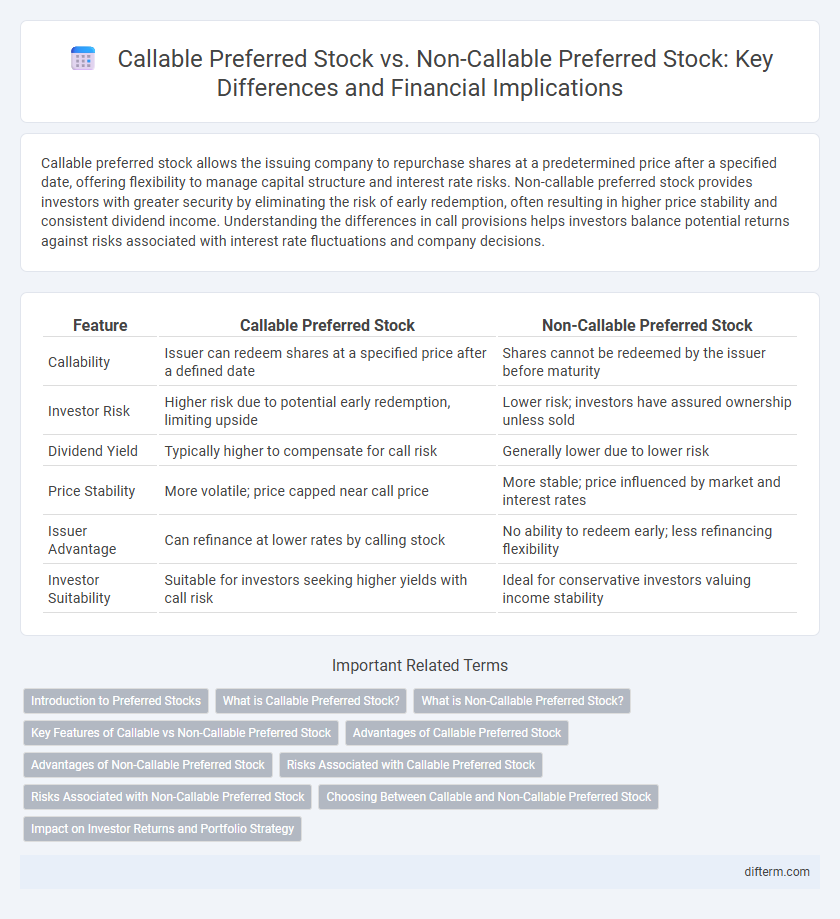
Callable preferred stock allows the issuing company to repurchase shares at a predetermined price after a specified date, offering flexibility to manage capital structure and interest rate risks. Non-callable preferred stock provides investors with greater security by eliminating the risk of early redemption, often resulting in higher price stability and consistent dividend income. Understanding the differences in call provisions helps investors balance potential returns against risks associated with interest rate fluctuations and company decisions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Callable Preferred Stock | Non-Callable Preferred Stock |
|---|---|---|
| Callability | Issuer can redeem shares at a specified price after a defined date | Shares cannot be redeemed by the issuer before maturity |
| Investor Risk | Higher risk due to potential early redemption, limiting upside | Lower risk; investors have assured ownership unless sold |
| Dividend Yield | Typically higher to compensate for call risk | Generally lower due to lower risk |
| Price Stability | More volatile; price capped near call price | More stable; price influenced by market and interest rates |
| Issuer Advantage | Can refinance at lower rates by calling stock | No ability to redeem early; less refinancing flexibility |
| Investor Suitability | Suitable for investors seeking higher yields with call risk | Ideal for conservative investors valuing income stability |
Introduction to Preferred Stocks
Preferred stocks represent a hybrid investment combining features of both equity and debt, offering fixed dividend payments with priority over common stock dividends. Callable preferred stock grants the issuer the right to repurchase shares at a predetermined price after a specific date, providing flexibility to refinance or reduce dividend costs. Non-callable preferred stock lacks this feature, ensuring investors a more stable dividend stream without the risk of early redemption.
What is Callable Preferred Stock?
Callable preferred stock is a type of preferred equity that grants the issuing company the right to repurchase shares at a predetermined price after a specified date. This feature allows firms to manage capital costs by redeeming higher-yielding preferred shares if interest rates decline. Investors in callable preferred stock face reinvestment risk but often receive higher dividend yields as compensation for this call provision.
What is Non-Callable Preferred Stock?
Non-callable preferred stock is a type of preferred equity that cannot be redeemed or repurchased by the issuing company before its maturity date, providing investors with a stable stream of dividends without the risk of early call. This feature offers greater predictability in income as the shares remain outstanding unless sold by the investor, contrasting with callable preferred stock which exposes holders to potential calls and reinvestment risk. Non-callable preferred stock is especially attractive in low-interest-rate environments where investors seek consistent returns without interruption.
Key Features of Callable vs Non-Callable Preferred Stock
Callable preferred stock grants the issuer the right to repurchase shares at a predetermined price after a specified date, providing flexibility in capital structure management. Non-callable preferred stock, in contrast, offers investors greater security with fixed dividend payments and protection from forced redemption, enhancing income stability. Investors weigh the potential for higher yields in callable preferred shares against the safety and predictable returns of non-callable preferred stocks.
Advantages of Callable Preferred Stock
Callable preferred stock offers issuers flexibility to manage capital structure by repurchasing shares at predetermined prices, often allowing refinancing at lower dividend rates during declining interest environments. Investors benefit from higher dividend yields compared to non-callable shares as compensation for call risk. This security feature also enables companies to optimize financial costs and adapt to changing market conditions efficiently.
Advantages of Non-Callable Preferred Stock
Non-callable preferred stock provides investors with greater security by eliminating the risk of the issuer redeeming shares before the maturity date, ensuring stable dividend income. This type of stock offers a predictable cash flow, which is particularly valuable in a low-interest-rate environment where income stability is crucial for portfolio management. Non-callable preferred shares can also enhance long-term capital appreciation potential by safeguarding investors from sudden capital losses triggered by issuer call actions.
Risks Associated with Callable Preferred Stock
Callable preferred stock exposes investors to reinvestment risk as the issuer can redeem the shares at a predetermined price before maturity, potentially when interest rates decline. This feature limits capital appreciation and may force investors to reinvest proceeds at lower yields, impacting income stability. Non-callable preferred stock eliminates this redemption risk, providing more predictable cash flows and protecting investors from sudden changes in investment value.
Risks Associated with Non-Callable Preferred Stock
Non-callable preferred stock carries the risk of limited flexibility for the issuer to refinance or repurchase shares during favorable market conditions, potentially resulting in higher long-term dividend obligations. Investors face interest rate risk as the fixed dividends may become less attractive compared to new issues with higher rates, impacting the stock's market value. Furthermore, non-callable preferred shares often lack the protection of call provisions, which may limit the issuer's ability to manage capital structure efficiently during financial distress.
Choosing Between Callable and Non-Callable Preferred Stock
Choosing between callable and non-callable preferred stock depends on balancing issuer flexibility and investor protections. Callable preferred stock grants issuers the right to repurchase shares at a predetermined price, often resulting in higher yields to compensate investors for call risk. Non-callable preferred stock offers investors stable dividends and reduced risk of premature redemption, typically appealing to risk-averse investors seeking consistent income streams.
Impact on Investor Returns and Portfolio Strategy
Callable preferred stock carries the risk of issuer call at a premium but may limit long-term investor returns due to potential early redemption, prompting reinvestment at lower yields. Non-callable preferred stock offers stable, predictable income, enhancing portfolio duration and reducing interest rate risk. Investors balance callable features against income stability to optimize yield and portfolio diversification strategies.
Callable Preferred Stock vs Non-Callable Preferred Stock Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com