Currency hedging minimizes risk by using financial instruments like forward contracts or options to protect against adverse currency fluctuations, ensuring more predictable cash flows for businesses and investors. Currency speculation involves taking calculated positions in foreign exchange markets to profit from expected currency movements, often leading to higher risk and potential gains or losses. Understanding the distinction between hedging and speculation is crucial for managing currency exposure effectively and aligning strategies with risk tolerance and financial goals.
Table of Comparison
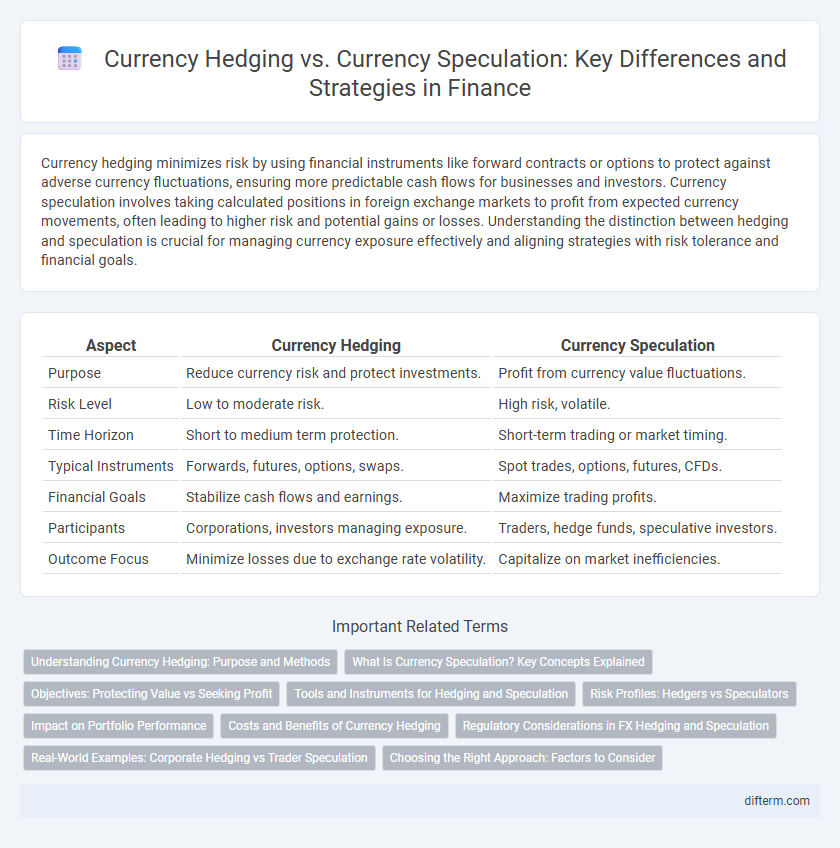
| Aspect | Currency Hedging | Currency Speculation |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Reduce currency risk and protect investments. | Profit from currency value fluctuations. |
| Risk Level | Low to moderate risk. | High risk, volatile. |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium term protection. | Short-term trading or market timing. |
| Typical Instruments | Forwards, futures, options, swaps. | Spot trades, options, futures, CFDs. |
| Financial Goals | Stabilize cash flows and earnings. | Maximize trading profits. |
| Participants | Corporations, investors managing exposure. | Traders, hedge funds, speculative investors. |
| Outcome Focus | Minimize losses due to exchange rate volatility. | Capitalize on market inefficiencies. |
Understanding Currency Hedging: Purpose and Methods
Currency hedging involves implementing financial instruments such as forward contracts, options, and futures to mitigate the risk of adverse currency fluctuations in international transactions and investments. The primary purpose of currency hedging is to protect businesses and investors from unpredictable exchange rate movements that can impact profitability and cash flow. Effective hedging strategies enhance financial stability by locking in exchange rates, thereby minimizing exposure to currency volatility in global markets.
What Is Currency Speculation? Key Concepts Explained
Currency speculation involves buying and selling foreign currencies to profit from fluctuations in exchange rates. Traders analyze economic indicators, geopolitical events, and market sentiment to predict currency movements, aiming for short-term gains. Unlike currency hedging, which mitigates risk, speculation assumes higher risk in pursuit of potential profits.
Objectives: Protecting Value vs Seeking Profit
Currency hedging aims to protect the value of assets or cash flows from adverse exchange rate fluctuations, minimizing financial risk for businesses and investors. Currency speculation involves taking calculated risks on currency movements to seek profit by capitalizing on predicted changes in exchange rates. While hedging prioritizes stability and risk management, speculation focuses on generating returns through active market positions.
Tools and Instruments for Hedging and Speculation
Currency hedging employs tools such as forward contracts, futures, options, and currency swaps to mitigate exchange rate risk by locking in prices or protecting against adverse currency movements. In contrast, currency speculation utilizes leverage through forex spot trades, options, and futures contracts to capitalize on short-term volatility and profit from currency price fluctuations. Both strategies rely heavily on derivatives markets, but hedging focuses on risk management while speculation targets profit generation.
Risk Profiles: Hedgers vs Speculators
Currency hedging involves managing foreign exchange risk by using financial instruments like forwards or options to protect investments from adverse currency fluctuations, resulting in lower risk exposure. Speculators actively seek to profit from currency movements by taking positions in the forex market, accepting higher risk for the potential of significant returns. Hedgers prioritize capital preservation and stability, whereas speculators embrace volatility and market uncertainty to maximize gains.
Impact on Portfolio Performance
Currency hedging stabilizes portfolio returns by minimizing exposure to foreign exchange risk, thereby reducing volatility and protecting against adverse currency movements. Currency speculation involves taking positions based on anticipated currency fluctuations, which can amplify returns but also increase portfolio risk and introduce significant performance variability. Effective portfolio management balances these strategies to optimize risk-adjusted returns while considering market conditions and investment objectives.
Costs and Benefits of Currency Hedging
Currency hedging reduces exposure to foreign exchange risk by locking in exchange rates, helping businesses stabilize cash flows and protect profit margins. While hedging incurs costs such as transaction fees, opportunity costs from missed exchange rate gains, and potential margin requirements, it offers predictability and reduces volatility in financial planning. These benefits often outweigh the expenses for companies with significant international operations seeking to manage currency fluctuations.
Regulatory Considerations in FX Hedging and Speculation
Regulatory considerations in currency hedging and speculation play a crucial role in managing compliance risks within the FX market. Financial authorities impose strict reporting requirements, position limits, and capital adequacy standards to mitigate systemic risk and ensure market stability. Differentiating between hedging, which aims to reduce exposure, and speculation, which seeks profit from currency movements, is essential for aligning with regulatory frameworks such as Dodd-Frank in the US and EMIR in the EU.
Real-World Examples: Corporate Hedging vs Trader Speculation
Corporate hedging involves multinational companies like Apple and Toyota using currency derivatives to mitigate risks from currency fluctuations, ensuring predictable cash flows and safeguarding profit margins. In contrast, trader speculation, exemplified by hedge funds such as Soros Fund Management, seeks to profit from currency movements by taking leveraged positions on expected changes in exchange rates. Real-world outcomes show hedging stabilizes financial performance, while speculation carries high risk with potential for significant gains or losses.
Choosing the Right Approach: Factors to Consider
Selecting between currency hedging and currency speculation depends on risk tolerance, investment objectives, and market knowledge. Hedging aims to minimize exposure to currency fluctuations by using instruments like forwards, options, or futures, providing stability for multinational corporations and investors with foreign assets. Speculation involves taking calculated risks to profit from currency movements, requiring deep understanding of forex markets and accepting potential volatility and losses.
Currency Hedging vs Currency Speculation Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com