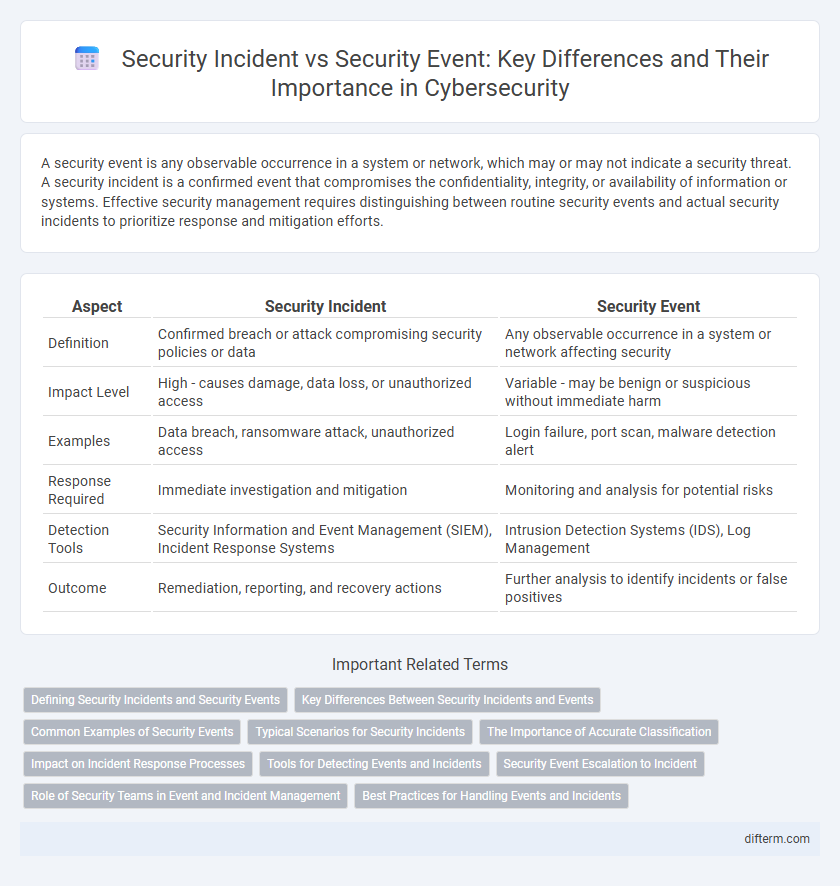
A security event is any observable occurrence in a system or network, which may or may not indicate a security threat. A security incident is a confirmed event that compromises the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of information or systems. Effective security management requires distinguishing between routine security events and actual security incidents to prioritize response and mitigation efforts.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Security Incident | Security Event |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Confirmed breach or attack compromising security policies or data | Any observable occurrence in a system or network affecting security |
| Impact Level | High - causes damage, data loss, or unauthorized access | Variable - may be benign or suspicious without immediate harm |
| Examples | Data breach, ransomware attack, unauthorized access | Login failure, port scan, malware detection alert |
| Response Required | Immediate investigation and mitigation | Monitoring and analysis for potential risks |
| Detection Tools | Security Information and Event Management (SIEM), Incident Response Systems | Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), Log Management |
| Outcome | Remediation, reporting, and recovery actions | Further analysis to identify incidents or false positives |
Defining Security Incidents and Security Events
A security event refers to any observable occurrence in a network or system that may have security relevance, such as login attempts, system alerts, or unusual traffic patterns. A security incident is a confirmed adverse event that compromises the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of information or systems, necessitating response and remediation actions. Differentiating security incidents from general security events is critical for effective monitoring and incident management in cybersecurity frameworks.
Key Differences Between Security Incidents and Events
Security events refer to any observable occurrences within a system or network that may indicate normal or abnormal activity, such as login attempts or system alerts. Security incidents are specific security events or series of events that result in a confirmed breach, unauthorized access, or harm to information assets, requiring immediate investigation and response. The key differences lie in impact and response urgency, where events are broader and monitored continuously, while incidents trigger active mitigation efforts due to their potential or actual threat to security.
Common Examples of Security Events
Common examples of security events include unauthorized login attempts, malware detections, system crashes, and unusual network traffic patterns. These events represent potential indicators of a security incident but do not necessarily confirm a breach or compromise. Monitoring tools generate security event logs to capture such activities for further analysis and incident response.
Typical Scenarios for Security Incidents
Security incidents typically involve unauthorized access, data breaches, malware infections, and denial-of-service attacks that compromise system integrity or confidentiality. Common scenarios include phishing campaigns targeting employee credentials, ransomware encrypting critical files, and insider threats exploiting privileged access. Recognizing and responding quickly to these incidents reduces potential damage and preserves organizational security posture.
The Importance of Accurate Classification
Accurate classification of security incidents versus security events is crucial for effective threat response and resource allocation in cybersecurity. Security events encompass any observable occurrences in a network or system, whereas security incidents represent verified threats that compromise system integrity, confidentiality, or availability. Misclassification can lead to either overlooked threats or unnecessary alerts, impacting organizational risk management and operational efficiency.
Impact on Incident Response Processes
A security event represents any observable occurrence in a system that may be relevant to security, while a security incident denotes an event or series of events that compromise the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of information assets. Incident response processes prioritize security incidents due to their potential impact, activating containment, eradication, and recovery procedures to mitigate damage. Efficient differentiation between security events and incidents enables faster triage, resource allocation, and minimizes operational disruptions.
Tools for Detecting Events and Incidents
Security event detection tools monitor network traffic, system logs, and user activities to identify potential anomalies indicating malicious behavior. Security information and event management (SIEM) platforms aggregate and analyze these events, correlating data to detect actual security incidents requiring immediate response. Endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions provide granular visibility and automated alerts, enhancing the detection of complex threats that escalate from benign events to confirmed incidents.
Security Event Escalation to Incident
A security event is any observable occurrence within a network or system, such as unusual login attempts or firewall alerts, whereas a security incident denotes a confirmed violation that compromises confidentiality, integrity, or availability. Security event escalation involves analyzing and correlating multiple events to identify patterns indicating a potential incident requiring immediate response. Effective escalation processes utilize automated tools and predefined criteria to prioritize and investigate suspicious events, minimizing false positives and enabling rapid containment of security incidents.
Role of Security Teams in Event and Incident Management
Security teams play a crucial role in distinguishing between security incidents and security events by monitoring, analyzing, and prioritizing alerts to identify potential threats. They implement incident response protocols to contain and mitigate confirmed security incidents, minimizing damage and preventing escalation. Continuous event management helps security teams enhance threat detection capabilities and improve organizational resilience against future attacks.
Best Practices for Handling Events and Incidents
Security events are raw, observable occurrences within systems, whereas security incidents are confirmed breaches or harmful activities impacting data integrity or availability. Best practices dictate immediate event monitoring and logging to detect anomalies early, followed by incident classification and response based on severity. Implementing automated alerting systems and maintaining detailed incident response plans ensure timely containment, eradication, and recovery from security incidents.
Security Incident vs Security Event Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com