Host-based Intrusion Detection Systems (HIDS) monitor and analyze the internal activities of individual devices, providing detailed insight into file integrity, system logs, and user behavior to detect suspicious actions. Network-based Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS) focus on monitoring packet traffic across the entire network, identifying potential threats by examining data flow and network patterns in real-time. Comparing HIDS and NIDS highlights the balance between comprehensive device-level security and broad network visibility essential for effective intrusion detection.
Table of Comparison
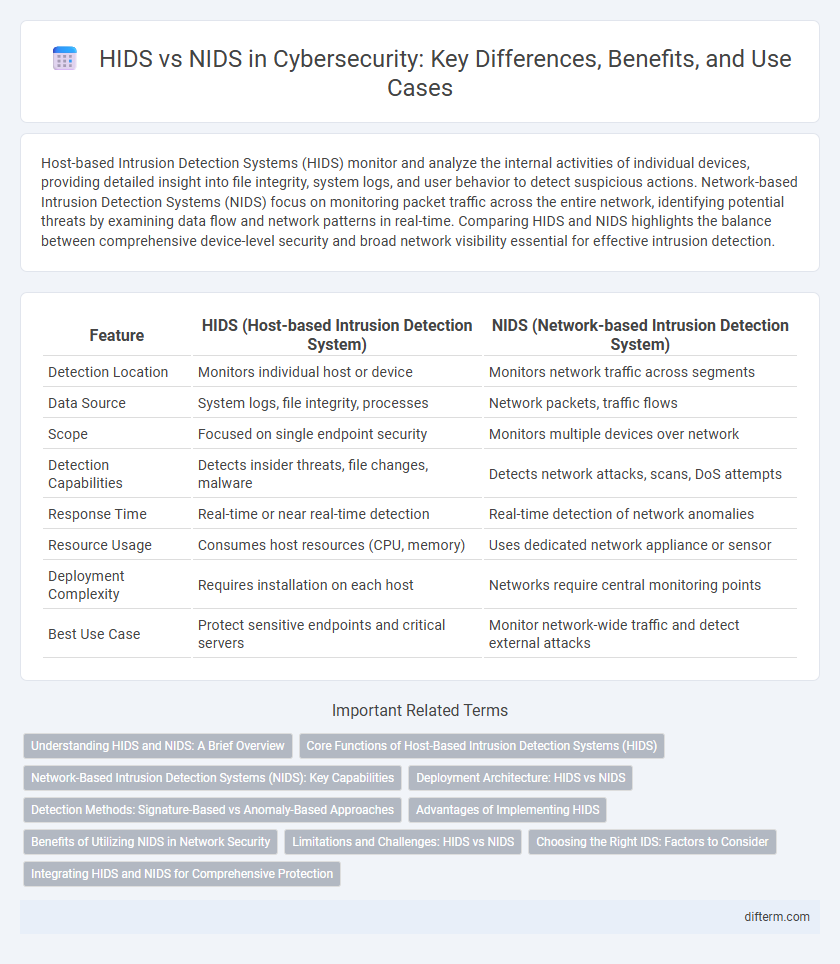
| Feature | HIDS (Host-based Intrusion Detection System) | NIDS (Network-based Intrusion Detection System) |
|---|---|---|
| Detection Location | Monitors individual host or device | Monitors network traffic across segments |
| Data Source | System logs, file integrity, processes | Network packets, traffic flows |
| Scope | Focused on single endpoint security | Monitors multiple devices over network |
| Detection Capabilities | Detects insider threats, file changes, malware | Detects network attacks, scans, DoS attempts |
| Response Time | Real-time or near real-time detection | Real-time detection of network anomalies |
| Resource Usage | Consumes host resources (CPU, memory) | Uses dedicated network appliance or sensor |
| Deployment Complexity | Requires installation on each host | Networks require central monitoring points |
| Best Use Case | Protect sensitive endpoints and critical servers | Monitor network-wide traffic and detect external attacks |
Understanding HIDS and NIDS: A Brief Overview
Host-based Intrusion Detection Systems (HIDS) monitor and analyze the internals of a computing system, detecting suspicious activities by examining system logs, file integrity, and user behavior. Network-based Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS) capture and analyze network traffic, identifying threats by monitoring data packets and detecting anomalies across communication channels. Both HIDS and NIDS are essential components in a layered security strategy, providing complementary insights into potential cyber threats.
Core Functions of Host-Based Intrusion Detection Systems (HIDS)
Host-Based Intrusion Detection Systems (HIDS) primarily monitor and analyze the internal activities of a single host or device, focusing on file integrity checking, system call monitoring, and log analysis to detect unauthorized changes or suspicious behavior. They provide detailed visibility into user activities, configuration modifications, and malware infections by scrutinizing system files, registry settings, and running processes. HIDS offers granular detection capabilities essential for identifying insider threats and device-specific compromises that network-based systems may overlook.
Network-Based Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS): Key Capabilities
Network-Based Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS) monitor and analyze network traffic in real time to detect suspicious activities, such as unauthorized access, malware propagation, and denial-of-service attacks. By deploying sensors at key network points, NIDS provide comprehensive visibility into network behavior, enabling early detection of threats and rapid incident response. These systems often integrate with firewalls and Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) platforms to enhance threat correlation and network security monitoring.
Deployment Architecture: HIDS vs NIDS
Host Intrusion Detection Systems (HIDS) are deployed directly on individual devices, monitoring internal system activities, log files, and configurations for suspicious behavior. Network Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS) are placed at strategic points within the network, such as gateways or network segments, to analyze incoming and outgoing traffic for patterns indicative of attacks. HIDS provides granular, host-specific insight, while NIDS offers a broad overview of network-wide threats, making their deployment architectures complementary for comprehensive security.
Detection Methods: Signature-Based vs Anomaly-Based Approaches
Host Intrusion Detection Systems (HIDS) primarily utilize signature-based detection methods, matching known patterns of malicious activity stored in a database to identify threats on individual devices. Network Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS) often rely on anomaly-based detection, analyzing traffic patterns across the network to detect deviations from established baselines that may indicate novel or unknown attacks. Combining signature-based and anomaly-based approaches enhances overall threat detection accuracy by leveraging the strengths of both predefined signatures and behavioral analysis.
Advantages of Implementing HIDS
Host-based Intrusion Detection Systems (HIDS) offer granular monitoring by analyzing system calls, application logs, and file integrity at the individual host level, providing early detection of insider threats and unauthorized changes. Unlike Network-based Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS), HIDS can detect attacks originating from within the network or from compromised endpoints, ensuring comprehensive protection. Implementing HIDS enhances real-time forensic capabilities and compliance with security policies through detailed event logging and tailored alerting mechanisms.
Benefits of Utilizing NIDS in Network Security
Network Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS) provide real-time monitoring by analyzing network traffic patterns and identifying suspicious activities across multiple devices, enhancing overall network visibility. NIDS can detect distributed attacks and unauthorized access attempts before reaching individual hosts, enabling faster incident response and reducing potential damage. Deploying NIDS complements host-based detection, offering comprehensive security against both external and internal threats.
Limitations and Challenges: HIDS vs NIDS
Host-based Intrusion Detection Systems (HIDS) face limitations such as resource consumption on individual hosts and difficulty detecting attacks that do not leave footprints on the host, whereas Network-based Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS) struggle with encrypted traffic visibility and high volumes of network data leading to potential false positives. HIDS provides deep visibility into host-specific activities but is challenged by scalability issues in large, distributed environments, while NIDS offers broad network coverage but can be bypassed by attackers using evasion techniques like fragmentation and protocol anomalies. Both systems encounter difficulties in correlating events across multiple sources, necessitating integration with advanced security information and event management (SIEM) solutions for comprehensive threat detection.
Choosing the Right IDS: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right Intrusion Detection System (IDS) requires evaluating factors such as network architecture, resource availability, and threat landscape. Host-based IDS (HIDS) offers detailed monitoring of individual devices and is ideal for protecting critical endpoints, while Network-based IDS (NIDS) provides broader traffic analysis suitable for detecting widespread network threats. Consider scalability, ease of deployment, and integration with existing security infrastructure to ensure optimal threat detection and response.
Integrating HIDS and NIDS for Comprehensive Protection
Integrating Host-based Intrusion Detection Systems (HIDS) with Network-based Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS) creates a robust security framework that monitors both endpoint activities and network traffic. This combination enhances threat detection capabilities by correlating host-specific data with network anomalies, improving incident response accuracy. Enterprises deploying both HIDS and NIDS benefit from layered defense mechanisms and a comprehensive view of potential security breaches across infrastructure.
HIDS vs NIDS Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com