Dividend yield measures the annual dividend income relative to the stock price, indicating the return an investor can expect from dividends alone. The dividend payout ratio reveals the proportion of earnings distributed to shareholders as dividends, reflecting a company's dividend policy sustainability. Understanding both metrics helps investors assess the balance between income generation and the company's reinvestment strategy.
Table of Comparison
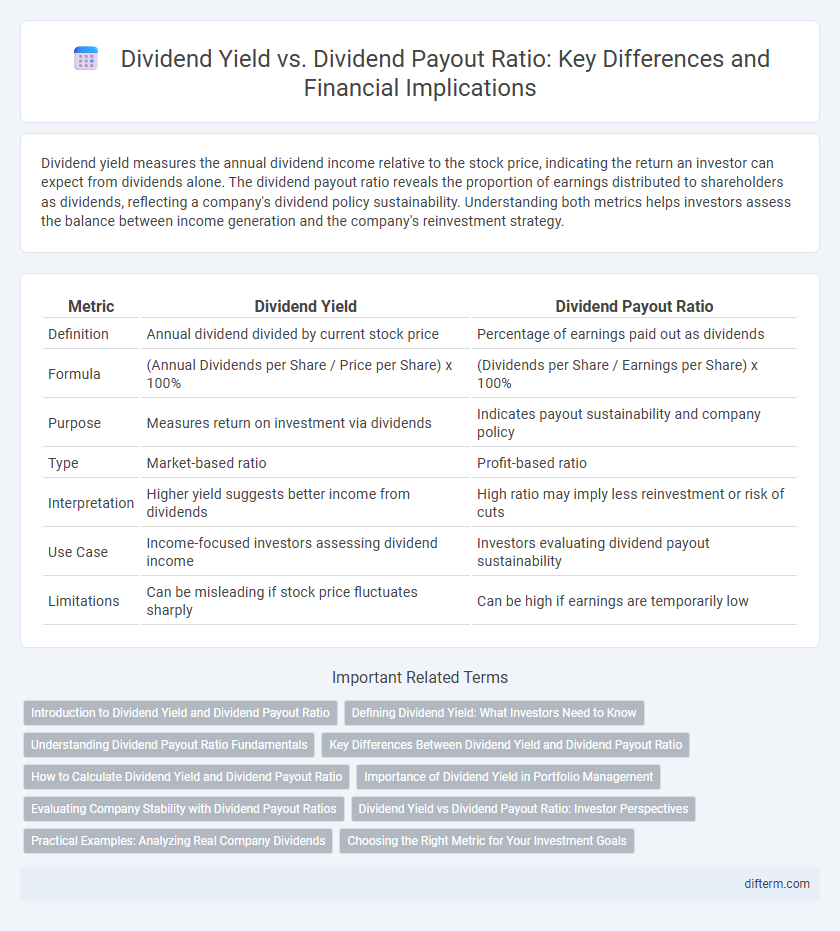
| Metric | Dividend Yield | Dividend Payout Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Annual dividend divided by current stock price | Percentage of earnings paid out as dividends |
| Formula | (Annual Dividends per Share / Price per Share) x 100% | (Dividends per Share / Earnings per Share) x 100% |
| Purpose | Measures return on investment via dividends | Indicates payout sustainability and company policy |
| Type | Market-based ratio | Profit-based ratio |
| Interpretation | Higher yield suggests better income from dividends | High ratio may imply less reinvestment or risk of cuts |
| Use Case | Income-focused investors assessing dividend income | Investors evaluating dividend payout sustainability |
| Limitations | Can be misleading if stock price fluctuates sharply | Can be high if earnings are temporarily low |
Introduction to Dividend Yield and Dividend Payout Ratio
Dividend yield measures the annual dividend income relative to the stock price, expressed as a percentage, helping investors assess the return on investment from dividends alone. The dividend payout ratio indicates the proportion of earnings distributed to shareholders as dividends, reflecting a company's policy on income retention versus distribution. Together, these metrics provide insights into a firm's dividend strategy and financial health, guiding investment decisions based on income generation and sustainability.
Defining Dividend Yield: What Investors Need to Know
Dividend yield measures the annual dividends paid by a company relative to its stock price, expressed as a percentage, providing investors insight into the return from dividends alone. It differs from the dividend payout ratio, which indicates the proportion of earnings distributed as dividends, revealing how much profit is returned versus retained. Understanding dividend yield helps investors assess income potential and compare dividend-paying stocks effectively within the finance sector.
Understanding Dividend Payout Ratio Fundamentals
Dividend payout ratio measures the proportion of earnings paid out as dividends to shareholders, indicating how much profit a company returns versus reinvests. A high dividend payout ratio suggests stable income but may signal limited growth potential, while a low ratio indicates retained earnings for expansion. Analyzing payout ratio alongside dividend yield helps investors assess dividend sustainability and income reliability in portfolio management.
Key Differences Between Dividend Yield and Dividend Payout Ratio
Dividend yield measures the annual dividend income relative to a stock's current price, indicating investment return potential, while the dividend payout ratio reflects the percentage of earnings distributed as dividends, revealing company dividend policy and sustainability. Dividend yield provides investors with insight into cash flow from dividends compared to market price, whereas the payout ratio highlights how much profit the company retains for growth versus paying out to shareholders. Understanding these distinct metrics enables clearer evaluation of dividend attractiveness and financial health of dividend-paying stocks.
How to Calculate Dividend Yield and Dividend Payout Ratio
Dividend yield is calculated by dividing the annual dividend per share by the current market price per share, expressed as a percentage, helping investors assess the income generated relative to stock price. The dividend payout ratio is determined by dividing the total dividends paid by the company's net income, indicating the percentage of earnings distributed to shareholders. Both metrics provide critical insights into a company's dividend policy and financial health for investment decisions.
Importance of Dividend Yield in Portfolio Management
Dividend yield is a critical metric in portfolio management because it directly reflects the cash return an investor receives relative to the stock's market price, providing insight into income stability and investment attractiveness. Unlike the dividend payout ratio, which indicates the proportion of earnings distributed as dividends, dividend yield helps investors assess the actual income generated and compare it across different assets or sectors. A higher dividend yield often appeals to income-focused investors seeking regular cash flows, making it essential for balancing risk and return in diversified portfolios.
Evaluating Company Stability with Dividend Payout Ratios
Dividend payout ratios provide critical insights into a company's financial stability by indicating the portion of earnings distributed as dividends, with lower ratios often signaling retained earnings for growth or debt reduction. In contrast, dividend yield reflects the annual dividend payment relative to the stock price, offering investors a snapshot of income return but less insight into sustainability. Evaluating dividend payout ratios alongside earnings consistency helps investors assess a company's long-term ability to maintain or increase dividends, ensuring stability in income generation.
Dividend Yield vs Dividend Payout Ratio: Investor Perspectives
Dividend yield measures the annual dividend income relative to the stock price, indicating the return investors receive from dividends alone, while dividend payout ratio reflects the proportion of earnings distributed as dividends, highlighting company reinvestment strategies. Investors prioritize dividend yield to assess income potential, particularly those seeking steady cash flow, whereas the payout ratio signals dividend sustainability and growth prospects, crucial for long-term investment decisions. Balancing yield and payout ratio helps investors evaluate risk, income stability, and the company's financial health for informed portfolio management.
Practical Examples: Analyzing Real Company Dividends
Dividend yield measures the annual dividend payment relative to the stock price, providing insight into income generation, while dividend payout ratio indicates the proportion of earnings distributed as dividends, reflecting company policy on profit retention. For example, Coca-Cola's dividend yield of approximately 3% combined with a payout ratio near 75% suggests stable income with moderate earnings reinvestment. Conversely, Apple's lower dividend yield around 0.5% but a payout ratio of about 15% highlights a growth-focused strategy with significant earnings retained for expansion.
Choosing the Right Metric for Your Investment Goals
Dividend yield measures the annual dividend income relative to a stock's current price, providing insight into cash flow potential for income-focused investors. Dividend payout ratio indicates the percentage of earnings distributed as dividends, helping assess dividend sustainability and company reinvestment capacity. Selecting between these metrics depends on investment goals: yield targets income generation, while payout ratio emphasizes financial health and growth prospects.
Dividend yield vs Dividend payout ratio Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com