Callable bonds allow issuers to redeem the bond before maturity, providing flexibility to refinance debt if interest rates decline. Noncallable bonds protect investors from early redemption risk, ensuring stable income until maturity with fixed interest payments. Investors weigh callable bonds' higher yields against potential reinvestment risk, while noncallable bonds offer predictable returns and lower risk.
Table of Comparison
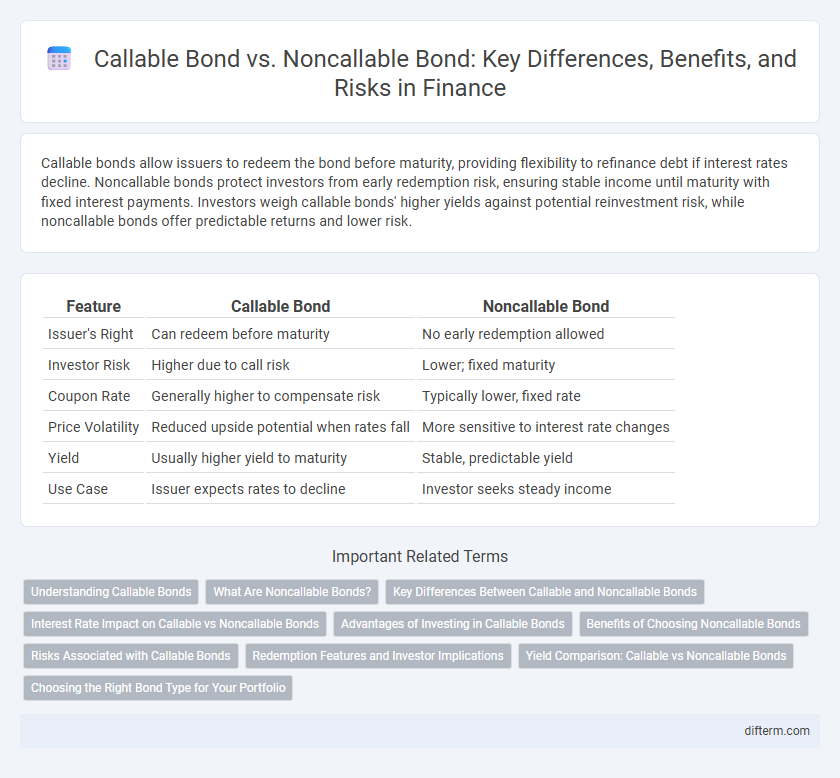
| Feature | Callable Bond | Noncallable Bond |
|---|---|---|
| Issuer's Right | Can redeem before maturity | No early redemption allowed |
| Investor Risk | Higher due to call risk | Lower; fixed maturity |
| Coupon Rate | Generally higher to compensate risk | Typically lower, fixed rate |
| Price Volatility | Reduced upside potential when rates fall | More sensitive to interest rate changes |
| Yield | Usually higher yield to maturity | Stable, predictable yield |
| Use Case | Issuer expects rates to decline | Investor seeks steady income |
Understanding Callable Bonds
Callable bonds give issuers the right to redeem the bond before its maturity date, usually at a predetermined call price, providing flexibility to refinance debt if interest rates decline. This feature exposes investors to reinvestment risk, as they may have to reinvest the principal at lower prevailing rates when the bond is called. Understanding callable bonds requires evaluating the call schedule, yield premium, and market interest rate trends to assess potential risks and rewards compared to noncallable bonds.
What Are Noncallable Bonds?
Noncallable bonds are fixed-income securities that cannot be redeemed by the issuer before their maturity date, providing investors with predictable interest payments and principal repayment. These bonds minimize reinvestment risk since the issuer lacks the option to call the bond early, making them attractive in declining interest rate environments. They typically offer lower yields compared to callable bonds due to the absence of call risk.
Key Differences Between Callable and Noncallable Bonds
Callable bonds allow issuers to redeem the bond before maturity, providing flexibility to refinance debt if interest rates decline, while noncallable bonds guarantee fixed terms with no early redemption option. Callable bonds typically offer higher coupon rates to compensate investors for call risk, whereas noncallable bonds usually have lower yields due to their stable cash flow profile. Investors prioritize callable bonds for potential yield enhancement despite reinvestment risk, whereas noncallable bonds appeal to those seeking predictable income and reduced interest rate risk.
Interest Rate Impact on Callable vs Noncallable Bonds
Callable bonds typically exhibit higher yields than noncallable bonds as investors demand a premium for the issuer's option to redeem early, which becomes more valuable when interest rates decline. In a falling interest rate environment, issuers are more likely to call bonds to refinance at lower rates, increasing reinvestment risk for investors. Noncallable bonds provide greater interest rate protection since their fixed coupons continue unchanged until maturity, offering more predictable income streams.
Advantages of Investing in Callable Bonds
Investing in callable bonds offers higher yields compared to noncallable bonds due to issuer call risk, attracting investors seeking enhanced income. Callable bonds provide portfolio diversification by including securities with embedded options, enabling investors to capitalize on interest rate fluctuations. The call feature allows issuers to refinance debt at lower rates, which may lead to early redemption premiums benefiting investors through potential capital gains.
Benefits of Choosing Noncallable Bonds
Noncallable bonds provide investors with predictable income streams by eliminating the issuer's right to redeem the bond before maturity, thereby reducing reinvestment risk. These bonds enhance portfolio stability through fixed interest payments over the bond's term, making them attractive in volatile interest rate environments. Investors benefit from higher market value consistency, as noncallable bonds avoid price depreciation caused by early calls in declining interest rate scenarios.
Risks Associated with Callable Bonds
Callable bonds carry higher reinvestment risk because issuers can redeem them before maturity when interest rates decline, forcing investors to reinvest at lower yields. Price volatility is greater in callable bonds due to embedded call options, which limit potential price appreciation compared to noncallable bonds. Investors face uncertainty in cash flow timing, making callable bonds more complex and riskier in portfolio management.
Redemption Features and Investor Implications
Callable bonds allow issuers to redeem the bonds before maturity, often when interest rates drop, posing reinvestment risk for investors who may receive lower yields on new investments. Noncallable bonds provide investors with predictable cash flows and protect against early redemption risk, ensuring steady income until maturity. Investors in callable bonds generally demand higher yields as compensation for the potential call risk embedded in the redemption features.
Yield Comparison: Callable vs Noncallable Bonds
Callable bonds typically offer higher yields than noncallable bonds to compensate investors for the call risk, which is the issuer's option to redeem the bond before maturity. The yield premium on callable bonds reflects the potential loss of future interest payments if the bond is called early. Noncallable bonds provide lower yields but greater price stability and certainty of income since they cannot be redeemed before maturity.
Choosing the Right Bond Type for Your Portfolio
Choosing the right bond type involves evaluating your risk tolerance and investment goals, as callable bonds typically offer higher yields to compensate for the issuer's right to redeem early, introducing reinvestment risk. Noncallable bonds provide greater predictability and stability in income, making them suitable for conservative portfolios seeking consistent cash flows. Assess market interest rate trends and portfolio duration needs to determine if the potential call features align with your return objectives and risk management strategy.
Callable Bond vs Noncallable Bond Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com