LPWAN and NB-IoT are both essential technologies for pet tracking, offering low-power, long-range connectivity suitable for monitoring pets in diverse environments. LPWAN provides broader coverage with simpler infrastructure, ideal for rural or less connected areas, while NB-IoT offers enhanced network reliability and better integration with existing cellular systems. Choosing between LPWAN and NB-IoT depends on specific needs such as coverage area, data transmission frequency, and network availability for optimal pet safety and tracking.
Table of Comparison
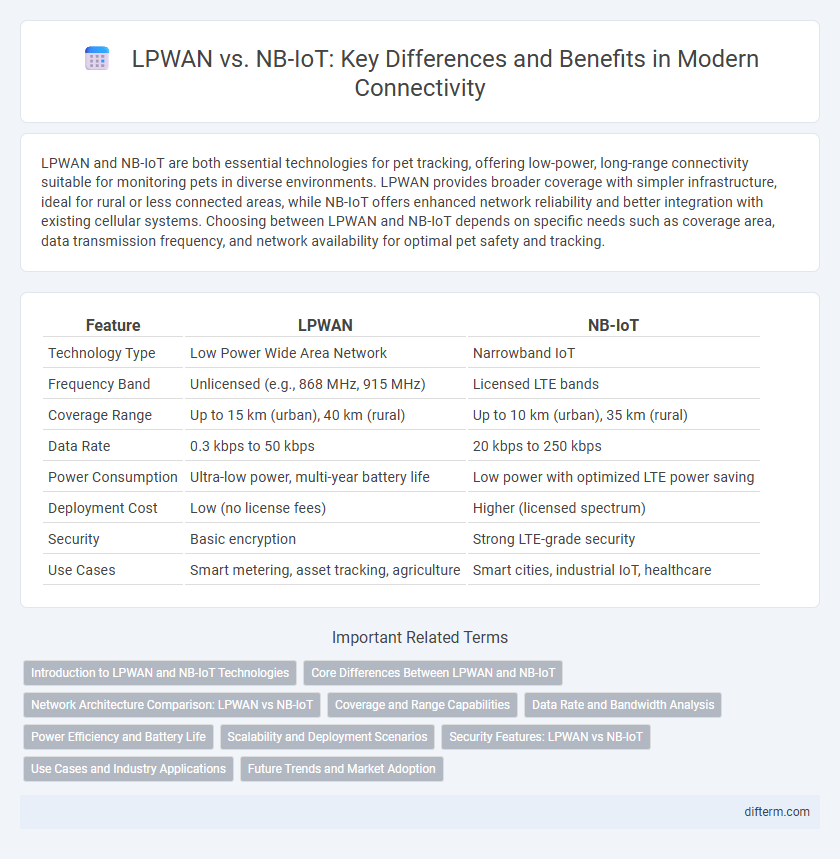
| Feature | LPWAN | NB-IoT |
|---|---|---|
| Technology Type | Low Power Wide Area Network | Narrowband IoT |
| Frequency Band | Unlicensed (e.g., 868 MHz, 915 MHz) | Licensed LTE bands |
| Coverage Range | Up to 15 km (urban), 40 km (rural) | Up to 10 km (urban), 35 km (rural) |
| Data Rate | 0.3 kbps to 50 kbps | 20 kbps to 250 kbps |
| Power Consumption | Ultra-low power, multi-year battery life | Low power with optimized LTE power saving |
| Deployment Cost | Low (no license fees) | Higher (licensed spectrum) |
| Security | Basic encryption | Strong LTE-grade security |
| Use Cases | Smart metering, asset tracking, agriculture | Smart cities, industrial IoT, healthcare |
Introduction to LPWAN and NB-IoT Technologies
LPWAN (Low Power Wide Area Network) technologies enable long-range communication with minimal power consumption, ideal for IoT devices requiring extended battery life and wide coverage. NB-IoT (Narrowband IoT), a type of LPWAN, operates within licensed cellular bands, offering enhanced indoor penetration, security, and reliable connectivity for massive IoT deployments. Both technologies serve diverse applications, including smart metering, agriculture, and asset tracking, by optimizing energy efficiency and network scalability.
Core Differences Between LPWAN and NB-IoT
LPWAN (Low Power Wide Area Network) primarily emphasizes long-range, low-power communication suitable for sparse, low-data IoT devices, while NB-IoT (Narrowband IoT) leverages licensed spectrum with enhanced cellular connectivity for deeper indoor coverage and better network reliability. LPWAN supports various proprietary and open standards like LoRaWAN and Sigfox, whereas NB-IoT operates within existing LTE infrastructure, enabling seamless integration with mobile networks. The core differences lie in spectrum usage, network architecture, data throughput, and coverage performance tailored to specific IoT deployment scenarios.
Network Architecture Comparison: LPWAN vs NB-IoT
LPWAN features a star network architecture optimized for long-range, low-power connectivity with minimal infrastructure complexity, ideal for sparse and widespread IoT deployments. NB-IoT operates on a cellular-based architecture integrated into existing LTE networks, providing robust coverage, enhanced security, and efficient spectrum utilization suitable for urban and high-density environments. The choice between LPWAN and NB-IoT depends on specific use cases, coverage requirements, and network scalability considerations.
Coverage and Range Capabilities
LPWAN technologies provide extensive coverage with ranges up to 15 kilometers in rural areas, making them ideal for wide-area sensor networks. NB-IoT offers superior indoor penetration and reliable connectivity within urban environments, supporting coverage up to 10 kilometers. Both technologies optimize low-power consumption and long-range communication but differ in geographic reach and network density suitability.
Data Rate and Bandwidth Analysis
LPWAN technologies typically offer lower data rates ranging from 0.3 to 50 kbps, optimized for long-range, low-power IoT applications with narrow bandwidths of 125 kHz or less. NB-IoT provides higher data rates up to 250 kbps by utilizing a bandwidth of 180 kHz within licensed spectrum, enabling more reliable and efficient connectivity for massive IoT deployments. The limited bandwidth in LPWAN constrains throughput but extends battery life, whereas NB-IoT balances enhanced data throughput with moderate power consumption due to optimized spectrum usage.
Power Efficiency and Battery Life
LPWAN technology generally offers higher power efficiency compared to NB-IoT, enabling devices to operate for up to 10 years on a single battery under typical low-data-rate applications. NB-IoT, while providing better network reliability and coverage in urban environments, tends to consume more power due to its cellular infrastructure and signaling overhead. Optimizing device firmware and selecting appropriate communication intervals are critical factors in maximizing battery life in both LPWAN and NB-IoT networks.
Scalability and Deployment Scenarios
LPWAN technologies offer extensive scalability for large-scale IoT deployments with low power consumption and broad coverage, making them ideal for rural and wide-area applications. NB-IoT supports massive device connectivity within existing cellular infrastructures, enabling seamless integration in urban environments with higher data throughput and enhanced security. Deployment scenarios favor LPWAN for cost-effective, long-range sensor networks, while NB-IoT excels in dense, metropolitan settings requiring reliable network access and mobility support.
Security Features: LPWAN vs NB-IoT
NB-IoT offers enhanced security features, including robust encryption standards and secure authentication protocols, making it ideal for sensitive IoT applications. LPWAN provides basic security measures suitable for low-power, low-data-rate communications but lacks the advanced protection mechanisms found in NB-IoT. Enterprises prioritizing data integrity and device authentication often prefer NB-IoT for its comprehensive threat mitigation capabilities.
Use Cases and Industry Applications
LPWAN technologies such as LoRaWAN and Sigfox provide long-range, low-power connectivity ideal for smart agriculture, environmental monitoring, and asset tracking, where infrequent data transmissions and extended battery life are critical. NB-IoT excels in urban and industrial environments with dense device deployments requiring reliable, secure cellular connectivity for applications like smart meters, connected elevators, and intelligent parking systems. The choice between LPWAN and NB-IoT depends on factors including coverage requirements, data throughput, network latency, and scalability within industry-specific IoT solutions.
Future Trends and Market Adoption
LPWAN technology, encompassing protocols such as LoRaWAN and Sigfox, is poised for widespread adoption due to its energy efficiency and low operational costs, making it ideal for smart city and industrial IoT deployments. NB-IoT is gaining rapid traction in cellular networks, driven by telecom operators' investments and integration with 5G infrastructure, promising improved coverage and scalability for massive IoT applications. Market forecasts predict a growing convergence of LPWAN and NB-IoT solutions, optimizing connectivity for diversified IoT use cases and accelerating global IoT ecosystem expansion.
LPWAN vs NB-IoT Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com