High-frequency trading (HFT) leverages ultra-fast execution speeds and low latency to capitalize on small price discrepancies in milliseconds, while quantitative trading uses complex mathematical models and algorithms to identify long-term market patterns and trends. HFT strategies rely heavily on technological infrastructure and real-time data processing, whereas quant trading emphasizes statistical analysis and predictive modeling across various timeframes. Both approaches aim to optimize returns but differ significantly in speed, strategy complexity, and market impact.
Table of Comparison
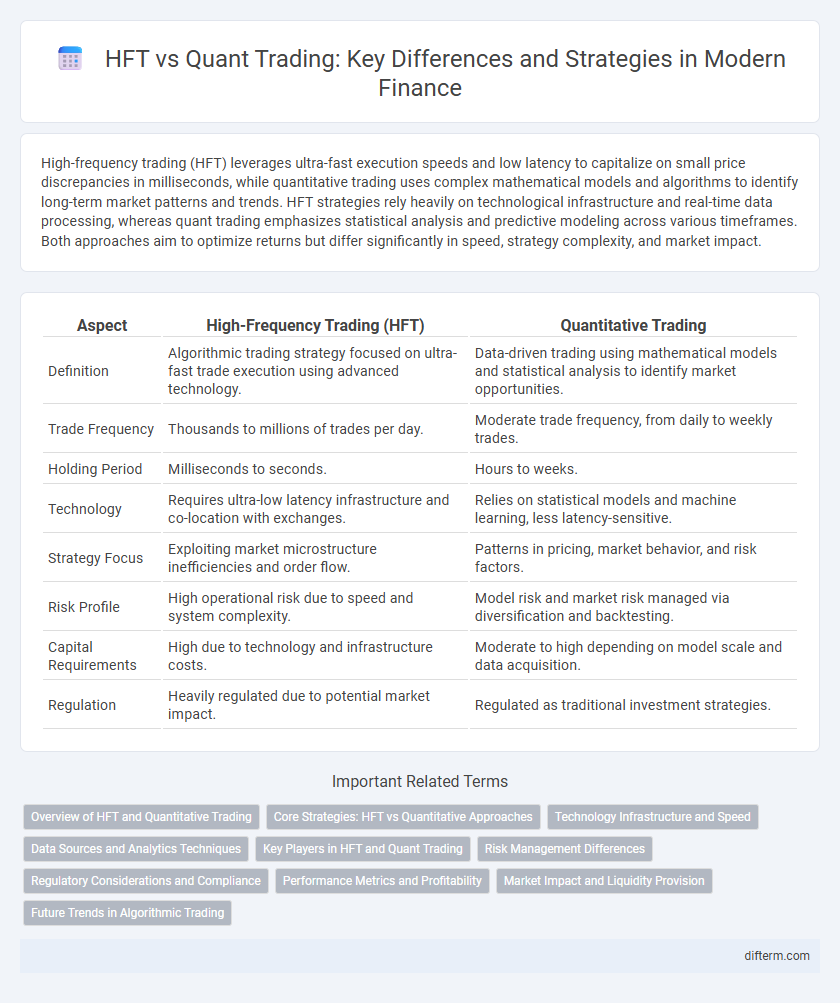
| Aspect | High-Frequency Trading (HFT) | Quantitative Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Algorithmic trading strategy focused on ultra-fast trade execution using advanced technology. | Data-driven trading using mathematical models and statistical analysis to identify market opportunities. |
| Trade Frequency | Thousands to millions of trades per day. | Moderate trade frequency, from daily to weekly trades. |
| Holding Period | Milliseconds to seconds. | Hours to weeks. |
| Technology | Requires ultra-low latency infrastructure and co-location with exchanges. | Relies on statistical models and machine learning, less latency-sensitive. |
| Strategy Focus | Exploiting market microstructure inefficiencies and order flow. | Patterns in pricing, market behavior, and risk factors. |
| Risk Profile | High operational risk due to speed and system complexity. | Model risk and market risk managed via diversification and backtesting. |
| Capital Requirements | High due to technology and infrastructure costs. | Moderate to high depending on model scale and data acquisition. |
| Regulation | Heavily regulated due to potential market impact. | Regulated as traditional investment strategies. |
Overview of HFT and Quantitative Trading
High-Frequency Trading (HFT) utilizes powerful algorithms and high-speed data networks to execute a large number of orders within milliseconds, capitalizing on minute market inefficiencies. Quantitative Trading relies on mathematical models and statistical analysis to identify investment opportunities, often holding positions longer than HFT strategies. Both approaches leverage advanced technology and data but differ primarily in trade frequency, execution speed, and strategic objectives within financial markets.
Core Strategies: HFT vs Quantitative Approaches
High-Frequency Trading (HFT) relies on ultra-fast execution and low-latency market access to capitalize on minuscule price discrepancies through strategies such as market making, arbitrage, and order anticipation. Quantitative trading employs complex mathematical models and large datasets to identify statistical patterns and exploit longer-term market inefficiencies, including momentum, mean reversion, and factor-based investing. While HFT emphasizes speed and technology infrastructure, quantitative approaches prioritize algorithmic decision-making based on data analysis and predictive modeling.
Technology Infrastructure and Speed
High-frequency trading (HFT) relies on ultra-low latency technology infrastructure, utilizing co-location servers, FPGA hardware, and direct market access to execute thousands of trades per second, where microseconds can determine profitability. Quant trading combines advanced algorithms with big data analytics on cloud-based platforms, prioritizing computational power over raw speed to identify strategic market patterns. The critical difference lies in HFT's emphasis on minimizing execution time through sophisticated network optimization, while quant trading focuses on extensive data processing and model complexity.
Data Sources and Analytics Techniques
High-Frequency Trading (HFT) relies on real-time market data feeds, order book information, and low-latency execution data, utilizing techniques such as algorithmic pattern recognition and statistical arbitrage for rapid trade decisions. Quantitative trading employs a broader range of data sources including historical price data, fundamental financial metrics, alternative data like social media sentiment, and macroeconomic indicators, analyzed through machine learning models and advanced statistical methods. While HFT emphasizes speed and microstructure signals, quant trading focuses on comprehensive data integration and predictive analytics to optimize portfolio performance.
Key Players in HFT and Quant Trading
Jane Street, Two Sigma, and Citadel Securities stand out as key players dominating the high-frequency trading (HFT) space, leveraging ultra-low latency technology to execute thousands of trades per second. In quantitative trading, firms like Renaissance Technologies, DE Shaw, and AQR Capital excel by employing advanced statistical models and machine learning algorithms to identify market inefficiencies. Both HFT and quant trading players rely heavily on cutting-edge technology and vast datasets to optimize trading strategies and maximize returns.
Risk Management Differences
High-Frequency Trading (HFT) prioritizes real-time risk controls and ultra-low latency systems to manage rapid market exposures, while Quantitative Trading employs statistical models and backtesting to assess and mitigate risk over longer time horizons. HFT risk management focuses on immediate execution risks, including flash crashes and liquidity gaps, whereas Quant strategies emphasize portfolio diversification, drawdown limits, and scenario analysis. Both approaches integrate algorithmic safeguards but differ fundamentally in time sensitivity and volatility adaptation.
Regulatory Considerations and Compliance
High-Frequency Trading (HFT) and Quantitative Trading operate under stringent regulatory frameworks designed to ensure market transparency and integrity, with agencies such as the SEC and CFTC enforcing rules like the Market Access Rule and Regulation NMS in the U.S. Compliance challenges for HFT include managing risks associated with market manipulation and latency arbitrage, while Quant Trading firms must adhere to strict data governance and algorithmic accountability standards. Effective regulatory compliance involves continuous monitoring, reporting obligations, and implementation of robust internal controls to mitigate systemic risks and avoid penalties.
Performance Metrics and Profitability
High-frequency trading (HFT) emphasizes low-latency execution and typically measures performance through metrics like order-to-trade ratio, latency, and execution speed, resulting in razor-thin profit margins on massive trade volumes. Quantitative trading leverages advanced statistical models and machine learning to identify market inefficiencies, prioritizing metrics such as Sharpe ratio, alpha generation, and risk-adjusted returns to enhance profitability over longer horizons. While HFT profits stem from microsecond advantages and rapid order flow, quant trading profitability depends on model accuracy and market adaptability.
Market Impact and Liquidity Provision
High-frequency trading (HFT) leverages ultra-low latency execution to capture fleeting price discrepancies, often providing substantial liquidity but risking increased market impact during rapid order executions. Quantitative trading employs algorithmic models to optimize trade execution by minimizing market impact and strategically timing order placement, enhancing liquidity provision without triggering significant price movements. Both strategies rely heavily on advanced analytics and real-time data to balance effective liquidity supply and market stability in electronic financial markets.
Future Trends in Algorithmic Trading
Future trends in algorithmic trading reveal a growing convergence between high-frequency trading (HFT) and quantitative trading strategies, leveraging advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning for enhanced predictive accuracy and execution speed. Increasing adoption of cloud computing and edge technologies enables real-time data processing and low-latency trade execution, critical for both HFT and quant models adapting to volatile markets. Regulatory frameworks are expected to evolve, emphasizing algorithm transparency and risk management to mitigate systemic risks inherent in complex automated trading ecosystems.
HFT vs Quant Trading Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com