Intraday trading involves buying and selling financial instruments within the same trading day to capitalize on short-term price movements, requiring quick decision-making and constant market monitoring. Positional trading, on the other hand, entails holding assets for days, weeks, or months to benefit from broader market trends and fundamental analysis. While intraday trading demands intense focus and speed, positional trading allows for a more strategic approach with less stress and transaction costs.
Table of Comparison
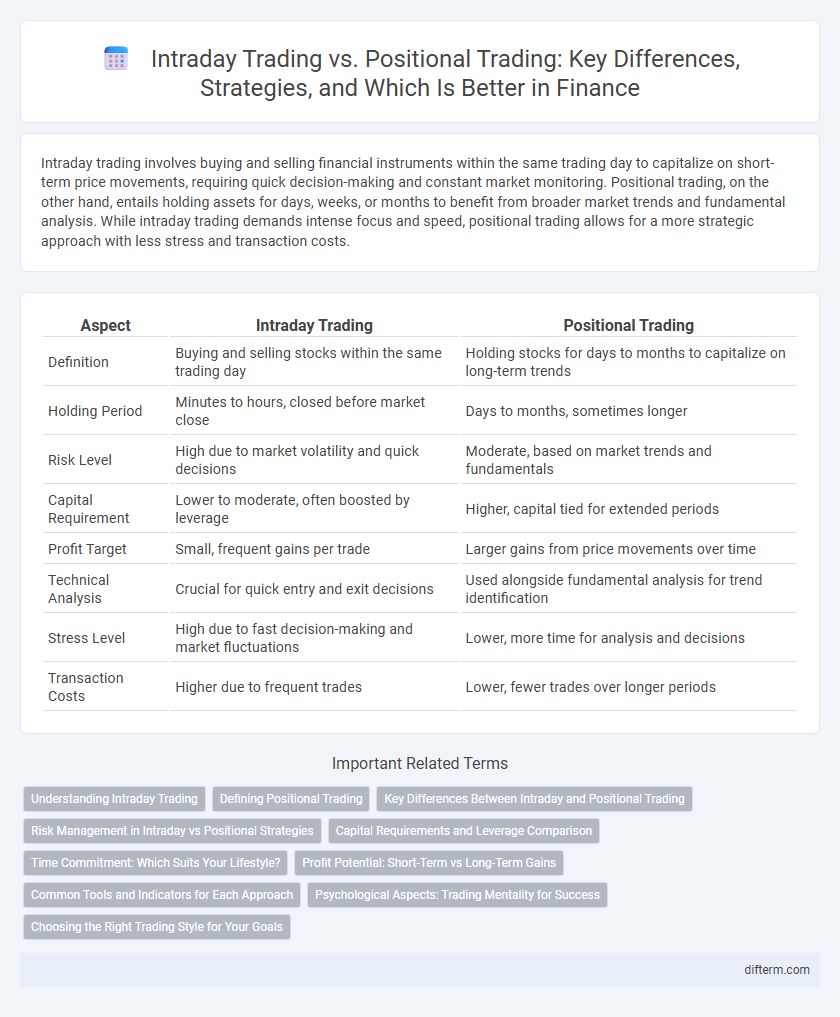
| Aspect | Intraday Trading | Positional Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Buying and selling stocks within the same trading day | Holding stocks for days to months to capitalize on long-term trends |
| Holding Period | Minutes to hours, closed before market close | Days to months, sometimes longer |
| Risk Level | High due to market volatility and quick decisions | Moderate, based on market trends and fundamentals |
| Capital Requirement | Lower to moderate, often boosted by leverage | Higher, capital tied for extended periods |
| Profit Target | Small, frequent gains per trade | Larger gains from price movements over time |
| Technical Analysis | Crucial for quick entry and exit decisions | Used alongside fundamental analysis for trend identification |
| Stress Level | High due to fast decision-making and market fluctuations | Lower, more time for analysis and decisions |
| Transaction Costs | Higher due to frequent trades | Lower, fewer trades over longer periods |
Understanding Intraday Trading
Intraday trading involves buying and selling financial instruments within the same trading day, aiming to capitalize on short-term price fluctuations and liquidity. Traders use technical analysis tools such as moving averages, candlestick patterns, and volume indicators to make quick decisions. Risk management strategies, including stop-loss orders and position sizing, are crucial to minimize losses in volatile market conditions.
Defining Positional Trading
Positional trading involves holding financial assets such as stocks or commodities for days to weeks, aiming to capitalize on medium- to long-term market trends and price movements. Traders analyze fundamental indicators, technical charts, and market sentiment to make informed decisions, prioritizing risk management and trend analysis over rapid trades. Unlike intraday trading, which focuses on quick buy-sell cycles within a single trading day, positional trading requires patience and a strategic approach to capture substantial gains.
Key Differences Between Intraday and Positional Trading
Intraday trading involves buying and selling financial instruments within the same trading day, focusing on short-term price movements and high liquidity to capitalize on market volatility. Positional trading, in contrast, entails holding assets for days to months based on fundamental analysis and long-term trends, aiming for substantial price appreciation. Risk management varies significantly, with intraday traders relying on tight stop-loss orders while positional traders implement broader risk assessments aligned with market fundamentals.
Risk Management in Intraday vs Positional Strategies
Intraday trading requires stringent risk management techniques such as tight stop-loss orders and real-time market analysis to mitigate rapid price fluctuations within a single trading day. Positional trading allows for broader risk tolerance, often utilizing wider stop-loss thresholds and fundamental analysis to manage exposure over days or weeks. Effective risk management in intraday trading emphasizes liquidity and volatility control, while positional strategies rely on trend evaluation and macroeconomic factors.
Capital Requirements and Leverage Comparison
Intraday trading typically requires higher leverage and lower capital, allowing traders to execute multiple trades within a single day to capitalize on small price movements. Positional trading demands greater capital due to the longer holding periods and lower leverage, which reduces risk exposure and margin requirements. Comparing leverage, intraday trading can offer ratios up to 20:1 or higher, whereas positional trading leverage is generally limited to 2:1 or 3:1, reflecting the differing risk and capital allocation strategies.
Time Commitment: Which Suits Your Lifestyle?
Intraday trading demands constant market monitoring and quick decision-making within the same trading day, making it ideal for those who can dedicate several hours daily. Positional trading involves holding assets for days or weeks, requiring less frequent attention and better suiting individuals with limited daily availability. Assessing your time commitment and lifestyle flexibility is crucial to determine which trading style aligns with your financial goals.
Profit Potential: Short-Term vs Long-Term Gains
Intraday trading focuses on capitalizing on short-term price fluctuations within a single trading day, offering the potential for quick profits but requiring precise timing and high market liquidity. Positional trading aims for long-term gains by holding assets over weeks or months, allowing traders to benefit from broader market trends and compound returns. While intraday trading can yield rapid profits, positional trading often delivers more substantial cumulative gains through sustained investment strategies.
Common Tools and Indicators for Each Approach
Intraday trading relies heavily on technical tools such as moving averages, Bollinger Bands, and Relative Strength Index (RSI) for quick decision-making within the trading day. Positional trading often incorporates fundamental analysis alongside tools like Fibonacci retracement, volume indicators, and trend lines to capture longer-term market movements. Both approaches utilize support and resistance levels, but the time frames and indicator sensitivity are adjusted to fit short-term versus extended holding periods.
Psychological Aspects: Trading Mentality for Success
Intraday trading demands rapid decision-making and emotional discipline to manage high volatility within short time frames, requiring traders to maintain focus and control over fear and greed. Positional trading emphasizes patience and confidence, as holding positions over days or weeks necessitates resilience against market fluctuations and delays in gratification. Successful traders develop tailored mental strategies to align their psychological strengths with the distinct pressures of each trading style.
Choosing the Right Trading Style for Your Goals
Intraday trading suits investors seeking quick profits by capitalizing on daily market volatility, requiring constant monitoring and fast decision-making. Positional trading aligns with long-term goals, allowing traders to hold assets for weeks or months, benefiting from broader market trends and reduced transaction costs. Selecting the right style depends on risk tolerance, capital availability, and time commitment, with intraday trading demanding high discipline and positional trading favoring strategic patience.
Intraday Trading vs Positional Trading Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com