Portfolio investment involves purchasing financial assets like stocks and bonds without gaining control over the companies, providing liquidity and diversification for investors. Direct investment entails acquiring a significant stake or establishing business operations, allowing investors to influence management and long-term strategy. Both investment types affect economic growth differently, with direct investment driving productivity and job creation, while portfolio investment enhances capital market efficiency.
Table of Comparison
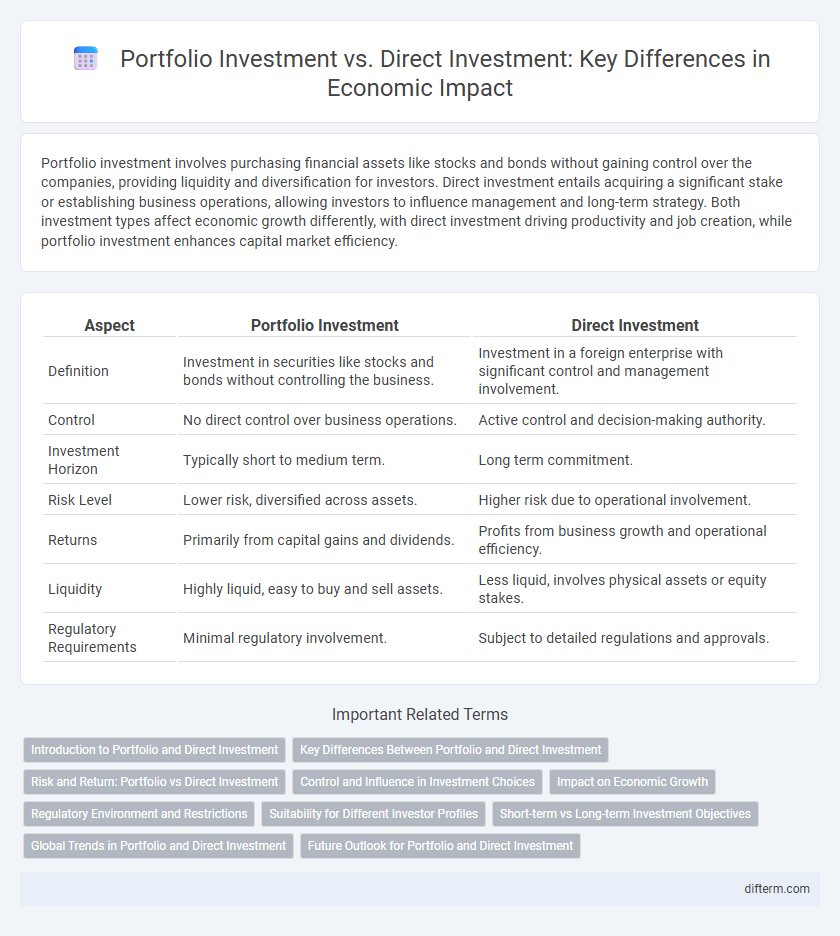
| Aspect | Portfolio Investment | Direct Investment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment in securities like stocks and bonds without controlling the business. | Investment in a foreign enterprise with significant control and management involvement. |
| Control | No direct control over business operations. | Active control and decision-making authority. |
| Investment Horizon | Typically short to medium term. | Long term commitment. |
| Risk Level | Lower risk, diversified across assets. | Higher risk due to operational involvement. |
| Returns | Primarily from capital gains and dividends. | Profits from business growth and operational efficiency. |
| Liquidity | Highly liquid, easy to buy and sell assets. | Less liquid, involves physical assets or equity stakes. |
| Regulatory Requirements | Minimal regulatory involvement. | Subject to detailed regulations and approvals. |
Introduction to Portfolio and Direct Investment
Portfolio investment involves purchasing financial assets such as stocks and bonds in foreign markets without seeking control over the business operations, emphasizing liquidity and risk diversification. Direct investment refers to acquiring a lasting interest in a foreign enterprise, typically through establishing ownership or significant influence, which directly impacts management and long-term business strategy. Both investment types play crucial roles in global capital flows, influencing economic growth and development in recipient countries.
Key Differences Between Portfolio and Direct Investment
Portfolio investment involves purchasing securities like stocks and bonds without acquiring control over the entities, emphasizing liquidity and diversification, while direct investment entails acquiring a substantial ownership stake or controlling interest in a foreign business or asset. Portfolio investments prioritize short-term financial gains and are more volatile, whereas direct investments focus on long-term involvement and active management in the enterprise. The key differences lie in control, investment horizon, risk exposure, and impact on the host economy.
Risk and Return: Portfolio vs Direct Investment
Portfolio investments typically involve higher liquidity and diversification, reducing risk but often yielding moderate returns compared to direct investments. Direct investments, such as acquiring or establishing businesses, carry higher risk due to market and operational exposure but offer potential for greater long-term returns and strategic control. Investors seeking balanced risk-return profiles often combine both to optimize their economic growth and capital preservation strategies.
Control and Influence in Investment Choices
Portfolio investment involves purchasing securities such as stocks and bonds without seeking control over the company's operations, leading to limited influence on managerial decisions. Direct investment, including foreign direct investment (FDI), entails acquiring a significant ownership stake or assets, granting substantial control and decision-making power in the business. The degree of influence in portfolio investment is typically passive, whereas direct investment allows investors to actively shape strategic and operational choices.
Impact on Economic Growth
Portfolio investment provides short-term capital inflows that enhance market liquidity but often lacks long-term commitment, which can result in volatile economic growth. Direct investment, through establishing or acquiring business assets, delivers sustained capital, technology transfer, and management expertise, significantly boosting productivity and long-term economic development. Empirical studies show that economies with higher levels of foreign direct investment experience stronger GDP growth rates compared to those relying predominantly on portfolio flows.
Regulatory Environment and Restrictions
Portfolio investments typically face fewer regulatory hurdles and allow more flexibility for foreign investors, as they involve purchasing securities without exerting control over the companies. Direct investments often encounter stricter regulatory scrutiny, including approvals, restrictions on ownership percentages, and compliance with local laws to protect national interests and economic stability. Governments impose these measures to balance attracting foreign capital with safeguarding strategic industries and maintaining economic sovereignty.
Suitability for Different Investor Profiles
Portfolio investment suits investors seeking liquidity and diversification through assets like stocks and bonds without direct management responsibilities. Direct investment appeals to investors willing to engage in operational control and accept higher risk for potentially greater returns via ownership stakes in companies or real estate. Institutional investors and high-net-worth individuals often prefer direct investment for strategic influence, while retail investors typically favor portfolio investment for ease and flexibility.
Short-term vs Long-term Investment Objectives
Portfolio investment emphasizes short-term investment objectives by allowing investors to buy and sell financial assets like stocks and bonds with high liquidity and market flexibility. Direct investment targets long-term goals through deeper business involvement, such as acquiring controlling stakes or establishing subsidiaries, fostering sustained growth and operational influence. The choice between these investments reflects differing risk tolerances and time horizons, with portfolio investment appealing to those seeking quick returns and direct investment attracting those pursuing strategic control and lasting value.
Global Trends in Portfolio and Direct Investment
Global trends indicate a significant shift in portfolio investment flows, with emerging markets attracting increased foreign capital due to higher returns and diversification opportunities. Direct investment remains focused on long-term strategic assets, such as infrastructure and technology sectors, particularly in Asia and Africa, driven by multinational corporations seeking operational control and market access. The interplay between portfolio and direct investment reflects evolving global economic dynamics, where liquidity preference contrasts with the pursuit of sustainable economic growth through tangible asset acquisition.
Future Outlook for Portfolio and Direct Investment
Portfolio investment is expected to grow as global markets become more interconnected and investors seek diversified assets with liquidity advantages. Direct investment is likely to expand in emerging economies driven by infrastructure development and increasing demand for manufactured goods, fostering long-term economic growth. Advances in technology and regulatory reforms will continue to shape the balance between portfolio investment and direct investment flows worldwide.
Portfolio investment vs Direct investment Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com