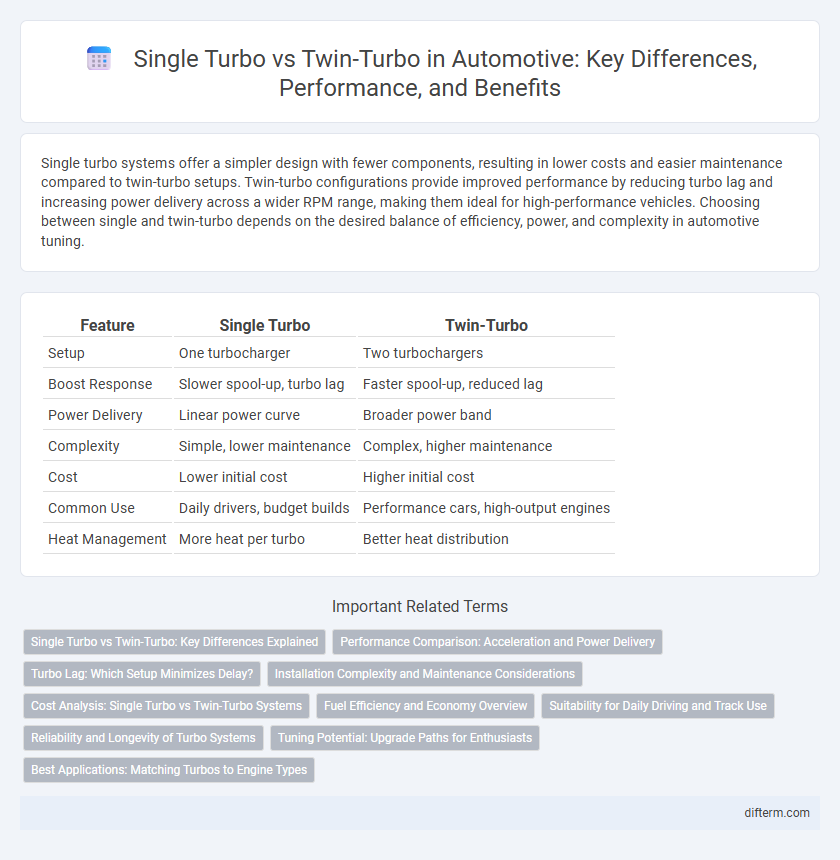
Single turbo systems offer a simpler design with fewer components, resulting in lower costs and easier maintenance compared to twin-turbo setups. Twin-turbo configurations provide improved performance by reducing turbo lag and increasing power delivery across a wider RPM range, making them ideal for high-performance vehicles. Choosing between single and twin-turbo depends on the desired balance of efficiency, power, and complexity in automotive tuning.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Single Turbo | Twin-Turbo |
|---|---|---|
| Setup | One turbocharger | Two turbochargers |
| Boost Response | Slower spool-up, turbo lag | Faster spool-up, reduced lag |
| Power Delivery | Linear power curve | Broader power band |
| Complexity | Simple, lower maintenance | Complex, higher maintenance |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost |
| Common Use | Daily drivers, budget builds | Performance cars, high-output engines |
| Heat Management | More heat per turbo | Better heat distribution |
Single Turbo vs Twin-Turbo: Key Differences Explained
Single turbochargers provide a straightforward boost in power with simpler installation and lower maintenance costs, making them ideal for everyday driving and moderate performance improvements. Twin-turbo setups utilize two smaller turbochargers to reduce turbo lag and increase responsiveness across a broader RPM range, enhancing acceleration and top-end power for high-performance vehicles. The choice between single turbo and twin-turbo depends on factors such as engine size, desired power delivery, and vehicle application, with twin-turbos often favored in sports cars and single turbos common in trucks and economy models.
Performance Comparison: Acceleration and Power Delivery
Single turbochargers provide a strong boost at higher RPMs, delivering consistent peak power ideal for linear acceleration. Twin-turbo setups improve low-end torque by utilizing smaller turbos to reduce lag, resulting in quicker throttle response and improved acceleration from a standstill. Overall, twin-turbo systems offer a more balanced power delivery across the RPM range, enhancing both acceleration and mid-range performance compared to single turbo configurations.
Turbo Lag: Which Setup Minimizes Delay?
Single turbo setups often experience noticeable turbo lag due to the larger turbine housing requiring more exhaust flow to spool up, resulting in delayed boost delivery. Twin-turbo configurations minimize turbo lag by using two smaller turbochargers that spool faster, providing quicker and more consistent boost across a wider RPM range. This setup optimizes engine response and enhances overall performance, especially in high-performance and forced induction vehicles.
Installation Complexity and Maintenance Considerations
Single turbocharger systems offer simpler installation processes due to fewer components and reduced plumbing, making them ideal for compact engine bays and cost-effective upgrades. Twin-turbo setups involve more intricate installation with additional piping, intercoolers, and control units, increasing labor time and complexity but providing enhanced performance balance. Maintenance for single turbos is generally straightforward with lower parts count, while twin-turbos require meticulous upkeep to manage synchronization and increased wear from dual units.
Cost Analysis: Single Turbo vs Twin-Turbo Systems
Single turbo systems generally offer lower upfront costs and simpler installation compared to twin-turbo setups, making them more budget-friendly for entry-level performance upgrades. Twin-turbo configurations, while pricier due to additional components and complex engineering, provide better boost response and power distribution, potentially delivering greater performance gains for high-output engines. Maintenance expenses also tend to be higher for twin-turbo systems because of increased mechanical complexity and more frequent servicing requirements.
Fuel Efficiency and Economy Overview
Single turbochargers generally offer better fuel efficiency due to their simpler design and lower weight, resulting in reduced parasitic losses and improved engine response at moderate RPMs. Twin-turbo setups, while providing superior performance and power across a wider RPM range, often consume more fuel due to increased mechanical complexity and higher boost pressures. Balancing fuel economy with performance, single turbos are preferable for daily commuting and efficiency-focused vehicles, whereas twin turbos are favored in performance-oriented models despite their higher fuel consumption.
Suitability for Daily Driving and Track Use
Single turbochargers provide consistent power delivery with simpler maintenance, making them ideal for daily driving due to better fuel efficiency and lower turbo lag. Twin-turbo systems offer superior performance and quicker spool times, enhancing acceleration and top-end power, which benefits track use and spirited driving. Choosing between single and twin-turbo setups depends on balancing everyday drivability with desired high-performance capabilities.
Reliability and Longevity of Turbo Systems
Single turbo systems generally offer greater reliability and longevity due to their simpler design and fewer moving parts, reducing the risk of mechanical failure. Twin-turbo setups, while delivering enhanced performance, involve more complex plumbing and increased thermal stress, which can negatively impact durability if not properly maintained. Proper oil supply, cooling systems, and periodic inspections are critical for extending the lifespan of both single and twin-turbo configurations in automotive applications.
Tuning Potential: Upgrade Paths for Enthusiasts
Single turbo setups offer straightforward tuning potential with fewer components, making upgrades more cost-effective and simpler to manage for enthusiasts seeking incremental power gains. Twin-turbo configurations provide enhanced tuning flexibility by allowing independent boost control and optimized power delivery across a wider RPM range, ideal for performance builds targeting both low-end torque and high-end horsepower. Upgrading turbochargers, intercoolers, and ECU mapping in either setup unlocks significant power potential, but twin-turbo systems often demand more complex tuning strategies and higher investment for maximum efficiency and reliability.
Best Applications: Matching Turbos to Engine Types
Single turbochargers excel in applications with smaller displacement engines or inline configurations, providing a balance of simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and improved low-end torque. Twin-turbo setups are ideal for larger engines, V6 or V8 configurations, delivering better power across the RPM range by reducing turbo lag and enhancing high-end performance. Matching the turbo configuration to engine type ensures optimized boost response, fuel efficiency, and overall driving dynamics tailored to specific automotive performance goals.
single turbo vs twin-turbo Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com