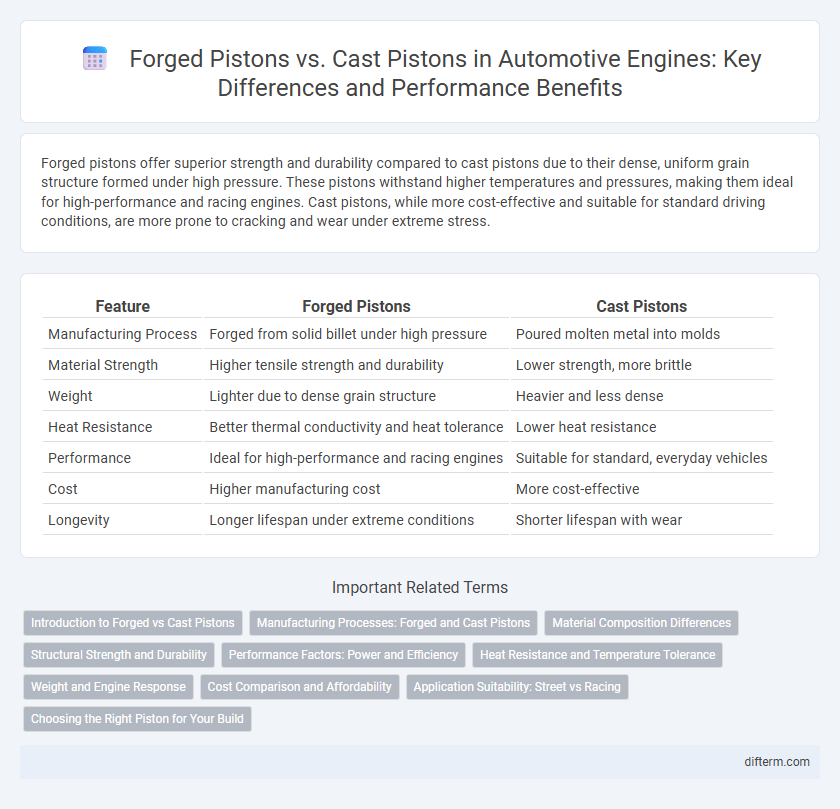
Forged pistons offer superior strength and durability compared to cast pistons due to their dense, uniform grain structure formed under high pressure. These pistons withstand higher temperatures and pressures, making them ideal for high-performance and racing engines. Cast pistons, while more cost-effective and suitable for standard driving conditions, are more prone to cracking and wear under extreme stress.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Forged Pistons | Cast Pistons |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Forged from solid billet under high pressure | Poured molten metal into molds |
| Material Strength | Higher tensile strength and durability | Lower strength, more brittle |
| Weight | Lighter due to dense grain structure | Heavier and less dense |
| Heat Resistance | Better thermal conductivity and heat tolerance | Lower heat resistance |
| Performance | Ideal for high-performance and racing engines | Suitable for standard, everyday vehicles |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing cost | More cost-effective |
| Longevity | Longer lifespan under extreme conditions | Shorter lifespan with wear |
Introduction to Forged vs Cast Pistons
Forged pistons are manufactured by compressing a solid billet of aluminum under high pressure, resulting in a denser, stronger piston ideal for high-performance and racing engines. Cast pistons are produced by pouring molten aluminum into molds, offering a more cost-effective solution suitable for standard engine applications with moderate stress levels. The choice between forged and cast pistons impacts engine durability, thermal conductivity, and overall performance characteristics.
Manufacturing Processes: Forged and Cast Pistons
Forged pistons are created by compressing a solid billet of aluminum or steel under high pressure, resulting in a dense, uniform grain structure that enhances strength and durability. Cast pistons, formed by pouring molten metal into a mold, offer complex shapes and cost-effective production but generally have lower mechanical strength due to porosity and less refined grain structure. Forged manufacturing processes provide superior resistance to high thermal and mechanical stresses typical in high-performance engines compared to the more economical cast approach.
Material Composition Differences
Forged pistons are typically made from high-strength aluminum alloys such as 2618 or 4032, featuring a denser grain structure due to the forging process, which enhances durability and thermal resistance. Cast pistons generally utilize aluminum-silicon alloys, offering better wear resistance but lower tensile strength and fatigue resistance compared to forged variants. The material composition differences result in forged pistons being preferred for high-performance and turbocharged engines, while cast pistons are common in standard production vehicles for cost efficiency.
Structural Strength and Durability
Forged pistons offer superior structural strength compared to cast pistons due to their denser grain structure and enhanced material integrity, which allows them to withstand higher combustion pressures and thermal stresses. This increased durability makes forged pistons ideal for high-performance and racing engines where extreme conditions are frequent. Cast pistons, while cost-effective and adequate for standard applications, are more prone to cracking and wear under prolonged high-stress environments.
Performance Factors: Power and Efficiency
Forged pistons offer superior strength and durability, allowing engines to withstand higher combustion pressures and temperatures, which translates to increased power output and improved fuel efficiency. Cast pistons, while more economical to produce, generally have lower tensile strength and may deform under extreme conditions, limiting maximum performance potential. The enhanced resilience of forged pistons supports more aggressive tuning and higher engine speeds, optimizing both performance and efficiency in high-performance automotive applications.
Heat Resistance and Temperature Tolerance
Forged pistons exhibit superior heat resistance and higher temperature tolerance compared to cast pistons due to their denser grain structure and enhanced mechanical strength. This increased durability allows forged pistons to withstand extreme combustion chamber temperatures in high-performance and forced induction engines without deformation or failure. Cast pistons, while more cost-effective, typically demonstrate lower thermal endurance and are prone to heat-related wear under intense operating conditions.
Weight and Engine Response
Forged pistons are significantly lighter than cast pistons, contributing to reduced reciprocating mass and improved engine response. This weight reduction enhances acceleration and throttle responsiveness by allowing the engine to rev more freely with less inertia. Consequently, vehicles equipped with forged pistons experience better overall performance and efficiency compared to those with heavier cast pistons.
Cost Comparison and Affordability
Forged pistons typically cost 50-70% more than cast pistons due to their labor-intensive manufacturing process and superior material strength. Cast pistons offer a more affordable option for standard performance engines, balancing cost and durability for everyday use. High-performance or racing engines favor forged pistons despite the higher expense, as their enhanced reliability and reduced risk of failure justify the investment.
Application Suitability: Street vs Racing
Forged pistons offer superior strength and durability, making them ideal for high-performance racing engines subjected to extreme stress and high RPMs. Cast pistons, being more cost-effective and sufficient in strength, are typically suited for everyday street applications where engine loads and temperatures are moderate. Racing applications prioritize forged pistons due to their resistance to thermal expansion and fatigue, while street vehicles benefit from the reliability and affordability of cast pistons.
Choosing the Right Piston for Your Build
Forged pistons offer superior strength and durability, making them ideal for high-performance automotive builds that demand increased power and resistance to extreme pressure. Cast pistons, while more cost-effective and suitable for standard engine applications, typically lack the enhanced metallurgical properties required for aggressive tuning and high RPM operation. Selecting the right piston depends on balancing factors like engine power goals, budget constraints, and the intended use of the vehicle to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
forged pistons vs cast pistons Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com