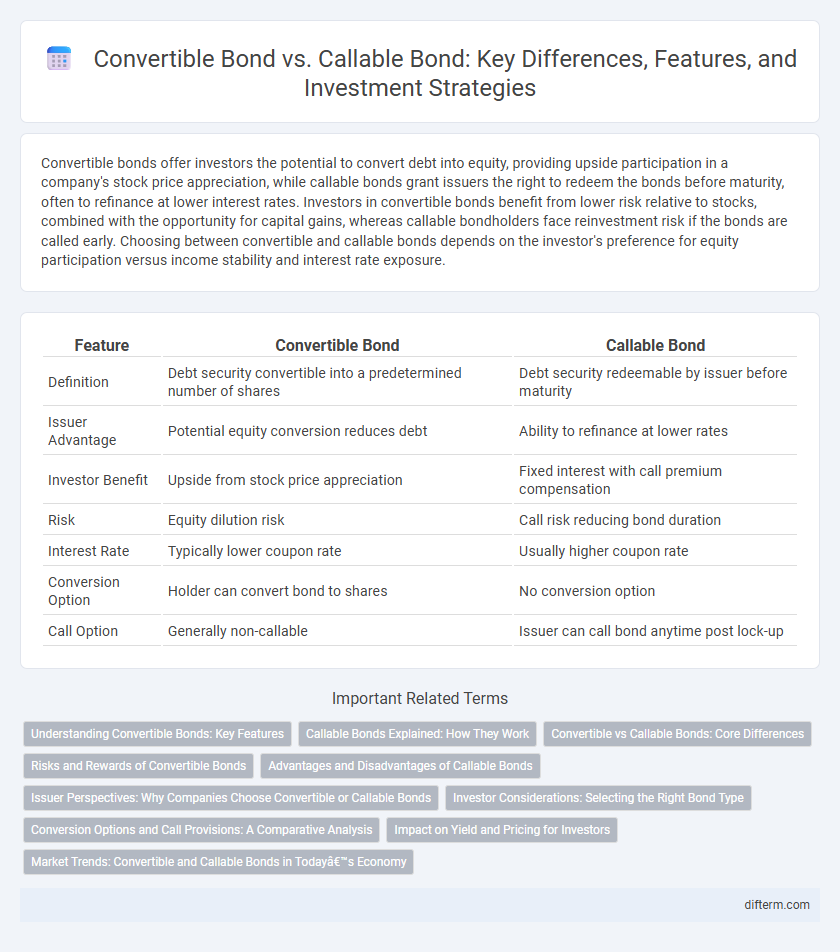
Convertible bonds offer investors the potential to convert debt into equity, providing upside participation in a company's stock price appreciation, while callable bonds grant issuers the right to redeem the bonds before maturity, often to refinance at lower interest rates. Investors in convertible bonds benefit from lower risk relative to stocks, combined with the opportunity for capital gains, whereas callable bondholders face reinvestment risk if the bonds are called early. Choosing between convertible and callable bonds depends on the investor's preference for equity participation versus income stability and interest rate exposure.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Convertible Bond | Callable Bond |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Debt security convertible into a predetermined number of shares | Debt security redeemable by issuer before maturity |
| Issuer Advantage | Potential equity conversion reduces debt | Ability to refinance at lower rates |
| Investor Benefit | Upside from stock price appreciation | Fixed interest with call premium compensation |
| Risk | Equity dilution risk | Call risk reducing bond duration |
| Interest Rate | Typically lower coupon rate | Usually higher coupon rate |
| Conversion Option | Holder can convert bond to shares | No conversion option |
| Call Option | Generally non-callable | Issuer can call bond anytime post lock-up |
Understanding Convertible Bonds: Key Features
Convertible bonds combine features of debt and equity by allowing bondholders to convert their bonds into a predetermined number of shares, offering potential upside participation in the issuing company's stock. These bonds typically provide lower coupon rates compared to callable bonds due to the added value of the conversion option. Investors benefit from downside protection as fixed-income holders, while retaining the opportunity to benefit from stock price appreciation upon conversion.
Callable Bonds Explained: How They Work
Callable bonds are debt securities that allow the issuer to redeem the bond before its maturity date, usually at a premium above the face value. This feature provides the issuer flexibility to refinance debt at lower interest rates if market conditions improve, potentially reducing interest expenses. Investors face reinvestment risk and typically demand higher yields as compensation for the possibility of early redemption.
Convertible vs Callable Bonds: Core Differences
Convertible bonds allow investors to convert their bonds into a predetermined number of the issuer's equity shares, providing potential upside if the stock price rises. Callable bonds give the issuer the right to redeem the bond before maturity, often at a premium, introducing reinvestment risk for investors. The key difference lies in convertible bonds offering equity participation options, while callable bonds primarily benefit the issuer through flexibility in managing debt.
Risks and Rewards of Convertible Bonds
Convertible bonds offer investors the advantage of fixed income with the potential for equity upside, but carry risks such as dilution of shares and price volatility tied to the underlying stock. Unlike callable bonds, which expose holders to reinvestment risk due to issuer redemption, convertible bonds face market risk arising from fluctuating stock prices and credit risk linked to the issuing company's financial health. The reward of capital appreciation in convertibles is balanced by lower yields compared to traditional bonds and the possibility of conversion timing affecting overall returns.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Callable Bonds
Callable bonds offer issuers the advantage of refinancing debt at lower interest rates if market rates decline, reducing overall financing costs. However, investors face reinvestment risk due to the issuer's option to redeem bonds before maturity, potentially resulting in lower returns. Callable bonds often feature higher coupon rates as compensation for this risk, balancing issuer flexibility with investor protection.
Issuer Perspectives: Why Companies Choose Convertible or Callable Bonds
Companies issue convertible bonds to attract investors by offering potential equity upside, lowering interest costs while preserving cash flow flexibility. Callable bonds provide issuers control over debt maturity, enabling refinance during favorable interest rate environments and managing debt load efficiently. The choice depends on balancing cost savings, capital structure goals, and market conditions to optimize financing strategy.
Investor Considerations: Selecting the Right Bond Type
Convertible bonds offer investors the potential for equity upside by allowing conversion into common stock, appealing to those seeking growth with some downside protection. Callable bonds provide issuers flexibility to refinance at lower rates, posing reinvestment risk to investors but often yield higher coupons as compensation. Investors should evaluate risk tolerance, income needs, and market outlook when selecting between convertible and callable bonds.
Conversion Options and Call Provisions: A Comparative Analysis
Convertible bonds offer investors the option to convert their bonds into a predetermined number of equity shares, providing potential upside through stock appreciation while retaining fixed income characteristics. Callable bonds grant issuers the right to redeem the bonds before maturity at a specified call price, allowing them to manage debt more flexibly but increasing reinvestment risk for investors. The conversion option in convertible bonds aligns investor and issuer interests toward equity participation, whereas the call provision in callable bonds primarily benefits issuers by enabling early debt retirement under favorable market conditions.
Impact on Yield and Pricing for Investors
Convertible bonds typically offer lower yields compared to callable bonds due to their embedded equity option, which adds value for investors through potential stock conversion. Callable bonds generally provide higher yields as compensation for the call risk, where issuers may redeem the bond before maturity, limiting upside for investors. Pricing of convertible bonds factors in volatility and potential stock appreciation, while callable bond pricing emphasizes interest rate risk and issuer call likelihood.
Market Trends: Convertible and Callable Bonds in Today’s Economy
Convertible bonds have gained traction in today's economy due to their hybrid nature, offering investors equity upside potential amid volatile markets, supported by low interest rates and corporate fundraising needs. Callable bonds remain popular for issuers aiming to refinance debt at lower rates, reflecting tightening monetary policies and fluctuating credit spreads. Market trends indicate increasing issuance of convertible bonds from technology and healthcare sectors, while callable bonds continue to be favored by utilities and financial institutions adjusting to economic cycles.
Convertible Bond vs Callable Bond Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com