RESTful APIs provide a structured approach with predefined endpoints and rely on multiple requests for different resources, which can lead to over-fetching or under-fetching of data. GraphQL offers a flexible query language that allows clients to request exactly the data they need in a single request, optimizing bandwidth and reducing latency. Choosing between RESTful API and GraphQL depends on application complexity, development speed, and specific data requirements.
Table of Comparison
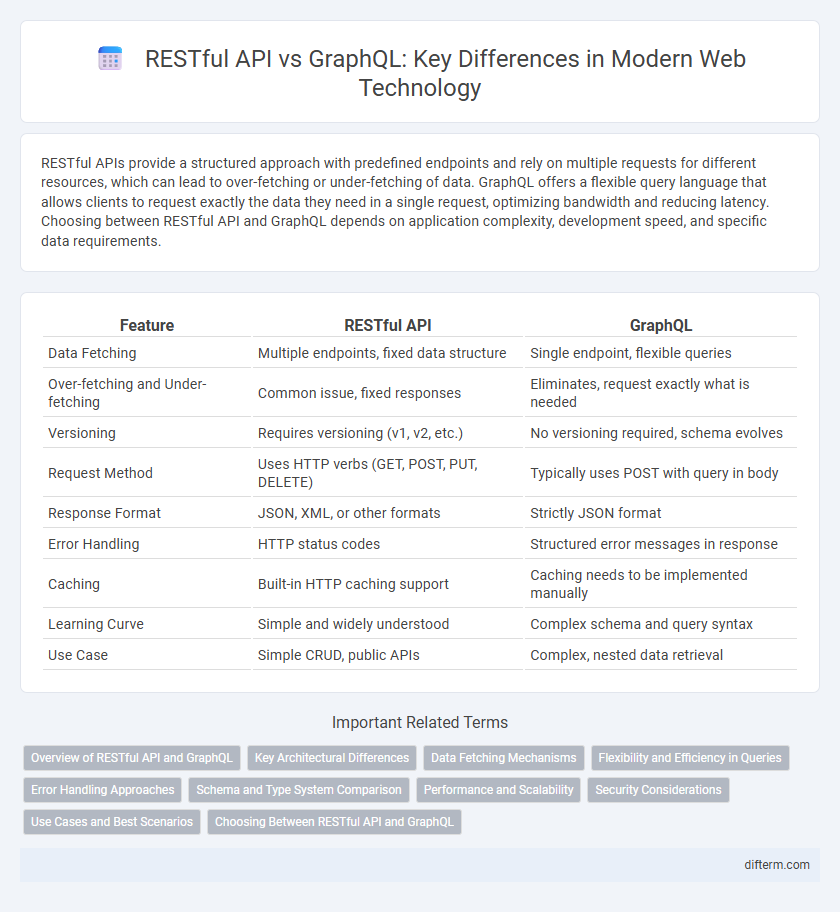
| Feature | RESTful API | GraphQL |
|---|---|---|
| Data Fetching | Multiple endpoints, fixed data structure | Single endpoint, flexible queries |
| Over-fetching and Under-fetching | Common issue, fixed responses | Eliminates, request exactly what is needed |
| Versioning | Requires versioning (v1, v2, etc.) | No versioning required, schema evolves |
| Request Method | Uses HTTP verbs (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) | Typically uses POST with query in body |
| Response Format | JSON, XML, or other formats | Strictly JSON format |
| Error Handling | HTTP status codes | Structured error messages in response |
| Caching | Built-in HTTP caching support | Caching needs to be implemented manually |
| Learning Curve | Simple and widely understood | Complex schema and query syntax |
| Use Case | Simple CRUD, public APIs | Complex, nested data retrieval |
Overview of RESTful API and GraphQL
RESTful API relies on predefined endpoints and HTTP methods to enable client-server communication, emphasizing stateless operations and resource-based architecture. GraphQL offers a flexible query language allowing clients to request specific data structures, reducing over-fetching and under-fetching issues typical in REST. Both technologies optimize data retrieval but differ in design philosophy, with REST focusing on multiple endpoints and GraphQL using a single endpoint with customizable queries.
Key Architectural Differences
RESTful API relies on multiple endpoints representing resources, each accessed via standard HTTP methods, emphasizing stateless client-server communication. GraphQL employs a single endpoint with flexible queries that allow clients to specify exactly the data they need, reducing over-fetching and under-fetching. While REST uses fixed data structures defined by server responses, GraphQL provides a strongly typed schema enabling dynamic and efficient data retrieval.
Data Fetching Mechanisms
RESTful APIs use fixed endpoints to fetch predefined data structures, requiring multiple requests for related resources and potentially causing over-fetching or under-fetching of data. GraphQL employs a flexible query language that allows clients to request exactly the data they need in a single request, reducing network overhead and improving efficiency. The data fetching mechanism in GraphQL can aggregate multiple resource types simultaneously, optimizing performance for complex client requirements.
Flexibility and Efficiency in Queries
RESTful APIs operate with fixed endpoints optimizing predefined data retrieval, which can lead to over-fetching or under-fetching of information. GraphQL provides flexibility by allowing clients to specify exact data requirements in a single query, minimizing data transfer and improving efficiency. This precision in queries enhances performance, especially in complex systems requiring tailored responses.
Error Handling Approaches
RESTful APIs use standard HTTP status codes (e.g., 404 for Not Found, 500 for Server Error) to communicate errors, providing a straightforward and widely understood mechanism for error handling. GraphQL, by contrast, returns errors within the response body under the "errors" key, allowing clients to receive partial data alongside detailed error information, facilitating more granular error management. The choice between these approaches impacts client error parsing, debugging efficiency, and user experience consistency across distributed systems.
Schema and Type System Comparison
RESTful APIs rely on fixed endpoints with predefined request and response structures, offering limited schema flexibility and type system enforcement. GraphQL employs a strongly typed schema defined using its Schema Definition Language (SDL), enabling precise type validation, introspection, and dynamic query capabilities. The robust type system in GraphQL enhances error handling and developer tooling, contrasting with REST's loosely typed JSON responses.
Performance and Scalability
RESTful APIs often require multiple endpoints for resource access, which can lead to over-fetching or under-fetching of data, impacting performance and scalability in complex applications. GraphQL improves efficiency by allowing clients to request exactly the data needed with a single query, reducing server load and network latency, which enhances scalability for large-scale systems. Both technologies can scale effectively, but GraphQL's flexible data querying typically provides better performance optimization in dynamic, data-intensive environments.
Security Considerations
RESTful API employs a rigid endpoint structure that can simplify authorization and rate-limiting enforcement, reducing the attack surface through predictable resource paths. GraphQL, with its flexible query capabilities, demands comprehensive query validation and depth limiting to prevent complex, resource-intensive queries that could expose sensitive data or lead to denial-of-service attacks. Effective security strategies for both include strict authentication protocols like OAuth, granular access controls, and monitoring to promptly detect and mitigate anomalies.
Use Cases and Best Scenarios
RESTful APIs excel in scenarios requiring simplicity, caching, and standardized operations across well-defined resources, making them ideal for public APIs with predictable data structures. GraphQL suits complex applications needing precise data retrieval, especially when clients require flexible queries and want to minimize over-fetching or under-fetching of data. Use RESTful APIs for CRUD operations on static resources, while GraphQL is preferable for interactive UIs with nested relational data or when optimizing mobile app performance by reducing network overhead.
Choosing Between RESTful API and GraphQL
Choosing between RESTful API and GraphQL depends on the specific needs of the application, such as data fetching requirements and flexibility. RESTful APIs are ideal for straightforward, stateless operations with fixed endpoints, ensuring simplicity and caching benefits. GraphQL excels in scenarios requiring dynamic queries, precise data retrieval, and reduced over-fetching, making it suitable for complex client-driven applications.
RESTful API vs GraphQL Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com