Bare metal servers provide direct access to physical hardware, delivering superior performance and enhanced security for technology pet applications. Virtual servers offer flexible resource allocation and scalability, enabling efficient management of evolving workloads without dedicated hardware. Choosing between bare metal and virtual servers depends on specific needs for speed, control, and cost-effectiveness in technology pet environments.
Table of Comparison
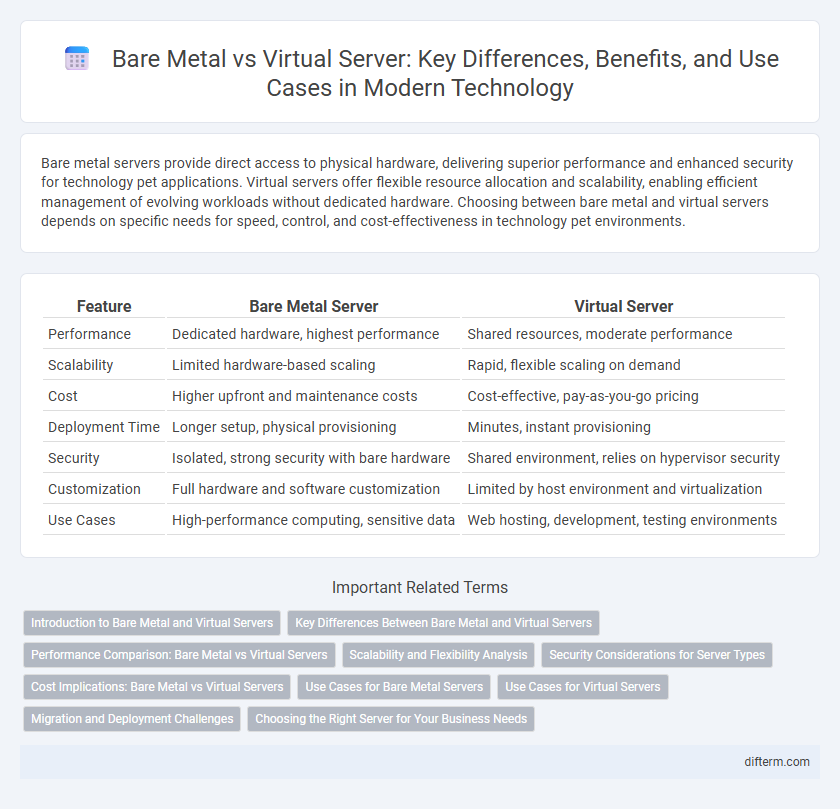
| Feature | Bare Metal Server | Virtual Server |
|---|---|---|
| Performance | Dedicated hardware, highest performance | Shared resources, moderate performance |
| Scalability | Limited hardware-based scaling | Rapid, flexible scaling on demand |
| Cost | Higher upfront and maintenance costs | Cost-effective, pay-as-you-go pricing |
| Deployment Time | Longer setup, physical provisioning | Minutes, instant provisioning |
| Security | Isolated, strong security with bare hardware | Shared environment, relies on hypervisor security |
| Customization | Full hardware and software customization | Limited by host environment and virtualization |
| Use Cases | High-performance computing, sensitive data | Web hosting, development, testing environments |
Introduction to Bare Metal and Virtual Servers
Bare metal servers provide dedicated physical hardware, offering unmatched performance and control by eliminating shared resources, ideal for high-demand applications and workloads. Virtual servers run on shared physical hardware using virtualization technology, enabling flexible resource allocation, scalability, and cost-efficiency for diverse computing needs. Choosing between bare metal and virtual servers depends on specific requirements such as workload intensity, security, and budget constraints.
Key Differences Between Bare Metal and Virtual Servers
Bare metal servers provide dedicated hardware resources, delivering superior performance and low latency compared to virtual servers, which run on shared physical machines using virtualization technology. Virtual servers offer greater flexibility and scalability, allowing rapid deployment and easy resource allocation, while bare metal servers excel in predictable workloads requiring maximum control and security. Key differences include resource isolation, customization capabilities, cost structure, and use cases, with bare metal suited for high-performance applications and virtual servers ideal for dynamic environments.
Performance Comparison: Bare Metal vs Virtual Servers
Bare metal servers deliver superior performance due to direct hardware access, eliminating the overhead caused by virtualization layers present in virtual servers. Virtual servers share physical resources among multiple tenants, which can lead to latency and reduced processing power during peak usage. Benchmark tests consistently show bare metal servers outperform virtual servers in CPU-intensive tasks, I/O operations, and network throughput.
Scalability and Flexibility Analysis
Bare metal servers provide dedicated hardware resources, ensuring maximum performance and low latency, but scalability is limited by physical hardware constraints and longer provisioning times. Virtual servers offer superior flexibility through rapid deployment, easy resource scaling, and dynamic allocation via hypervisors, making them ideal for fluctuating workloads and cloud-native applications. Hybrid environments leverage both technologies to optimize scalability and flexibility according to specific application demands and cost-efficiency goals.
Security Considerations for Server Types
Bare metal servers offer enhanced security by providing dedicated hardware, reducing risks associated with hypervisor vulnerabilities and tenant data breaches common in virtual servers. Virtual servers rely on shared resources, increasing the attack surface and requiring robust isolation mechanisms such as hypervisor-level security and frequent patching. Choosing bare metal servers can mitigate risks related to noisy neighbors and VM escape attacks, crucial for compliance-focused and sensitive data environments.
Cost Implications: Bare Metal vs Virtual Servers
Bare metal servers often require higher upfront capital expenditure due to dedicated hardware procurement and setup costs, while virtual servers reduce initial investment by leveraging shared infrastructure and pay-as-you-go pricing models. Operating expenses for bare metal include maintenance and physical space costs, whereas virtual servers benefit from automated management and scalability, lowering overall operational costs. Cost efficiency depends on workload demands; bare metal excels in predictable, resource-intensive applications, while virtual servers optimize expenses for variable, scalable workloads.
Use Cases for Bare Metal Servers
Bare metal servers excel in high-performance computing environments requiring direct access to hardware resources, such as big data analytics, machine learning workloads, and real-time processing. Industries like finance, gaming, and healthcare leverage bare metal servers for low-latency applications, resource-intensive databases, and regulatory compliance demanding physical server isolation. Organizations prioritizing predictable performance and enhanced security benefit from deploying dedicated bare metal infrastructure over virtualized environments.
Use Cases for Virtual Servers
Virtual servers are ideal for businesses requiring scalable, cost-effective solutions that support dynamic workloads and rapid provisioning. They facilitate efficient resource utilization for web hosting, application testing, and development environments without the need for physical hardware investments. Cloud-based virtual servers also enable disaster recovery and remote workforce support, ensuring business continuity and flexibility.
Migration and Deployment Challenges
Migrating from bare metal to virtual servers often encounters challenges such as hardware dependency issues and complex compatibility requirements that demand thorough testing and configuration adjustments. Deployment complexity increases due to the need for virtualization layers, resource allocation strategies, and ensuring consistent performance across shared environments. Efficient migration planning and automation tools can mitigate downtime and streamline transitions between bare metal infrastructure and virtualized platforms.
Choosing the Right Server for Your Business Needs
Bare metal servers deliver dedicated hardware resources, offering superior performance and security ideal for high-demand applications and critical workloads. Virtual servers provide scalability and cost-efficiency by utilizing shared physical resources through virtualization, making them suitable for businesses with fluctuating traffic and budget constraints. Evaluating factors such as workload intensity, budget limitations, security requirements, and scalability needs enables businesses to select the optimal server type aligned with their operational goals.
bare metal vs virtual server Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com