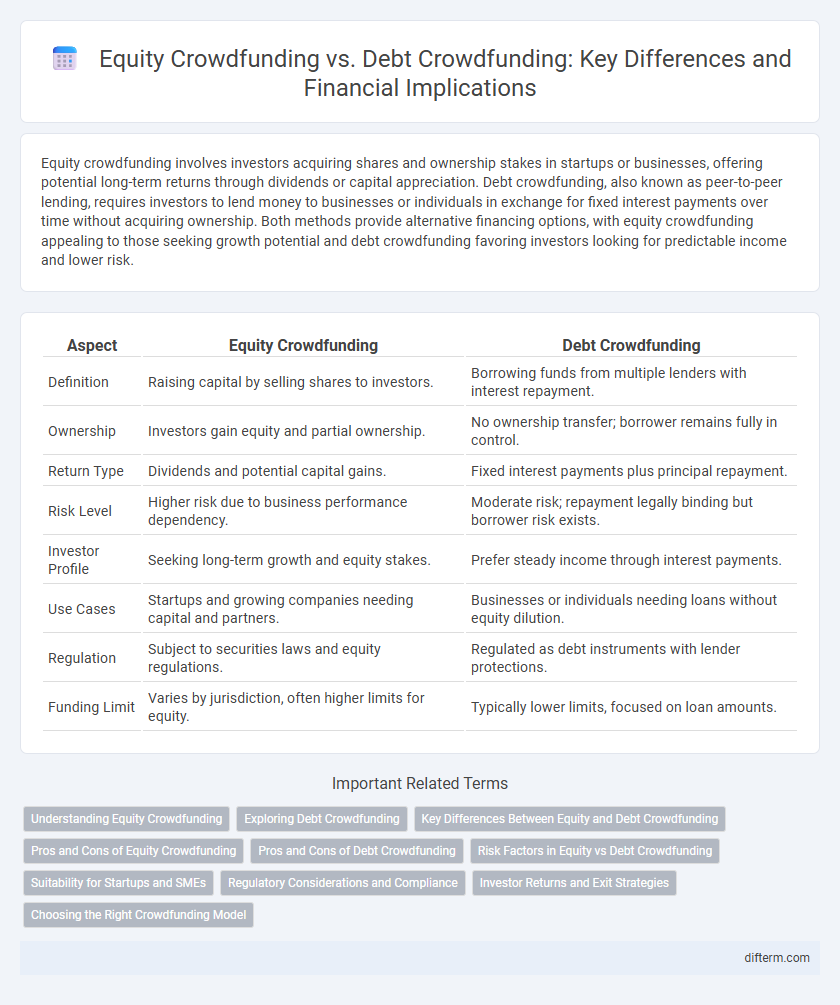
| Aspect | Equity Crowdfunding | Debt Crowdfunding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Raising capital by selling shares to investors. | Borrowing funds from multiple lenders with interest repayment. |
| Ownership | Investors gain equity and partial ownership. | No ownership transfer; borrower remains fully in control. |
| Return Type | Dividends and potential capital gains. | Fixed interest payments plus principal repayment. |
| Risk Level | Higher risk due to business performance dependency. | Moderate risk; repayment legally binding but borrower risk exists. |
| Investor Profile | Seeking long-term growth and equity stakes. | Prefer steady income through interest payments. |
| Use Cases | Startups and growing companies needing capital and partners. | Businesses or individuals needing loans without equity dilution. |
| Regulation | Subject to securities laws and equity regulations. | Regulated as debt instruments with lender protections. |
| Funding Limit | Varies by jurisdiction, often higher limits for equity. | Typically lower limits, focused on loan amounts. |
Understanding Equity Crowdfunding
Equity crowdfunding allows investors to acquire ownership stakes in startups or growing companies, providing businesses with capital in exchange for equity shares. This model aligns investor interests with company performance, potentially yielding high returns through dividends or capital gains. Unlike debt crowdfunding, which involves fixed repayments, equity crowdfunding carries higher risk but offers substantial growth opportunities tied to company success.
Exploring Debt Crowdfunding
Debt crowdfunding allows businesses to raise capital by borrowing funds from multiple investors, offering fixed interest repayments over a defined period. Unlike equity crowdfunding, which entails sharing ownership and future profits, debt crowdfunding enables entrepreneurs to retain full control while accessing necessary funds. This financing method appeals to startups and SMEs seeking predictable repayment schedules without diluting equity stakes.
Key Differences Between Equity and Debt Crowdfunding
Equity crowdfunding involves investors receiving shares and ownership stakes in a company, aligning their returns with the company's growth and profitability, whereas debt crowdfunding requires borrowers to repay the principal amount with interest, reflecting a loan-based investment. In equity crowdfunding, investors assume higher risk with potential for substantial rewards tied to company valuation, while debt crowdfunding offers more predictable returns through fixed interest payments but limited upside. The choice between equity and debt crowdfunding impacts control, risk exposure, return expectations, and regulatory compliance for both entrepreneurs and investors.
Pros and Cons of Equity Crowdfunding
Equity crowdfunding allows investors to gain ownership stakes in startups, offering potential high returns if the company succeeds, but it carries significant risks including dilution of shares and lack of liquidity. Companies benefit from access to capital without incurring debt, yet they must share profits and decision-making power with a large pool of shareholders. Unlike debt crowdfunding, equity crowdfunding involves no repayment obligations, but the complexity of managing multiple investors and compliance with securities regulations can pose challenges.
Pros and Cons of Debt Crowdfunding
Debt crowdfunding offers businesses access to capital without diluting ownership, making it an attractive option for maintaining control. This financing method typically features fixed interest rates and predetermined repayment schedules, providing predictability but requiring consistent cash flow to meet obligations. However, the risk of default and potential impact on credit ratings pose significant challenges for companies relying heavily on debt crowdfunding.
Risk Factors in Equity vs Debt Crowdfunding
Equity crowdfunding carries higher risk as investors face potential dilution and loss of their entire investment if the startup fails, whereas debt crowdfunding involves fixed repayments, offering lower risk but limited returns. In equity crowdfunding, returns depend on the company's growth and profitability, making it inherently uncertain. Debt crowdfunding provides more predictable cash flow through scheduled interest payments but exposes investors to borrower default risk.
Suitability for Startups and SMEs
Equity crowdfunding is well-suited for startups and SMEs seeking capital in exchange for ownership stakes, enabling access to a broad investor base without immediate repayment obligations. Debt crowdfunding appeals to businesses preferring structured loan repayments and interest without diluting equity, ideal for companies with predictable cash flows and strong credit profiles. Both methods provide flexible funding options, but equity crowdfunding aligns better with high-growth ventures, while debt crowdfunding suits stable businesses focused on maintaining control.
Regulatory Considerations and Compliance
Equity crowdfunding involves issuing shares to investors, requiring compliance with securities regulations such as the SEC's Regulation Crowdfunding, including disclosure obligations and investor limits. Debt crowdfunding, characterized by loan agreements, falls under lending laws like the Truth in Lending Act and must adhere to interest rate caps and borrower repayment disclosures. Regulatory frameworks for both models emphasize investor protection and transparency, mandating thorough due diligence and ongoing reporting to ensure compliance and mitigate legal risks.
Investor Returns and Exit Strategies
Equity crowdfunding offers investors potential returns through capital appreciation and dividends by acquiring ownership stakes, with exit strategies typically involving company buyouts, IPOs, or secondary sales. Debt crowdfunding provides fixed-income returns via interest payments over predetermined loan terms, offering predictable cash flow without ownership rights. Exit strategies in debt crowdfunding conclude upon loan maturity or early repayment, limiting upside but reducing risk compared to equity investments.
Choosing the Right Crowdfunding Model
Equity crowdfunding allows investors to acquire shares in a startup, aligning their returns with the company's growth potential, while debt crowdfunding involves lending money with fixed interest repayments, offering more predictable returns. Startups seeking long-term partnership and potential for large capital influx may prefer equity crowdfunding, whereas businesses prioritizing immediate funding without diluting ownership often opt for debt crowdfunding. Evaluating factors such as risk tolerance, capital needs, and desired investor relationship is crucial for choosing the right crowdfunding model in finance.
Equity Crowdfunding vs Debt Crowdfunding Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com