Key rotation involves regularly updating cryptographic keys to minimize the risk of key compromise and maintain system integrity, ensuring ongoing secure communications. Key revocation permanently invalidates a compromised or outdated key to prevent unauthorized access and mitigate security breaches. Effective security protocols integrate both key rotation and key revocation to provide robust protection against evolving threats.
Table of Comparison
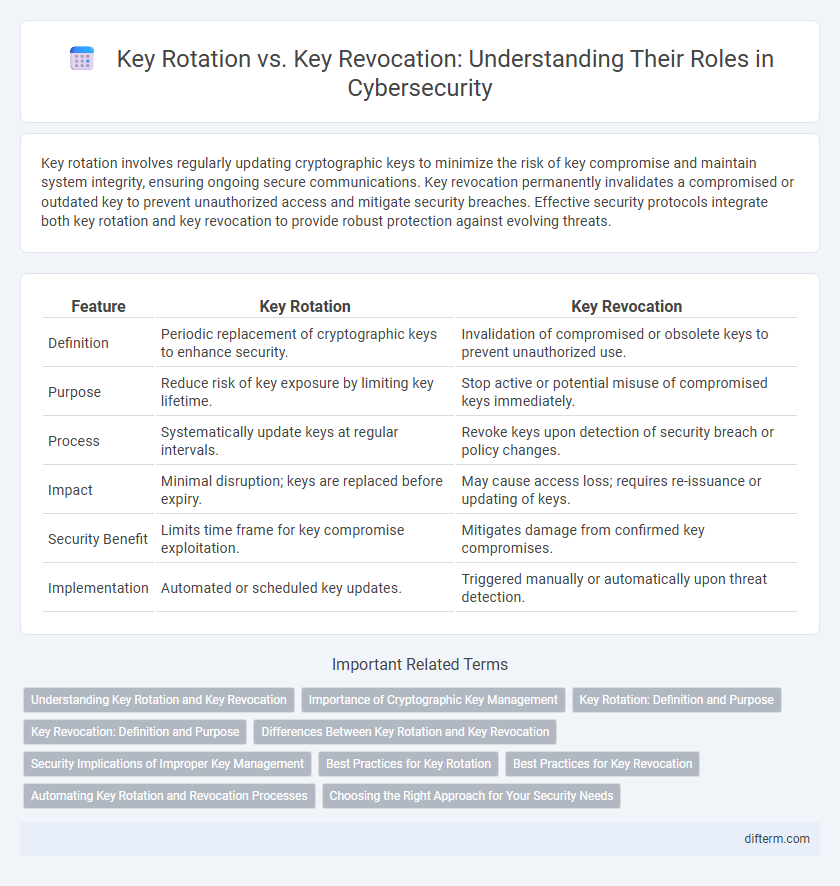
| Feature | Key Rotation | Key Revocation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Periodic replacement of cryptographic keys to enhance security. | Invalidation of compromised or obsolete keys to prevent unauthorized use. |
| Purpose | Reduce risk of key exposure by limiting key lifetime. | Stop active or potential misuse of compromised keys immediately. |
| Process | Systematically update keys at regular intervals. | Revoke keys upon detection of security breach or policy changes. |
| Impact | Minimal disruption; keys are replaced before expiry. | May cause access loss; requires re-issuance or updating of keys. |
| Security Benefit | Limits time frame for key compromise exploitation. | Mitigates damage from confirmed key compromises. |
| Implementation | Automated or scheduled key updates. | Triggered manually or automatically upon threat detection. |
Understanding Key Rotation and Key Revocation
Key Rotation involves periodically updating cryptographic keys to limit exposure time and reduce the risk of compromise, ensuring continuous data protection. Key Revocation refers to invalidating a previously issued key when it is suspected to be compromised or is no longer trusted, preventing its further use in securing communications. Both practices are essential components of effective cryptographic key management strategies to maintain system security.
Importance of Cryptographic Key Management
Effective cryptographic key management is critical in maintaining data confidentiality and integrity by ensuring secure key rotation and revocation processes. Regular key rotation minimizes the risk of key compromise by limiting the lifespan of cryptographic keys, while timely key revocation prevents unauthorized access from compromised or obsolete keys. Implementing robust key lifecycle management protocols strengthens overall security posture and reduces vulnerabilities within cryptographic systems.
Key Rotation: Definition and Purpose
Key rotation refers to the systematic process of replacing cryptographic keys at regular intervals to minimize the risk of key compromise and maintain data security. This practice ensures that even if a key is exposed, its limited lifespan reduces potential damage, supporting compliance with security standards like PCI DSS and NIST. By continuously updating encryption keys, organizations enhance the integrity and confidentiality of sensitive information across digital communications and storage.
Key Revocation: Definition and Purpose
Key revocation is the process of invalidating a cryptographic key before its scheduled expiration to prevent unauthorized access or mitigate security breaches. It is essential in maintaining the integrity of secure communication by ensuring compromised or outdated keys are promptly removed from use. Effective key revocation mechanisms, such as certificate revocation lists (CRLs) or online certificate status protocol (OCSP), help organizations quickly respond to potential threats and enforce strict access control policies.
Differences Between Key Rotation and Key Revocation
Key rotation involves regularly replacing cryptographic keys to minimize the risk of compromise, enhancing security by limiting the lifespan of any single key. Key revocation, on the other hand, is the process of invalidating a key before its scheduled expiration due to suspected compromise or misuse. While key rotation is a proactive maintenance practice, key revocation is a reactive response to a specific security incident.
Security Implications of Improper Key Management
Improper key management, including failure to perform timely key rotation and key revocation, exposes systems to increased risk of unauthorized access and data breaches. Key rotation reduces the window of vulnerability by regularly updating encryption keys, while key revocation invalidates compromised or outdated keys to prevent misuse. Neglecting these practices can lead to prolonged exposure of sensitive information and weaken overall cryptographic security.
Best Practices for Key Rotation
Best practices for key rotation involve regularly updating cryptographic keys to minimize the risk of compromise and ensure continued data protection. Implement automated rotation schedules aligned with the sensitivity of the data and compliance requirements, while securely archiving old keys for audit purposes. Ensuring seamless integration with existing security infrastructure and rigorous access controls during the rotation process enhances overall system resilience against unauthorized access.
Best Practices for Key Revocation
Effective key revocation practices include promptly invalidating compromised cryptographic keys to prevent unauthorized access and ensuring all dependent systems recognize the revocation through updated Certificate Revocation Lists (CRLs) or Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP). Maintaining an automated monitoring system to detect key compromise and enforce timely revocation significantly reduces security risks. Regular auditing and secure archival of revoked keys facilitate compliance and forensic investigations without exposing sensitive data.
Automating Key Rotation and Revocation Processes
Automating key rotation and revocation processes enhances security by reducing human error and ensuring timely updates of cryptographic keys. Implementing automated systems allows seamless replacement of keys at predefined intervals while promptly invalidating compromised keys to prevent unauthorized access. Integration with centralized key management platforms streamlines policy enforcement and audit logging, promoting compliance and operational efficiency.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Security Needs
Key rotation involves regularly updating cryptographic keys to minimize exposure and limit the impact of potential key compromise, ensuring ongoing data protection. Key revocation immediately invalidates a compromised or outdated key, preventing unauthorized access but requiring a swift reissue process to maintain system functionality. Selecting the right approach depends on your organization's threat model, operational complexity, and compliance requirements, balancing proactive key management with rapid incident response.
Key Rotation vs Key Revocation Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com