Dividend yield measures the annual dividend income relative to the stock price, providing investors with insight into the cash flow generated from dividends. Earnings yield compares a company's earnings per share to its stock price, reflecting overall profitability and potential growth. Investors use dividend yield for income-focused strategies, while earnings yield offers a broader view of a company's financial health and valuation.
Table of Comparison
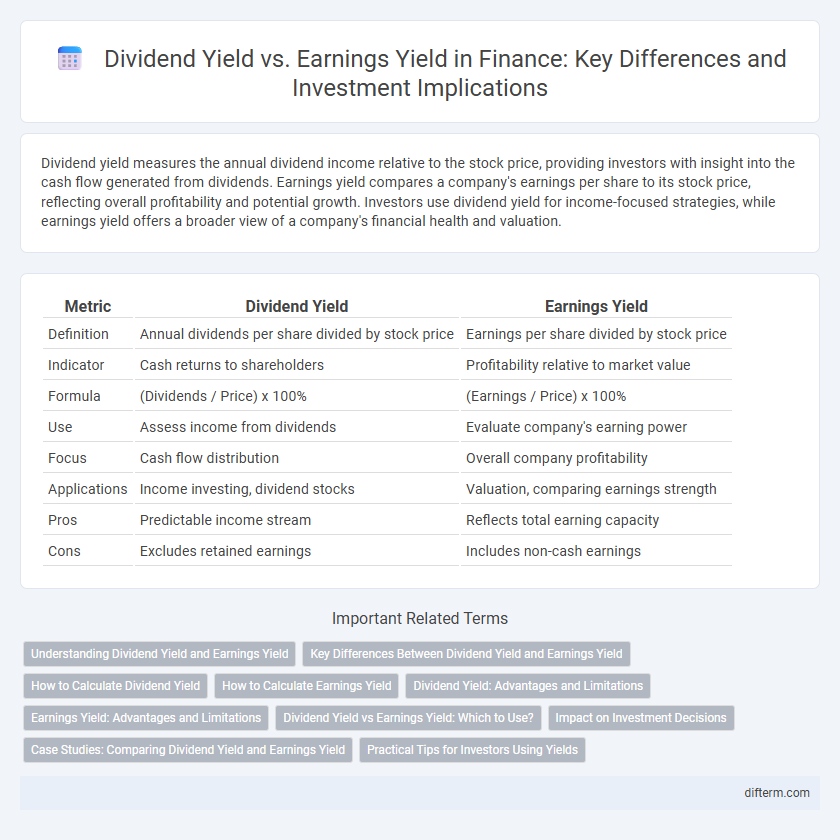
| Metric | Dividend Yield | Earnings Yield |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Annual dividends per share divided by stock price | Earnings per share divided by stock price |
| Indicator | Cash returns to shareholders | Profitability relative to market value |
| Formula | (Dividends / Price) x 100% | (Earnings / Price) x 100% |
| Use | Assess income from dividends | Evaluate company's earning power |
| Focus | Cash flow distribution | Overall company profitability |
| Applications | Income investing, dividend stocks | Valuation, comparing earnings strength |
| Pros | Predictable income stream | Reflects total earning capacity |
| Cons | Excludes retained earnings | Includes non-cash earnings |
Understanding Dividend Yield and Earnings Yield
Dividend yield measures the annual dividend payment as a percentage of the stock price, indicating income return on investment, while earnings yield compares a company's earnings per share to its current stock price, reflecting profitability relative to market valuation. Investors use dividend yield to assess income potential, whereas earnings yield provides insight into valuation and growth prospects. Understanding both metrics helps evaluate whether a stock offers sustainable income or attractive earnings relative to its price.
Key Differences Between Dividend Yield and Earnings Yield
Dividend yield measures the annual dividend income relative to the stock price, reflecting the cash flow an investor receives from dividends. Earnings yield, calculated as earnings per share divided by the stock price, assesses overall profitability and potential return on investment. While dividend yield emphasizes income distribution, earnings yield provides insights into a company's earnings performance and valuation.
How to Calculate Dividend Yield
Dividend yield is calculated by dividing the annual dividends per share by the stock's current market price, expressed as a percentage. This metric helps investors assess the income generated from an investment relative to its price. Accurate calculation requires up-to-date dividend data and current share price from reliable financial sources.
How to Calculate Earnings Yield
Earnings yield is calculated by dividing a company's earnings per share (EPS) by its current stock price, expressed as a percentage. This metric provides investors with an indication of the return they can expect from earnings relative to the stock price, serving as a valuable tool for comparing the attractiveness of different investments. Unlike dividend yield, which only accounts for dividend income, earnings yield reflects the overall profitability of a company.
Dividend Yield: Advantages and Limitations
Dividend yield offers investors a tangible measure of income generated from a stock relative to its current price, making it a preferred metric for income-focused portfolios and dividend reinvestment strategies. This yield provides a clear view of cash flow from dividends, which can signal company stability and financial health, but it may not fully capture growth potential or earnings volatility. Its limitations include sensitivity to stock price fluctuations and the risk of high yields stemming from declining stock prices or unsustainable dividend payouts.
Earnings Yield: Advantages and Limitations
Earnings yield, calculated as earnings per share divided by the stock price, offers a clear measure of a company's profitability relative to its market value, making it a valuable tool for comparing investments across sectors. It highlights the percentage of each dollar invested in the stock that was earned by the company, aiding investors in assessing potential returns. However, earnings yield can be limited by accounting distortions, earnings volatility, and failure to account for growth prospects, which may lead to misinterpretation if used in isolation.
Dividend Yield vs Earnings Yield: Which to Use?
Dividend yield measures the return investors receive from dividends relative to the stock price, while earnings yield compares earnings per share to the stock price, reflecting overall profitability. Dividend yield suits income-focused investors seeking regular cash flow, whereas earnings yield provides a broader view of a company's financial performance and potential growth. Choosing between them depends on investment goals: dividend yield for steady income and earnings yield for assessing valuation and growth prospects.
Impact on Investment Decisions
Dividend yield measures the annual dividend income relative to a stock's price, offering investors insight into immediate cash returns, while earnings yield reflects the company's profitability compared to its market value, indicating potential growth and valuation. Investors prioritize dividend yield for income-focused strategies, especially in stable or dividend-paying sectors, whereas earnings yield guides those seeking undervalued stocks with strong earnings potential. Balancing both metrics enhances investment decisions by providing a comprehensive view of income generation and company profitability.
Case Studies: Comparing Dividend Yield and Earnings Yield
Case studies comparing dividend yield and earnings yield highlight their distinct implications for investment decisions, where dividend yield measures the annual dividend income relative to stock price, while earnings yield indicates profitability by comparing earnings per share to stock price. Research reveals that companies with high earnings yield but low dividend yield may reinvest profits for growth, whereas firms with high dividend yield often attract income-focused investors seeking stable returns. Evaluations of firms like ExxonMobil and Apple illustrate how variations in these yields reflect different corporate strategies and investor preferences, crucial for portfolio diversification.
Practical Tips for Investors Using Yields
Dividend yield offers investors a direct measure of income generated relative to stock price, helping to identify income-focused investments. Earnings yield, calculated as earnings per share divided by stock price, provides insight into a company's overall profitability and potential valuation. Practical tips for investors include using dividend yield to assess steady cash flow and earnings yield to evaluate growth prospects and relative cheapness in the market.
Dividend yield vs earnings yield Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com