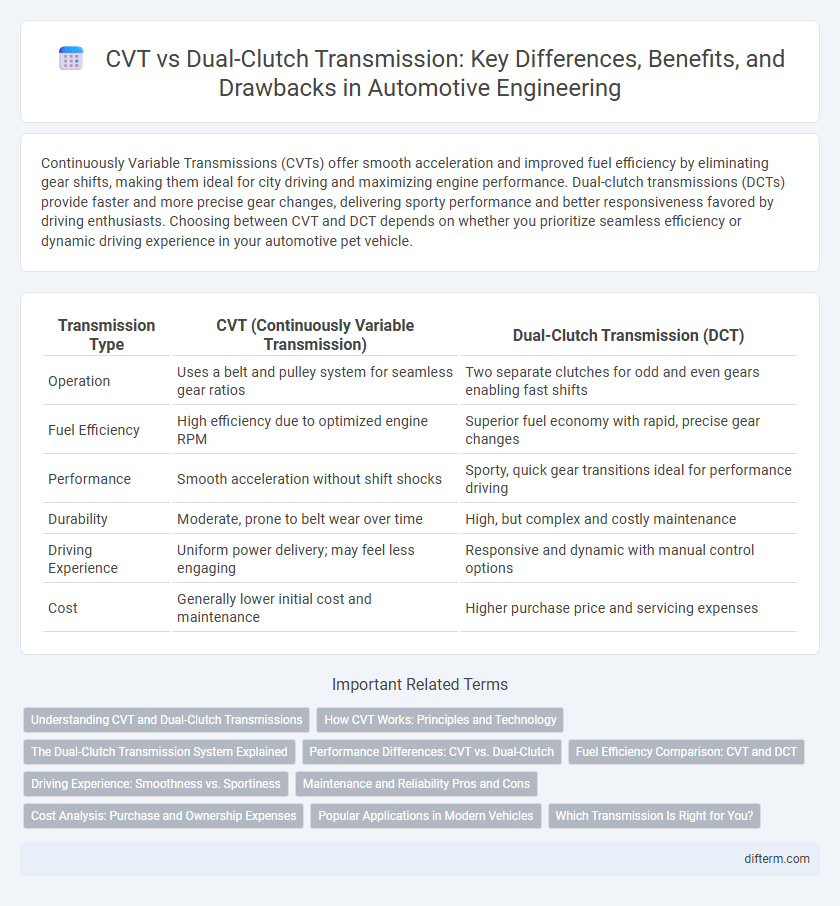
Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVTs) offer smooth acceleration and improved fuel efficiency by eliminating gear shifts, making them ideal for city driving and maximizing engine performance. Dual-clutch transmissions (DCTs) provide faster and more precise gear changes, delivering sporty performance and better responsiveness favored by driving enthusiasts. Choosing between CVT and DCT depends on whether you prioritize seamless efficiency or dynamic driving experience in your automotive pet vehicle.
Table of Comparison
| Transmission Type | CVT (Continuously Variable Transmission) | Dual-Clutch Transmission (DCT) |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Uses a belt and pulley system for seamless gear ratios | Two separate clutches for odd and even gears enabling fast shifts |
| Fuel Efficiency | High efficiency due to optimized engine RPM | Superior fuel economy with rapid, precise gear changes |
| Performance | Smooth acceleration without shift shocks | Sporty, quick gear transitions ideal for performance driving |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to belt wear over time | High, but complex and costly maintenance |
| Driving Experience | Uniform power delivery; may feel less engaging | Responsive and dynamic with manual control options |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost and maintenance | Higher purchase price and servicing expenses |
Understanding CVT and Dual-Clutch Transmissions
Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVTs) offer seamless acceleration through an infinite range of gear ratios, optimizing fuel efficiency and smooth driving experiences without traditional gear shifts. Dual-Clutch Transmissions (DCTs) utilize two separate clutches for odd and even gears, delivering lightning-fast gear changes and enhanced performance ideal for sporty and high-performance vehicles. Understanding the mechanical differences highlights CVTs' efficiency benefits and DCTs' superior responsiveness and driving dynamics.
How CVT Works: Principles and Technology
Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT) operates using a system of pulleys and a flexible belt or chain to provide seamless gear ratio changes, enabling smooth acceleration and optimal engine performance. Unlike traditional transmissions, CVTs eliminate fixed gear steps by continuously adjusting the pulley diameters, which maximizes fuel efficiency and enhances driving comfort. Advanced sensor controls and hydraulic mechanisms manage the pulley tension and ratio variations, ensuring efficient power delivery and reduced mechanical losses.
The Dual-Clutch Transmission System Explained
Dual-clutch transmission (DCT) uses two separate clutches for odd and even gear sets, allowing seamless gear shifts and reducing power interruption compared to conventional systems. This system enhances acceleration and fuel efficiency by pre-selecting the next gear while maintaining continuous torque flow. DCT is favored in performance and luxury vehicles for its quick shift times and improved driving dynamics over CVT systems.
Performance Differences: CVT vs. Dual-Clutch
Dual-clutch transmissions (DCT) offer faster and more precise gear shifts compared to continuously variable transmissions (CVT), resulting in enhanced acceleration and sporty driving dynamics. CVTs provide seamless and stepless gear ratios, optimizing fuel efficiency and smoothness but often at the expense of immediate power delivery and responsiveness. Performance-focused vehicles typically favor DCTs for their quick torque transfer and improved driving engagement, while CVTs are common in economy models prioritizing efficiency and comfort.
Fuel Efficiency Comparison: CVT and DCT
Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVTs) offer superior fuel efficiency by maintaining the engine at its optimal RPM range through seamless gear ratio adjustments. Dual-Clutch Transmissions (DCTs) provide rapid, precise gear shifts that enhance performance but often result in slightly higher fuel consumption compared to CVTs. Studies show CVTs can improve fuel economy by up to 10-15% over DCTs in typical urban and highway driving conditions.
Driving Experience: Smoothness vs. Sportiness
Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVTs) deliver an exceptionally smooth driving experience by providing seamless acceleration without noticeable gear shifts, ideal for urban commuting and fuel efficiency. In contrast, dual-clutch transmissions (DCTs) offer quick, precise gear changes that enhance sportiness and responsiveness, appealing to drivers seeking a dynamic and engaging ride. The choice between CVT and DCT significantly influences vehicle performance characteristics, balancing comfort with driving excitement.
Maintenance and Reliability Pros and Cons
Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVTs) typically require less frequent maintenance due to fewer moving parts and the absence of clutch replacements, but they may suffer from belt or pulley wear leading to costly repairs. Dual-clutch transmissions (DCTs) offer quicker gear shifts and higher efficiency, yet their complex clutch packs and hydraulic systems demand more regular maintenance and can be prone to reliability issues under heavy use. Choosing between CVT and DCT hinges on balancing the lower routine maintenance of CVTs against the potentially higher performance maintenance costs and occasional reliability concerns of DCTs.
Cost Analysis: Purchase and Ownership Expenses
Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVTs) generally have a lower initial purchase price compared to dual-clutch transmissions (DCTs) due to simpler mechanical design and fewer components. However, CVTs may incur higher long-term maintenance costs because of belt and pulley wear, while DCTs often require expensive clutch replacements but benefit from better fuel efficiency and performance. Total cost of ownership varies by vehicle usage and driving conditions, with CVTs favored for cost-sensitive buyers and DCTs appealing to those prioritizing performance and durability.
Popular Applications in Modern Vehicles
CVT (Continuously Variable Transmission) is commonly found in hybrid vehicles and compact cars such as the Toyota Prius and Honda Civic, offering smooth acceleration and improved fuel efficiency. Dual-clutch transmissions (DCT) are popular in high-performance models like the Volkswagen Golf GTI and Ford Focus RS, providing rapid gear shifts and enhanced driving dynamics. Both transmission types cater to specific automotive applications, balancing efficiency and performance according to vehicle design and driver preferences.
Which Transmission Is Right for You?
CVT transmissions offer seamless acceleration and improved fuel efficiency, making them ideal for city driving and smooth performance. Dual-clutch transmissions provide faster gear shifts and sportier handling, suited for drivers seeking a dynamic and responsive driving experience. Choosing the right transmission depends on your driving style, fuel economy priorities, and preference for either smoothness or performance.
CVT vs dual-clutch transmission Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com