The start-stop system automatically shuts off the engine when the vehicle is stationary to reduce fuel consumption and emissions, whereas the idle control system manages engine speed at low RPMs to maintain smooth operation during idling. Start-stop systems are designed for efficiency during stops, improving overall fuel economy, while idle control systems enhance engine stability and reduce vibration when the vehicle is not moving. Both systems contribute to reduced environmental impact but operate at different stages of vehicle idling.
Table of Comparison
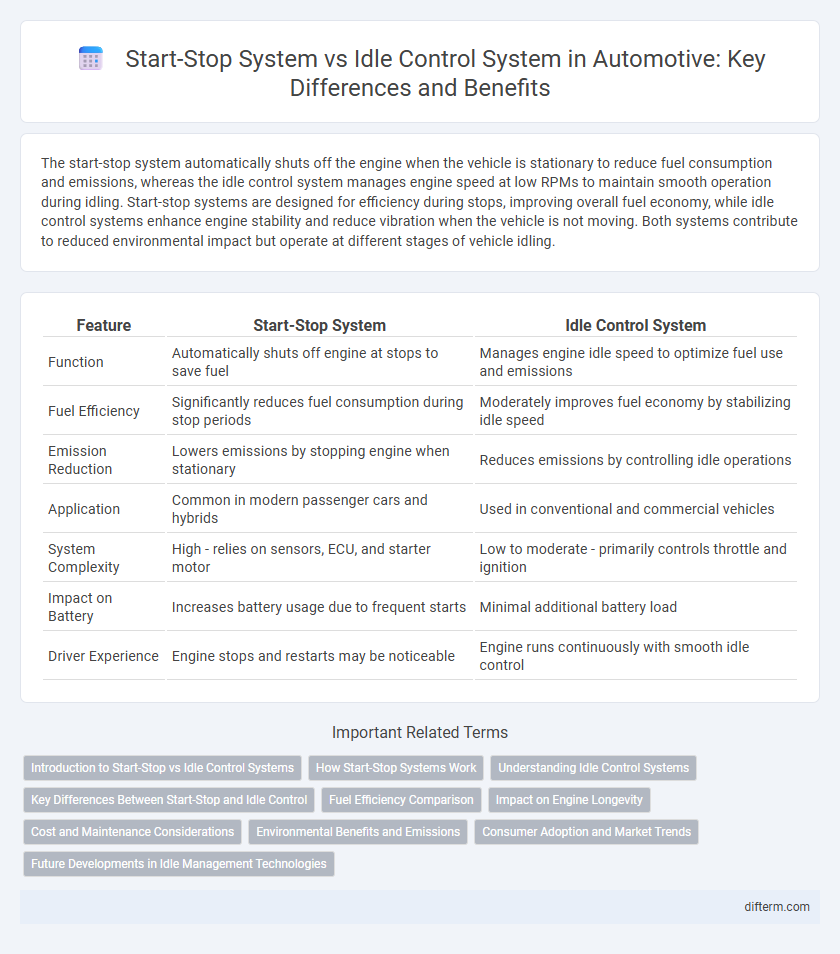
| Feature | Start-Stop System | Idle Control System |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Automatically shuts off engine at stops to save fuel | Manages engine idle speed to optimize fuel use and emissions |
| Fuel Efficiency | Significantly reduces fuel consumption during stop periods | Moderately improves fuel economy by stabilizing idle speed |
| Emission Reduction | Lowers emissions by stopping engine when stationary | Reduces emissions by controlling idle operations |
| Application | Common in modern passenger cars and hybrids | Used in conventional and commercial vehicles |
| System Complexity | High - relies on sensors, ECU, and starter motor | Low to moderate - primarily controls throttle and ignition |
| Impact on Battery | Increases battery usage due to frequent starts | Minimal additional battery load |
| Driver Experience | Engine stops and restarts may be noticeable | Engine runs continuously with smooth idle control |
Introduction to Start-Stop vs Idle Control Systems
Start-stop systems automatically shut off the engine when the vehicle is stationary, reducing fuel consumption and emissions during idle periods, and restart the engine instantly when the driver is ready to move. Idle control systems maintain engine operation at low RPMs while the vehicle is stationary, optimizing performance and minimizing fuel use without shutting down the engine. These technologies enhance fuel efficiency and environmental sustainability in modern automotive design by managing engine operation during stops.
How Start-Stop Systems Work
Start-stop systems automatically turn off the engine when the vehicle is stationary, such as at traffic lights, to reduce fuel consumption and emissions. These systems use sensors to detect when the vehicle stops and a battery-powered starter motor quickly restarts the engine when the driver releases the brake pedal. Integrated with the vehicle's engine management system, start-stop technology optimizes energy use by minimizing idle time without compromising performance.
Understanding Idle Control Systems
Idle control systems regulate engine speed when the vehicle is stationary, optimizing fuel consumption and reducing emissions by maintaining a stable idle RPM. Unlike start-stop systems that shut off the engine during stops to save fuel, idle control systems adjust throttle or use electronic controls to prevent stalling and ensure smooth engine operation. Modern idle control systems integrate sensors and actuators to respond to changes in load, temperature, and accessory usage, enhancing overall engine efficiency and drivability.
Key Differences Between Start-Stop and Idle Control
The start-stop system automatically shuts off the engine when the vehicle is stationary, such as at traffic lights, to reduce fuel consumption and emissions, while the idle control system regulates engine speed during idling to maintain smooth operation and prevent stalling. Start-stop technology primarily aims at enhancing fuel efficiency and lowering carbon footprint during frequent stops, whereas idle control systems focus on engine stability and minimizing vibrations during idle periods. Key differences include the start-stop system's active engine shutdown and restart process, contrasted with idle control's continuous engine operation and speed adjustments.
Fuel Efficiency Comparison
Start-stop systems significantly enhance fuel efficiency by shutting off the engine during idle moments, reducing fuel consumption by up to 10-15% in urban driving conditions. Idle control systems primarily manage engine speed to prevent stalling but do not eliminate fuel use during stops, resulting in lower overall fuel savings. Comparing both, start-stop technology offers superior fuel economy benefits, particularly in stop-and-go traffic environments.
Impact on Engine Longevity
Start-stop systems reduce engine idling time by automatically shutting off the engine at stops, decreasing wear on components and improving fuel efficiency. Idle control systems maintain engine operation during stops, which can lead to increased fuel consumption and accelerated wear on the engine's timing and valve components. Studies show that start-stop technology can extend engine longevity by minimizing heat and friction damage caused by prolonged idling in traditional idle control setups.
Cost and Maintenance Considerations
Start-stop systems typically incur higher upfront costs due to advanced sensors and battery requirements, while idle control systems remain more cost-effective with simpler components. Maintenance for start-stop systems demands specialized battery checks and potentially more frequent replacements, whereas idle control systems require standard engine maintenance without added complexity. Choosing between the two depends on balancing initial investment against long-term maintenance expenses and vehicle usage patterns.
Environmental Benefits and Emissions
Start-stop systems significantly reduce fuel consumption and lower CO2 emissions by automatically shutting off the engine during idle periods, such as at traffic lights, thus minimizing unnecessary fuel use. Idle control systems optimize engine operation during idling to maintain smooth performance and reduce emissions, but they do not cut fuel consumption as effectively as start-stop technology. The combined effect of these systems contributes to improved air quality and compliance with stringent environmental regulations in modern automotive design.
Consumer Adoption and Market Trends
Start-stop systems have gained significant consumer adoption due to their fuel-saving benefits and reduced emissions, especially in urban driving conditions where frequent stops occur. Idle control systems, while effective in minimizing unnecessary engine idling, are less favored because they provide limited fuel efficiency improvements compared to start-stop technology. Market trends indicate a growing preference for start-stop systems in both gasoline and diesel vehicles, supported by regulatory pressures for lower emissions and rising fuel costs.
Future Developments in Idle Management Technologies
Future developments in idle management technologies are gravitating towards more intelligent start-stop systems that integrate with advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and vehicle electrification trends, enhancing fuel efficiency and emission reductions. Innovations include predictive algorithms using real-time traffic data and machine learning to optimize engine shutdown durations, minimizing unnecessary restarts and improving battery longevity. The evolution from traditional idle control systems to adaptive, eco-friendly management solutions is pivotal in meeting stricter environmental regulations and consumer demand for sustainable mobility.
start-stop system vs idle control system Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com