A Bastion Host serves as a secure gateway, tightly controlled and hardened to protect internal networks by allowing access only to authorized users and logging all connections. A Jump Server often functions similarly but may provide broader administrative control, enabling users to connect and manage multiple servers within a protected environment. Both enhance security by segmenting access, but the Bastion Host is typically more specialized for strict access control and monitoring.
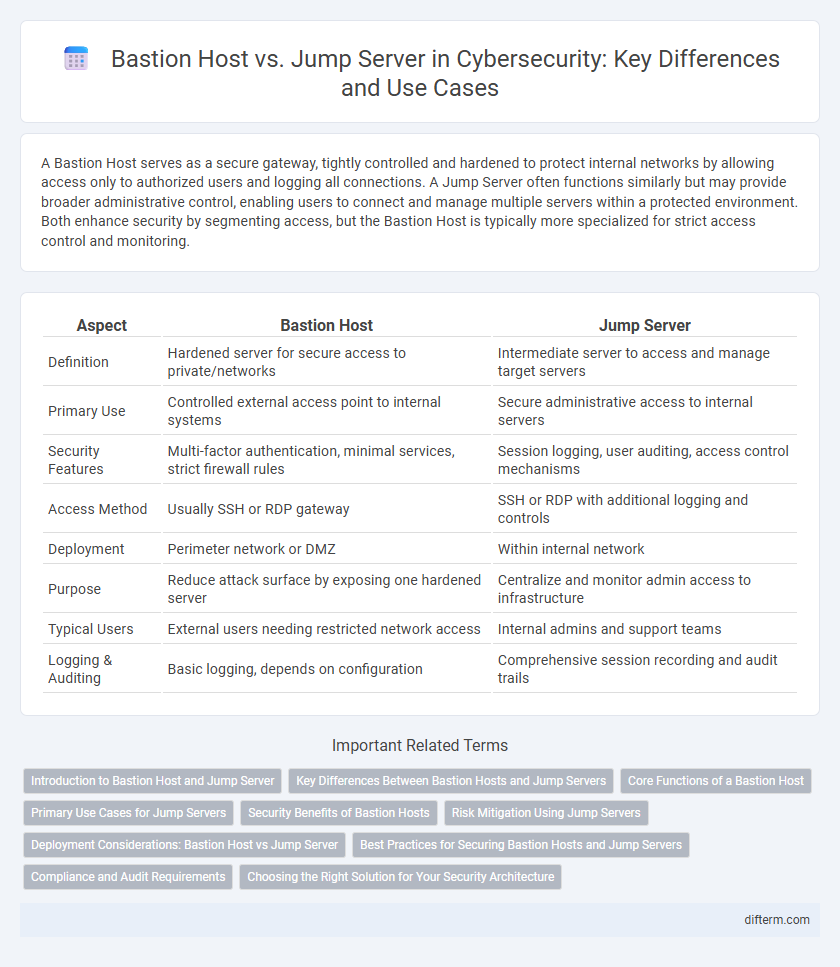
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Bastion Host | Jump Server |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hardened server for secure access to private/networks | Intermediate server to access and manage target servers |
| Primary Use | Controlled external access point to internal systems | Secure administrative access to internal servers |
| Security Features | Multi-factor authentication, minimal services, strict firewall rules | Session logging, user auditing, access control mechanisms |
| Access Method | Usually SSH or RDP gateway | SSH or RDP with additional logging and controls |
| Deployment | Perimeter network or DMZ | Within internal network |
| Purpose | Reduce attack surface by exposing one hardened server | Centralize and monitor admin access to infrastructure |
| Typical Users | External users needing restricted network access | Internal admins and support teams |
| Logging & Auditing | Basic logging, depends on configuration | Comprehensive session recording and audit trails |
Introduction to Bastion Host and Jump Server
A Bastion Host is a highly secured server designed to withstand attacks and provide controlled access to internal networks from external sources, often acting as a gateway for administrative tasks. A Jump Server, similarly, serves as an intermediary, allowing authorized users to access and manage devices within a restricted network environment, enhancing security by reducing direct exposure. Both play critical roles in network security by enforcing authentication, logging access, and minimizing attack surfaces in sensitive infrastructure.
Key Differences Between Bastion Hosts and Jump Servers
Bastion Hosts are specialized, highly secured servers designed to withstand attacks and provide controlled access to an internal network, often hardened with minimal services and strict firewall rules. Jump Servers serve as intermediary devices allowing administrators to connect and manage multiple devices within a network, facilitating secure access by centralizing authentication and logging user activity. While both enhance network security by restricting direct access, Bastion Hosts emphasize defense and minimal exposure, whereas Jump Servers prioritize connectivity management and session auditing.
Core Functions of a Bastion Host
A bastion host serves as a hardened, highly secured gateway that controls access to an internal network, primarily focusing on filtering traffic and providing a single point of entry to critical systems. Its core functions include strong authentication mechanisms, detailed logging for auditing purposes, and strict access control policies to minimize attack surfaces. Unlike a jump server, which often acts as an administrative tool for remote management, a bastion host is specifically designed to enforce security boundaries and monitor all inbound and outbound connections.
Primary Use Cases for Jump Servers
Jump servers primarily provide secure, audited access to internal network resources by acting as controlled gateways for administrators and users. They are used to centralize access control, enforce multi-factor authentication, and monitor all session activities to prevent unauthorized lateral movement within the network. Jump servers enable compliance with security policies by segregating access points and facilitating detailed access logging in high-security environments.
Security Benefits of Bastion Hosts
Bastion hosts enhance security by acting as a secure gateway between an external network and internal resources, minimizing attack surfaces through strict access controls and monitoring. They are typically hardened and configured to allow only authorized traffic, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and lateral movement within the network. Compared to jump servers, bastion hosts offer centralized logging and audit capabilities, enabling better detection and response to potential security threats.
Risk Mitigation Using Jump Servers
Jump servers reduce security risks by acting as controlled gateways that limit direct access to sensitive systems, enforcing strict access controls and logging all user activities to prevent unauthorized intrusions. Unlike bastion hosts, jump servers provide detailed session monitoring and multi-factor authentication, enhancing accountability and reducing the attack surface. This approach significantly mitigates risks by isolating administrative access and ensuring secure, auditable connections within complex network architectures.
Deployment Considerations: Bastion Host vs Jump Server
Bastion Hosts require minimal deployment with strict access controls and are typically hardened to withstand direct exposure to untrusted networks, making them ideal for single-point access management. Jump Servers involve more complex deployment strategies, including integrating with existing identity and access management (IAM) systems and supporting multi-factor authentication (MFA) to enable secure, auditable access across multiple environments. Both solutions demand continuous monitoring and patch management, but Jump Servers often provide enhanced scalability and detailed session logging for enterprise-grade security needs.
Best Practices for Securing Bastion Hosts and Jump Servers
Implement strict access controls by enforcing multi-factor authentication and role-based permissions to secure Bastion Hosts and Jump Servers. Regularly update and patch these systems to mitigate vulnerabilities and reduce attack surfaces. Employ comprehensive logging and monitoring to detect suspicious activities and ensure accountability during remote access sessions.
Compliance and Audit Requirements
Bastion Hosts enforce strict access controls and logging mechanisms essential for meeting compliance standards such as PCI DSS, HIPAA, and GDPR, ensuring detailed audit trails for external access to sensitive systems. Jump Servers provide secure intermediary points with authentication and session recording, facilitating auditability and regulatory adherence by monitoring user actions within critical network segments. Both solutions support thorough compliance requirements through centralized access management and comprehensive logging, crucial for passing security audits and incident investigations.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Security Architecture
Selecting between a Bastion Host and a Jump Server depends on your organization's security requirements, network architecture, and compliance needs. Bastion Hosts provide a hardened, single-entry point strictly controlled and monitored to reduce attack surfaces, while Jump Servers offer controlled access for administrators to manage multiple internal servers efficiently. Evaluating factors such as scalability, logging capabilities, and integration with identity management systems ensures the chosen solution strengthens your security posture without compromising operational efficiency.
Bastion Host vs Jump Server Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com