Gross yield measures the total income generated from an investment before expenses, representing the overall return percentage. Net yield accounts for all costs and fees deducted from the gross income, reflecting the actual profit earned by the investor. Understanding the difference between gross yield and net yield is essential for making informed financial decisions and accurately assessing investment performance.
Table of Comparison
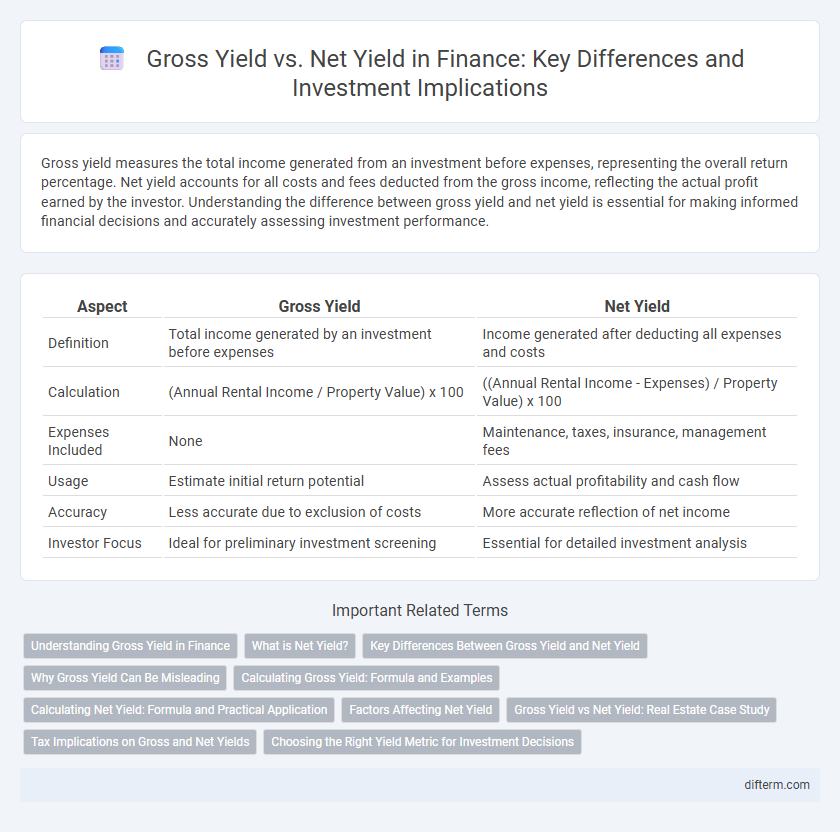
| Aspect | Gross Yield | Net Yield |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Total income generated by an investment before expenses | Income generated after deducting all expenses and costs |
| Calculation | (Annual Rental Income / Property Value) x 100 | ((Annual Rental Income - Expenses) / Property Value) x 100 |
| Expenses Included | None | Maintenance, taxes, insurance, management fees |
| Usage | Estimate initial return potential | Assess actual profitability and cash flow |
| Accuracy | Less accurate due to exclusion of costs | More accurate reflection of net income |
| Investor Focus | Ideal for preliminary investment screening | Essential for detailed investment analysis |
Understanding Gross Yield in Finance
Gross yield in finance represents the total income generated from an investment before deducting any expenses such as taxes, fees, or maintenance costs. It is calculated by dividing the annual income (typically rent or dividends) by the total investment cost and expressed as a percentage. Understanding gross yield is essential for comparing the raw return potential of different assets without considering the impact of associated costs.
What is Net Yield?
Net yield represents the actual return on an investment after deducting all associated expenses, including taxes, maintenance, and management fees. It provides a more accurate measure of profitability compared to gross yield, which only accounts for total income before expenses. Investors rely on net yield to assess the true income potential and make informed financial decisions.
Key Differences Between Gross Yield and Net Yield
Gross yield represents the total income generated from an investment before any expenses or deductions, typically expressed as a percentage of the investment's value. Net yield accounts for all costs such as maintenance, taxes, and management fees, providing a more accurate reflection of the investor's actual return. Understanding the key difference--gross yield shows potential income while net yield reveals true profitability--helps investors make informed decisions in property or asset evaluation.
Why Gross Yield Can Be Misleading
Gross yield represents the total income generated by an investment property before expenses, often inflating perceived profitability by ignoring costs such as maintenance, taxes, and vacancies. Net yield provides a more accurate measure of actual returns by deducting operating expenses, offering investors a clearer picture of cash flow and investment performance. Relying solely on gross yield can mislead investors into overestimating potential profits, leading to suboptimal financial decisions in property investment.
Calculating Gross Yield: Formula and Examples
Gross yield is calculated by dividing the total annual rental income by the property's current market value and multiplying by 100 to express it as a percentage. For example, a property generating $12,000 in annual rent with a market value of $200,000 has a gross yield of 6% ($12,000 / $200,000 x 100). This metric helps investors quickly assess the income-generating potential of a property before accounting for expenses.
Calculating Net Yield: Formula and Practical Application
Net yield is calculated by subtracting all associated costs, such as property taxes, management fees, maintenance expenses, and insurance, from the gross yield, then dividing the result by the total investment amount and multiplying by 100 to express it as a percentage. The formula is: Net Yield (%) = [(Gross Income - Expenses) / Investment] x 100. This measure provides a more accurate reflection of an investment's profitability by accounting for real-world costs affecting the overall return.
Factors Affecting Net Yield
Net yield is influenced by various factors including operating expenses, property taxes, insurance costs, and maintenance fees that reduce the gross yield of an investment. Vacancy rates and management fees also play crucial roles in determining the net return by impacting the actual income received. Understanding these expenses and adjustments helps investors accurately assess the profitability and risk associated with real estate or financial investments.
Gross Yield vs Net Yield: Real Estate Case Study
Gross yield in real estate measures the total rental income as a percentage of the property's purchase price, providing a straightforward indicator of potential returns before expenses. Net yield accounts for all operational costs, taxes, and maintenance, delivering a more accurate reflection of actual profitability for investors. Analyzing both yields enables investors to evaluate the true financial performance of rental properties and make well-informed decisions based on risk-adjusted returns.
Tax Implications on Gross and Net Yields
Gross yield represents the total income generated by an investment before any expenses or taxes are deducted, providing a raw measure of profitability. Net yield accounts for all costs, including property management fees, maintenance, and most importantly, taxes, reflecting the true return an investor receives. Tax implications significantly reduce net yield compared to gross yield, as investors must pay income tax on rental earnings and capital gains tax on asset sales, highlighting the need to consider these factors when evaluating investment returns.
Choosing the Right Yield Metric for Investment Decisions
Gross yield represents the total income generated from an investment property before expenses, providing a quick snapshot of potential returns. Net yield accounts for all operating costs, taxes, and fees, offering a more accurate measure of actual profitability. Investors prioritizing precise cash flow analysis should rely on net yield to make informed decisions and assess true investment performance.
Gross Yield vs Net Yield Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com