Cybersecurity focuses on protecting digital systems, networks, and data from unauthorized access, attacks, and damage, emphasizing the defense of internet-connected technologies. Information security encompasses a broader scope, safeguarding all forms of information, whether digital or physical, to ensure confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Both fields are crucial for organizational resilience but differ in their specific areas of emphasis and strategies.
Table of Comparison
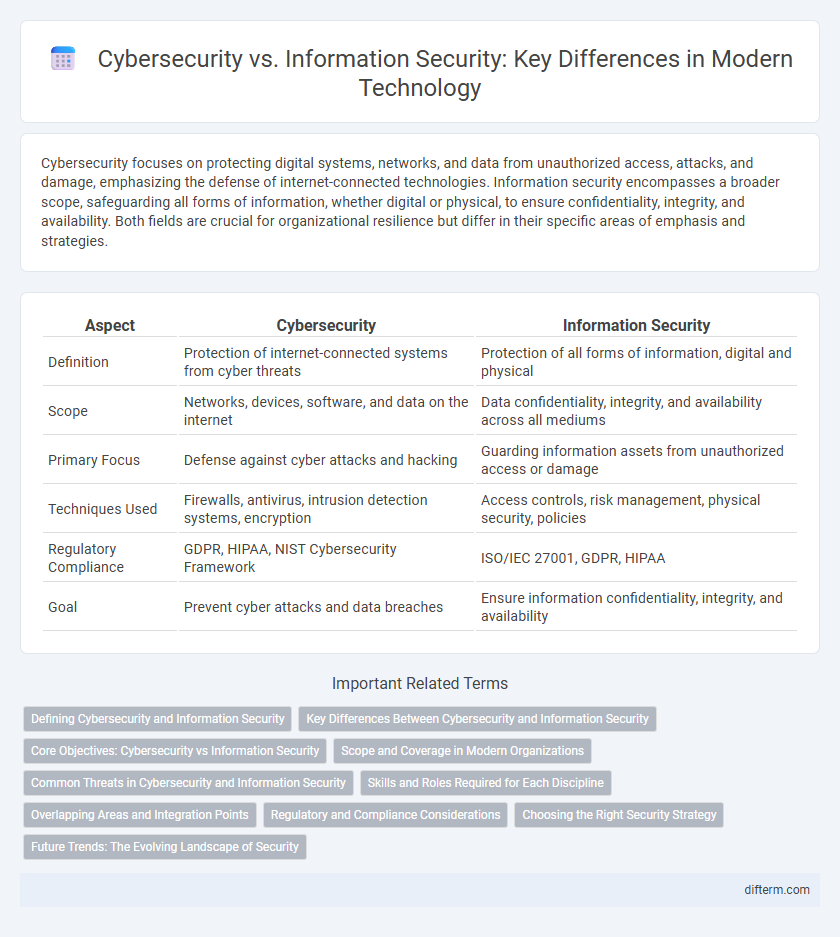
| Aspect | Cybersecurity | Information Security |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Protection of internet-connected systems from cyber threats | Protection of all forms of information, digital and physical |
| Scope | Networks, devices, software, and data on the internet | Data confidentiality, integrity, and availability across all mediums |
| Primary Focus | Defense against cyber attacks and hacking | Guarding information assets from unauthorized access or damage |
| Techniques Used | Firewalls, antivirus, intrusion detection systems, encryption | Access controls, risk management, physical security, policies |
| Regulatory Compliance | GDPR, HIPAA, NIST Cybersecurity Framework | ISO/IEC 27001, GDPR, HIPAA |
| Goal | Prevent cyber attacks and data breaches | Ensure information confidentiality, integrity, and availability |
Defining Cybersecurity and Information Security
Cybersecurity focuses on protecting computer systems, networks, and data from digital attacks, unauthorized access, and cyber threats such as malware and ransomware. Information Security encompasses a broader scope that includes safeguarding all forms of information, whether digital or physical, by implementing policies, procedures, and controls to ensure confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Both disciplines are essential for maintaining organizational security but differ primarily in their scope and specific protection targets.
Key Differences Between Cybersecurity and Information Security
Cybersecurity focuses on protecting digital assets and networks from cyber threats such as hacking, malware, and data breaches, emphasizing the defense of internet-connected systems, including hardware and software. Information security encompasses a broader scope by safeguarding all forms of information, whether digital or physical, through policies, procedures, and controls designed to maintain confidentiality, integrity, and availability. The key difference lies in cybersecurity's specific focus on cyber threats and technology-based protections, while information security addresses overall information protection regardless of format or medium.
Core Objectives: Cybersecurity vs Information Security
Cybersecurity focuses on protecting digital assets, networks, and systems from cyber threats such as malware, hacking, and data breaches, ensuring confidentiality, integrity, and availability of electronic information. Information Security encompasses a broader scope, safeguarding all forms of information--digital, physical, and intellectual property--through policies, risk management, and compliance measures to prevent unauthorized access, disclosure, or destruction. The core objective of cybersecurity is defending against cyber attacks, while information security aims to protect the overall information lifecycle across an organization.
Scope and Coverage in Modern Organizations
Cybersecurity focuses on protecting digital assets, networks, and systems from cyber threats, whereas information security encompasses a broader scope, safeguarding both digital and physical information across entire organizational processes. Modern organizations integrate cybersecurity measures like firewalls, encryption, and intrusion detection alongside information security policies such as access control, data classification, and compliance management. This dual approach ensures comprehensive protection against data breaches, insider threats, and regulatory violations in increasingly complex digital environments.
Common Threats in Cybersecurity and Information Security
Common threats in cybersecurity and information security include malware, phishing attacks, insider threats, and ransomware, which target both digital systems and sensitive data. Cybersecurity primarily focuses on protecting networks, devices, and software from unauthorized access and cyberattacks, while information security broadly safeguards the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of all forms of data. Both domains address vulnerabilities related to human error, weak passwords, and unpatched software, making effective threat detection and response critical to maintaining robust security frameworks.
Skills and Roles Required for Each Discipline
Cybersecurity requires specialized skills in threat detection, ethical hacking, and incident response to protect networks from external attacks. Information security encompasses broader competencies including risk management, compliance, and data governance to safeguard organizational information assets. Professionals in cybersecurity roles often hold certifications like CEH or CISSP, while information security experts focus on certifications such as CISM or ISO/IEC 27001 auditor credentials.
Overlapping Areas and Integration Points
Cybersecurity and information security both aim to protect data confidentiality, integrity, and availability, with cybersecurity focusing on defending networks, systems, and applications from cyber threats, while information security encompasses broader strategies including physical and administrative controls. Their overlapping areas include risk management, access control, encryption, and incident response, enabling a cohesive defense mechanism against both digital and physical threats. Integration points occur in unified policies, cross-functional teams, and comprehensive security frameworks that ensure continuous monitoring and adaptive protection across all information assets.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
Cybersecurity primarily addresses the protection of digital systems and networks against unauthorized access, emphasizing compliance with standards such as NIST, GDPR, and HIPAA. Information Security encompasses a broader scope, including physical and administrative safeguards, to ensure data confidentiality, integrity, and availability in accordance with ISO/IEC 27001 and SOC 2 frameworks. Regulatory considerations require organizations to implement risk management strategies and conduct regular audits to meet sector-specific compliance mandates and mitigate legal liabilities.
Choosing the Right Security Strategy
Cybersecurity focuses on protecting digital systems, networks, and data from cyberattacks, while information security encompasses a broader scope, securing all forms of information, whether digital or physical. Choosing the right security strategy requires assessing organizational risks, regulatory requirements, and the specific vulnerabilities of IT infrastructure and information assets. Integrating both cybersecurity measures and comprehensive information security policies ensures maximum protection against evolving threats.
Future Trends: The Evolving Landscape of Security
Emerging trends in cybersecurity emphasize advanced AI-driven threat detection and zero-trust architectures, reshaping defenses against increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks. Information security evolves to integrate comprehensive data privacy measures, regulatory compliance frameworks such as GDPR and CCPA, and the protection of cloud-native environments. Future landscapes prioritize seamless collaboration between cybersecurity and information security to create resilient, adaptive systems capable of mitigating risks from quantum computing and pervasive IoT vulnerabilities.
Cybersecurity vs Information Security Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com