Liquidity measures a company's ability to meet short-term obligations using its most liquid assets, ensuring operational stability and creditor confidence. Solvency assesses long-term financial health by comparing total assets to liabilities, indicating the firm's capacity to sustain operations and grow. A balanced approach to managing both liquidity and solvency is crucial for maintaining financial resilience and investor trust.
Table of Comparison
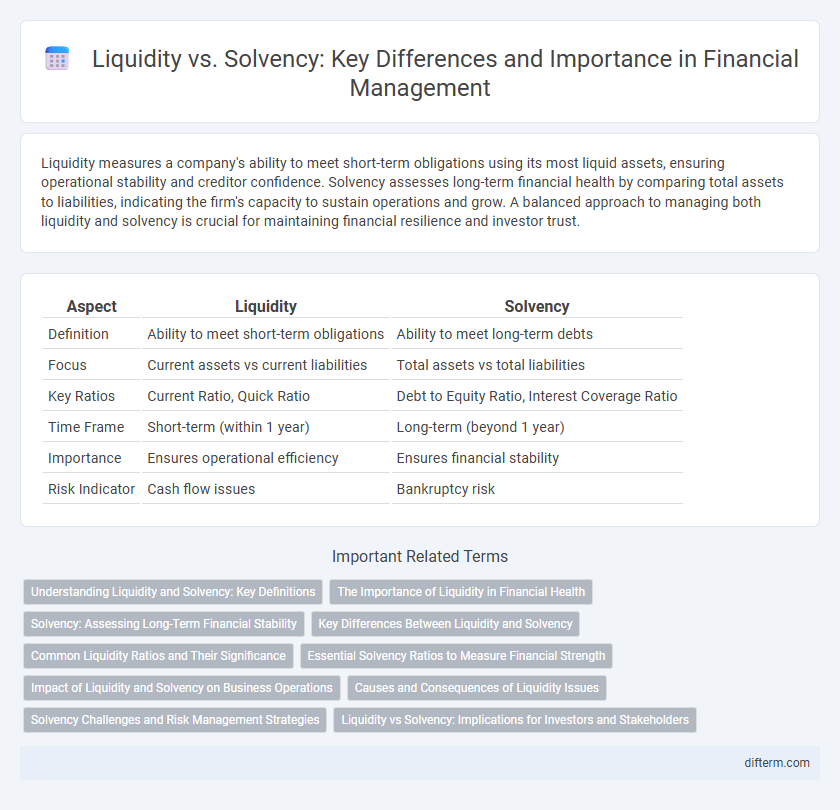
| Aspect | Liquidity | Solvency |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to meet short-term obligations | Ability to meet long-term debts |
| Focus | Current assets vs current liabilities | Total assets vs total liabilities |
| Key Ratios | Current Ratio, Quick Ratio | Debt to Equity Ratio, Interest Coverage Ratio |
| Time Frame | Short-term (within 1 year) | Long-term (beyond 1 year) |
| Importance | Ensures operational efficiency | Ensures financial stability |
| Risk Indicator | Cash flow issues | Bankruptcy risk |
Understanding Liquidity and Solvency: Key Definitions
Liquidity refers to a company's ability to meet its short-term obligations using readily available assets such as cash or marketable securities. Solvency measures a firm's capacity to cover long-term liabilities and sustain operations over time by maintaining a positive net worth. Understanding these key definitions is critical for assessing a business's financial health and risk management strategies.
The Importance of Liquidity in Financial Health
Liquidity measures a company's ability to meet short-term obligations using readily available assets, crucial for maintaining operational stability and avoiding insolvency risks. High liquidity ensures smooth cash flow, enabling businesses to cover expenses like payroll, supplier payments, and unexpected costs without relying on external financing. Assessing liquidity ratios such as the current ratio and quick ratio provides valuable insights into a company's immediate financial health and resilience.
Solvency: Assessing Long-Term Financial Stability
Solvency measures a company's ability to meet long-term obligations and sustain operations over time, highlighting its financial stability beyond immediate liquidity concerns. Key solvency ratios include the debt-to-equity ratio and interest coverage ratio, which quantify the balance between debt load and equity financing. Maintaining strong solvency ensures investors and creditors that the business can withstand economic fluctuations without risking insolvency or bankruptcy.
Key Differences Between Liquidity and Solvency
Liquidity measures a company's ability to meet short-term obligations using available cash or assets easily convertible to cash, often assessed through the current ratio or quick ratio. Solvency evaluates long-term financial stability by analyzing the company's capacity to cover total liabilities with its total assets, with key ratios including the debt-to-equity ratio and interest coverage ratio. The primary difference lies in liquidity focusing on immediate financial health, while solvency reflects overall financial viability and risk over the long term.
Common Liquidity Ratios and Their Significance
Common liquidity ratios, such as the Current Ratio, Quick Ratio, and Cash Ratio, serve as critical indicators of a company's ability to meet short-term obligations without raising external capital. The Current Ratio measures total current assets against current liabilities, highlighting overall liquidity, while the Quick Ratio excludes inventory, providing a stricter assessment of liquid assets. These ratios are significant for creditors and investors to evaluate financial health and operational efficiency in managing working capital.
Essential Solvency Ratios to Measure Financial Strength
Essential solvency ratios such as the debt-to-equity ratio, interest coverage ratio, and equity ratio efficiently gauge a company's financial strength by assessing its long-term ability to meet obligations. The debt-to-equity ratio highlights the balance between debt financing and shareholders' equity, indicating risk exposure. Interest coverage ratio evaluates a firm's capacity to pay interest on outstanding debt, while the equity ratio reflects the proportion of assets financed by shareholders, all critical for assessing solvency.
Impact of Liquidity and Solvency on Business Operations
Liquidity directly influences a business's ability to meet short-term obligations, ensuring smooth daily operations and preventing disruptions caused by cash shortages. Solvency affects long-term financial stability and the capacity to sustain operations through market fluctuations, impacting investor confidence and creditworthiness. Together, liquidity and solvency determine operational resilience, enabling companies to manage risks and capitalize on growth opportunities effectively.
Causes and Consequences of Liquidity Issues
Liquidity issues often stem from mismatched cash flow timing, poor working capital management, or sudden declines in asset liquidity. These problems reduce a company's ability to meet short-term obligations, triggering increased borrowing costs or forced asset sales. Prolonged liquidity shortages can escalate into solvency crises, jeopardizing long-term financial stability and credit ratings.
Solvency Challenges and Risk Management Strategies
Solvency challenges arise when a company's long-term liabilities exceed its asset base, threatening its ability to meet debt obligations and sustain operations. Effective risk management strategies include maintaining adequate capital reserves, diversifying revenue streams, and regularly stress-testing financial models to anticipate adverse market conditions. Monitoring solvency ratios such as the debt-to-equity and interest coverage ratio provides critical insights for timely interventions and strategic decision-making.
Liquidity vs Solvency: Implications for Investors and Stakeholders
Liquidity measures a company's ability to meet short-term obligations using its current assets, directly impacting operational stability and investor confidence. Solvency evaluates long-term financial health by assessing total assets against liabilities, influencing stakeholders' perception of sustained viability. Understanding the balance between liquidity and solvency is crucial for investors and stakeholders to assess risk exposure and make informed decisions on asset allocation and debt management.
Liquidity vs Solvency Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com