Callable bonds allow issuers to redeem the bond before maturity, providing flexibility to refinance debt if interest rates decline, while exposing investors to reinvestment risk. Convertible bonds offer investors the option to convert bonds into a predetermined number of the issuer's shares, combining fixed income features with potential equity upside. Choosing between callable and convertible bonds depends on the investor's risk tolerance and preference for income stability versus growth potential.
Table of Comparison
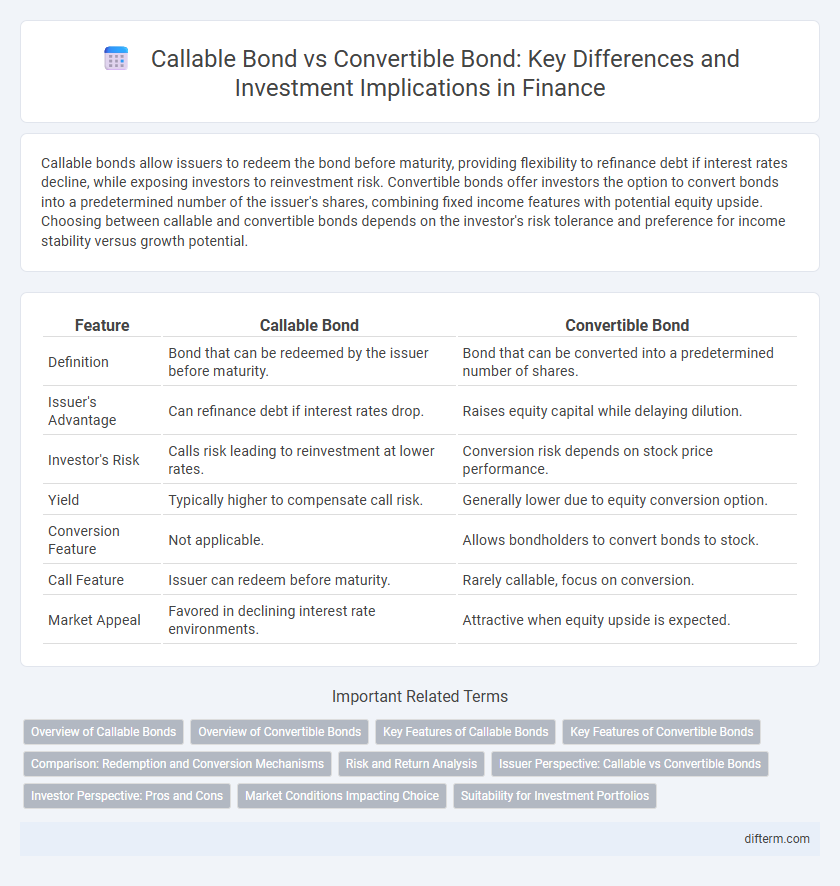
| Feature | Callable Bond | Convertible Bond |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Bond that can be redeemed by the issuer before maturity. | Bond that can be converted into a predetermined number of shares. |
| Issuer's Advantage | Can refinance debt if interest rates drop. | Raises equity capital while delaying dilution. |
| Investor's Risk | Calls risk leading to reinvestment at lower rates. | Conversion risk depends on stock price performance. |
| Yield | Typically higher to compensate call risk. | Generally lower due to equity conversion option. |
| Conversion Feature | Not applicable. | Allows bondholders to convert bonds to stock. |
| Call Feature | Issuer can redeem before maturity. | Rarely callable, focus on conversion. |
| Market Appeal | Favored in declining interest rate environments. | Attractive when equity upside is expected. |
Overview of Callable Bonds
Callable bonds allow the issuer to redeem the bond before its maturity date, typically at a premium, providing flexibility to manage debt in changing interest rate environments. These bonds usually offer higher yields compared to non-callable bonds to compensate investors for the call risk. The issuer's option to call the bond can limit the investor's upside potential, especially if interest rates decline.
Overview of Convertible Bonds
Convertible bonds are hybrid financial instruments that combine features of traditional bonds with the option to convert into a predetermined number of common shares. These bonds offer investors fixed interest payments with the potential for capital appreciation through equity conversion, aligning bondholder incentives with company growth. Convertible bonds provide companies a lower cost of debt compared to straight bonds, often resulting in less dilution of ownership until conversion occurs.
Key Features of Callable Bonds
Callable bonds allow issuers to redeem the bond before maturity, typically at a premium, providing flexibility to manage debt in response to fluctuating interest rates. These bonds often offer higher yields to compensate investors for the call risk, where potential early redemption can limit capital gains. Call provisions impact bond pricing and yield, making callable bonds sensitive to interest rate movements and issuer credit quality.
Key Features of Convertible Bonds
Convertible bonds combine features of debt and equity, allowing bondholders to convert their bonds into a predetermined number of common shares, providing potential upside if the company's stock price rises. These bonds typically offer lower interest rates compared to regular bonds due to the conversion option's value, and the conversion ratio and conversion price are critical parameters impacting investor returns. Convertible bonds also offer downside protection through fixed interest payments and principal repayment, making them attractive in volatile markets where equity performance is uncertain.
Comparison: Redemption and Conversion Mechanisms
Callable bonds allow the issuer to redeem the bond before maturity at a predetermined call price, providing flexibility to manage interest costs when rates decline. Convertible bonds offer bondholders the option to convert their bonds into a specified number of common shares, combining fixed income with potential equity upside. The key difference lies in redemption being issuer-driven for callable bonds, while conversion is bondholder-initiated, affecting valuation and risk profiles.
Risk and Return Analysis
Callable bonds carry higher reinvestment risk due to the issuer's right to redeem before maturity, often resulting in capped upside returns while maintaining steady coupon payments. Convertible bonds offer potential equity upside with lower default risk, as bondholders can convert to shares, but this feature may lead to diluted returns if the underlying stock performs poorly. Risk-adjusted returns for callable bonds tend to be more predictable but limited, whereas convertible bonds present a hybrid risk-return profile influenced by both bond characteristics and equity market volatility.
Issuer Perspective: Callable vs Convertible Bonds
From the issuer's perspective, callable bonds offer greater control by allowing the company to redeem the debt before maturity, typically when interest rates decline, reducing financing costs. Convertible bonds provide a lower coupon rate due to the equity conversion option, which can dilute ownership but improve cash flow flexibility. Issuers balance callable bonds' cost savings against convertible bonds' potential for equity financing and investor appeal.
Investor Perspective: Pros and Cons
Callable bonds offer investors higher yields as compensation for the issuer's option to redeem the bond early, but they carry reinvestment risk if called before maturity. Convertible bonds provide potential upside through equity conversion, allowing investors to participate in the issuer's stock appreciation while generally offering lower coupon rates. However, convertible bonds expose investors to market volatility and dilution risks if the stock price underperforms or the company issues additional shares.
Market Conditions Impacting Choice
Callable bonds tend to perform better in declining interest rate environments, allowing issuers to refinance debt at lower costs, while investors face reinvestment risk. Convertible bonds gain appeal in bullish equity markets, offering potential upside through conversion to common stock alongside fixed income benefits. Market volatility and interest rate trends significantly influence investor preference between the flexible downside protection of callable bonds and the equity participation opportunity of convertible bonds.
Suitability for Investment Portfolios
Callable bonds offer issuers the flexibility to redeem the bond before maturity, making them suitable for investors who seek higher yields but can tolerate reinvestment risk, especially in declining interest rate environments. Convertible bonds provide investors the opportunity to convert debt into equity, appealing to those aiming for capital appreciation with lower downside risk, often fitting growth-oriented or diversified portfolios. Selecting between callable and convertible bonds depends on risk tolerance, income needs, and the investor's market outlook.
Callable Bond vs Convertible Bond Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com