Asset allocation involves distributing investments across various asset classes to balance risk and return, whereas asset selection focuses on choosing specific securities within those classes to maximize potential gains. Effective asset allocation provides a strategic framework for portfolio diversification, reducing volatility and improving risk-adjusted returns. Asset selection then fine-tunes the portfolio by identifying high-performing assets, leveraging market insights and analysis for enhanced profit opportunities.
Table of Comparison
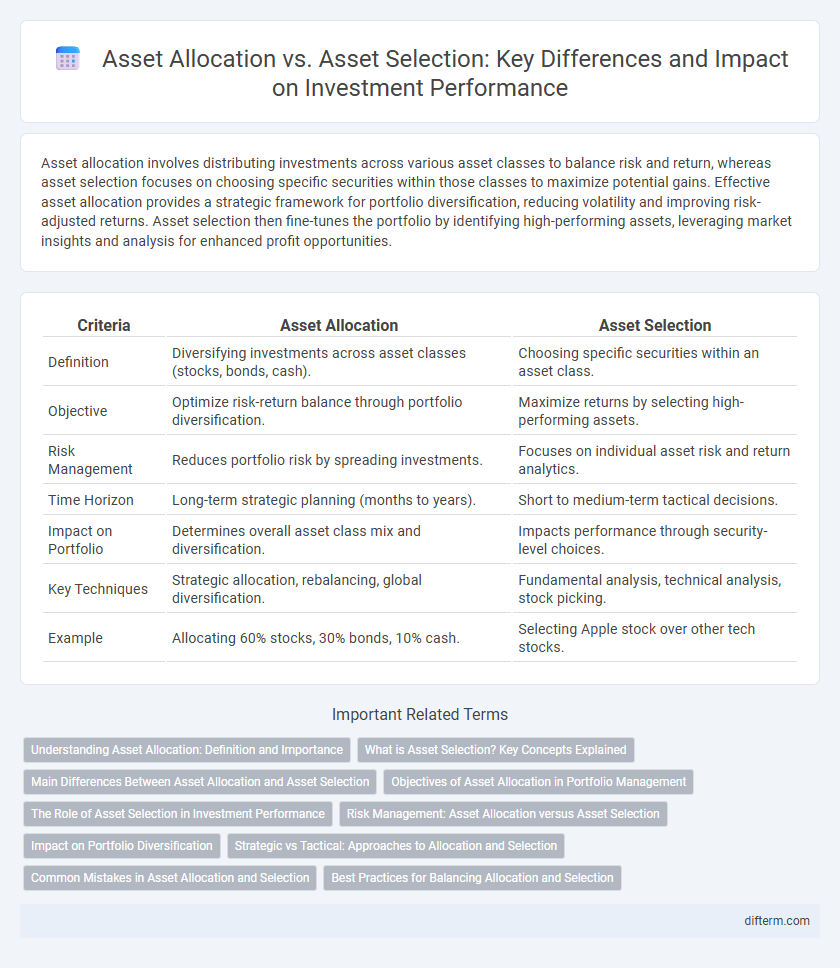
| Criteria | Asset Allocation | Asset Selection |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Diversifying investments across asset classes (stocks, bonds, cash). | Choosing specific securities within an asset class. |
| Objective | Optimize risk-return balance through portfolio diversification. | Maximize returns by selecting high-performing assets. |
| Risk Management | Reduces portfolio risk by spreading investments. | Focuses on individual asset risk and return analytics. |
| Time Horizon | Long-term strategic planning (months to years). | Short to medium-term tactical decisions. |
| Impact on Portfolio | Determines overall asset class mix and diversification. | Impacts performance through security-level choices. |
| Key Techniques | Strategic allocation, rebalancing, global diversification. | Fundamental analysis, technical analysis, stock picking. |
| Example | Allocating 60% stocks, 30% bonds, 10% cash. | Selecting Apple stock over other tech stocks. |
Understanding Asset Allocation: Definition and Importance
Asset allocation involves distributing investments among different asset categories, such as stocks, bonds, and cash, to balance risk and return based on an investor's goals and risk tolerance. This strategic approach is crucial for managing portfolio volatility and achieving long-term financial objectives by diversifying exposure to varying market conditions. Proper asset allocation enhances portfolio resilience against market fluctuations, optimizing risk-adjusted returns over time.
What is Asset Selection? Key Concepts Explained
Asset selection involves choosing individual securities within asset classes to maximize portfolio returns while managing risk, emphasizing detailed analysis of stocks, bonds, or other instruments. Key concepts include evaluating financial metrics like price-to-earnings ratios, dividend yields, and credit ratings to identify undervalued or high-growth assets. Effective asset selection leverages both quantitative models and qualitative factors to refine the investment portfolio beyond broad asset allocation decisions.
Main Differences Between Asset Allocation and Asset Selection
Asset allocation involves distributing investments across various asset classes such as stocks, bonds, and real estate to balance risk and reward according to an investor's goals. Asset selection focuses on picking specific securities within those asset classes based on criteria like performance, risk, and valuation. The main difference lies in asset allocation's macro-level strategy for portfolio diversification, while asset selection is a micro-level process targeting individual investment opportunities.
Objectives of Asset Allocation in Portfolio Management
The primary objectives of asset allocation in portfolio management are to optimize risk-adjusted returns, ensure diversification across various asset classes, and align the investment strategy with the investor's financial goals and risk tolerance. Effective asset allocation reduces portfolio volatility by distributing investments among equities, bonds, real estate, and cash equivalents, mitigating the impact of market fluctuations. This strategic distribution serves as the foundation for long-term portfolio stability and growth, contrasting with asset selection, which focuses on choosing specific securities within each asset class.
The Role of Asset Selection in Investment Performance
Asset selection plays a crucial role in investment performance by determining the specific securities within each asset class, directly impacting returns and risk management. While asset allocation establishes the strategic framework across equities, bonds, and cash, asset selection fine-tunes the portfolio through careful analysis of individual stocks, bonds, and alternative investments. Effective asset selection leverages detailed financial metrics, company fundamentals, and market trends to enhance portfolio alpha beyond the benefits of broad asset allocation.
Risk Management: Asset Allocation versus Asset Selection
Effective risk management in finance hinges on the distinction between asset allocation and asset selection. Asset allocation diversifies investments across asset classes to mitigate systemic risk, while asset selection focuses on identifying individual securities to enhance returns and manage specific risks. Balancing broad diversification with targeted investment choices optimizes portfolio risk-adjusted performance.
Impact on Portfolio Diversification
Asset allocation determines the broad distribution of investments across asset classes, significantly influencing portfolio diversification by balancing risk and return. Asset selection focuses on choosing specific securities within those classes, refining diversification by targeting individual assets with unique risk-return profiles. Together, effective asset allocation and asset selection optimize portfolio diversification, reducing unsystematic risk and enhancing overall financial performance.
Strategic vs Tactical: Approaches to Allocation and Selection
Strategic asset allocation establishes long-term investment targets based on risk tolerance and financial goals, maintaining a consistent portfolio mix across market cycles. Tactical asset allocation adjusts these targets temporarily to capitalize on short-term market opportunities, aiming for excess returns by shifting weights among asset classes. Asset selection within strategic allocation prioritizes core holdings for stability, while tactical selection emphasizes active choices to exploit prevailing market conditions and enhance portfolio performance.
Common Mistakes in Asset Allocation and Selection
Common mistakes in asset allocation include overconcentration in a single asset class and failure to adjust allocations based on risk tolerance or market conditions. In asset selection, investors often overlook diversification, chase past performance, or ignore fees and liquidity constraints. Both errors can lead to suboptimal portfolio performance and increased financial risk.
Best Practices for Balancing Allocation and Selection
Effective asset allocation establishes a strategic framework by diversifying investments across asset classes such as equities, bonds, and cash to manage risk and optimize returns. Asset selection focuses on choosing specific securities within each asset class based on fundamental and technical analysis to enhance portfolio performance. Best practices for balancing allocation and selection include regularly rebalancing to maintain target allocation percentages and conducting thorough due diligence on individual assets to align with investment objectives and risk tolerance.
Asset Allocation vs Asset Selection Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com