Capital flight and brain drain both pose significant challenges to economic development by depleting essential resources, with capital flight draining financial assets and brain drain extracting skilled human capital. The loss of investments hampers infrastructure growth and economic stability, while the emigration of educated professionals undermines innovation and productivity. Addressing these issues requires strategic policies to retain both financial resources and talent, fostering sustainable economic progress.
Table of Comparison
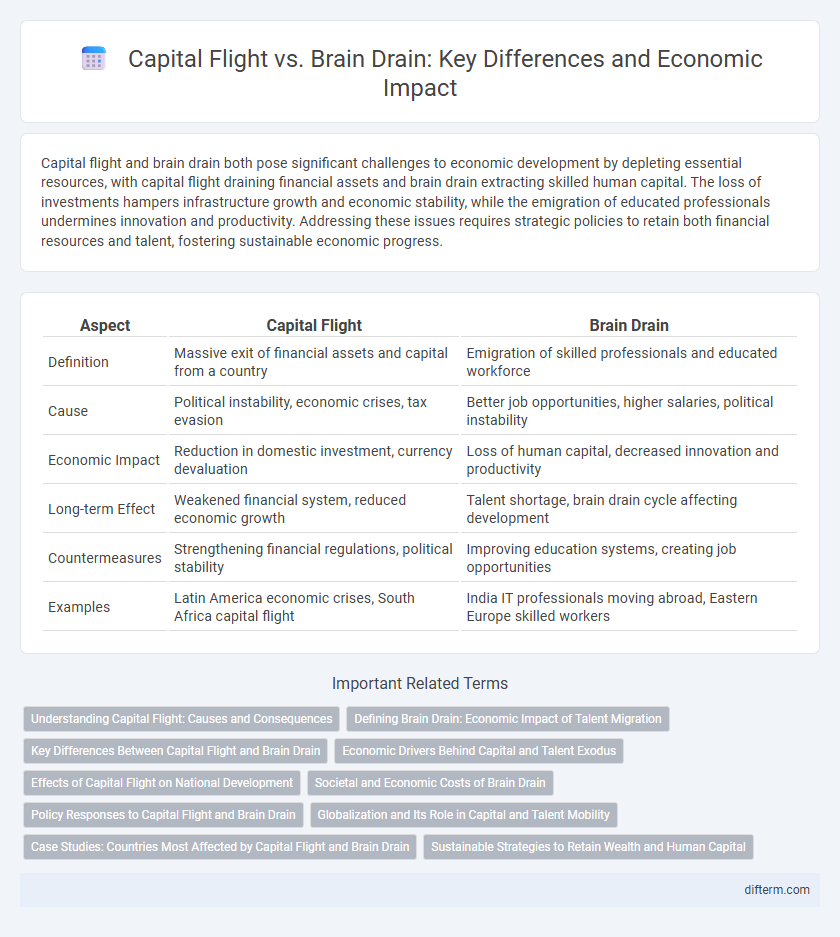
| Aspect | Capital Flight | Brain Drain |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Massive exit of financial assets and capital from a country | Emigration of skilled professionals and educated workforce |
| Cause | Political instability, economic crises, tax evasion | Better job opportunities, higher salaries, political instability |
| Economic Impact | Reduction in domestic investment, currency devaluation | Loss of human capital, decreased innovation and productivity |
| Long-term Effect | Weakened financial system, reduced economic growth | Talent shortage, brain drain cycle affecting development |
| Countermeasures | Strengthening financial regulations, political stability | Improving education systems, creating job opportunities |
| Examples | Latin America economic crises, South Africa capital flight | India IT professionals moving abroad, Eastern Europe skilled workers |
Understanding Capital Flight: Causes and Consequences
Capital flight refers to the rapid outflow of financial assets and capital from a country due to economic instability, political uncertainty, or unfavorable regulatory environments. This movement of capital undermines domestic investment, weakens currency stability, and hinders economic growth by reducing available funds for development. Understanding these causes and consequences is crucial for implementing policies that stabilize the economy and encourage capital retention.
Defining Brain Drain: Economic Impact of Talent Migration
Brain drain refers to the migration of highly skilled and educated professionals from one country to another, leading to a significant loss of human capital in the originating economy. This talent migration undermines economic development by reducing innovation, decreasing productivity, and limiting the ability to compete globally. The resulting gap in skilled labor hampers long-term growth, creating challenges in sectors such as healthcare, technology, and education.
Key Differences Between Capital Flight and Brain Drain
Capital flight refers to the rapid outflow of financial assets and capital from a country, often driven by political instability or economic uncertainty, while brain drain involves the emigration of highly skilled professionals seeking better opportunities abroad. Capital flight primarily affects a nation's financial reserves and investment potential, whereas brain drain impacts the labor market quality and innovation capacity. Both phenomena undermine economic growth, but capital flight depletes monetary resources, and brain drain erodes human capital essential for long-term development.
Economic Drivers Behind Capital and Talent Exodus
Capital flight and brain drain both stem from underlying economic drivers such as political instability, unfavorable regulatory environments, and lack of investment opportunities. High taxes, weak financial institutions, and deteriorating infrastructure propel investors and skilled professionals to seek more stable and prosperous economies. These economic pressures result in the dual loss of financial capital and human talent, exacerbating domestic economic challenges and reducing long-term growth potential.
Effects of Capital Flight on National Development
Capital flight severely undermines national development by depleting the financial resources necessary for investment in infrastructure, education, and healthcare, resulting in slower economic growth. This outflow of capital reduces government revenue, limiting the capacity to fund public services and social programs essential for long-term development. Persistent capital flight also erodes investor confidence, leading to decreased foreign direct investment and further stifling economic progress.
Societal and Economic Costs of Brain Drain
Brain drain imposes severe societal and economic costs, including reduced innovation and productivity as skilled professionals migrate abroad, depleting the domestic talent pool essential for development. This phenomenon undermines public investments in education and healthcare, as the benefit of training skilled workers dissipates when they leave the country. Unlike capital flight, which primarily affects financial assets, brain drain erodes human capital, leading to long-term economic stagnation and weakened institutional capacity.
Policy Responses to Capital Flight and Brain Drain
Effective policy responses to capital flight include strengthening financial regulations, enhancing transparency in asset reporting, and promoting political stability to restore investor confidence. To mitigate brain drain, governments invest in education, improve labor market conditions, and create innovation hubs that offer competitive opportunities for skilled professionals. Coordinated strategies addressing both capital flight and brain drain can stabilize economic growth and sustain human and financial capital within a country.
Globalization and Its Role in Capital and Talent Mobility
Globalization intensifies capital flight and brain drain by easing the movement of financial assets and skilled labor across borders, impacting emerging economies significantly. Multinational corporations and international markets facilitate the rapid relocation of capital seeking higher returns, while professionals migrate to developed countries for better opportunities, leading to talent depletion in home nations. This dual mobility challenges policymakers to create environments that retain both financial resources and human capital, fostering sustainable economic growth.
Case Studies: Countries Most Affected by Capital Flight and Brain Drain
Countries like Nigeria and Venezuela illustrate severe capital flight, with billions of dollars leaving annually due to economic instability and corruption, undermining domestic investment and growth. Simultaneously, India and the Philippines experience significant brain drain as thousands of skilled professionals emigrate yearly for better opportunities, impacting healthcare and technology sectors. Both phenomena exacerbate economic challenges by draining vital resources, capital, and human talent from their home countries.
Sustainable Strategies to Retain Wealth and Human Capital
Sustainable strategies to retain wealth and human capital require addressing both capital flight and brain drain through integrated economic reforms and investment incentives. Strengthening institutional frameworks, improving governance transparency, and enhancing local investment opportunities stimulate domestic confidence and reduce financial outflows. Simultaneously, fostering innovation hubs, improving education quality, and aligning labor market policies with global demand retain skilled professionals and encourage knowledge-based economic growth.
Capital Flight vs Brain Drain Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com