A Security Operations Center (SOC) provides continuous monitoring, threat detection, and incident response by a team of security analysts, whereas a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system is a technology platform that aggregates and analyzes security data from various sources. The SOC leverages SIEM tools to correlate logs, identify suspicious activities, and orchestrate defensive actions in real-time. Choosing between SOC and SIEM depends on whether an organization needs a managed security team or a software solution to enhance its cybersecurity infrastructure.
Table of Comparison
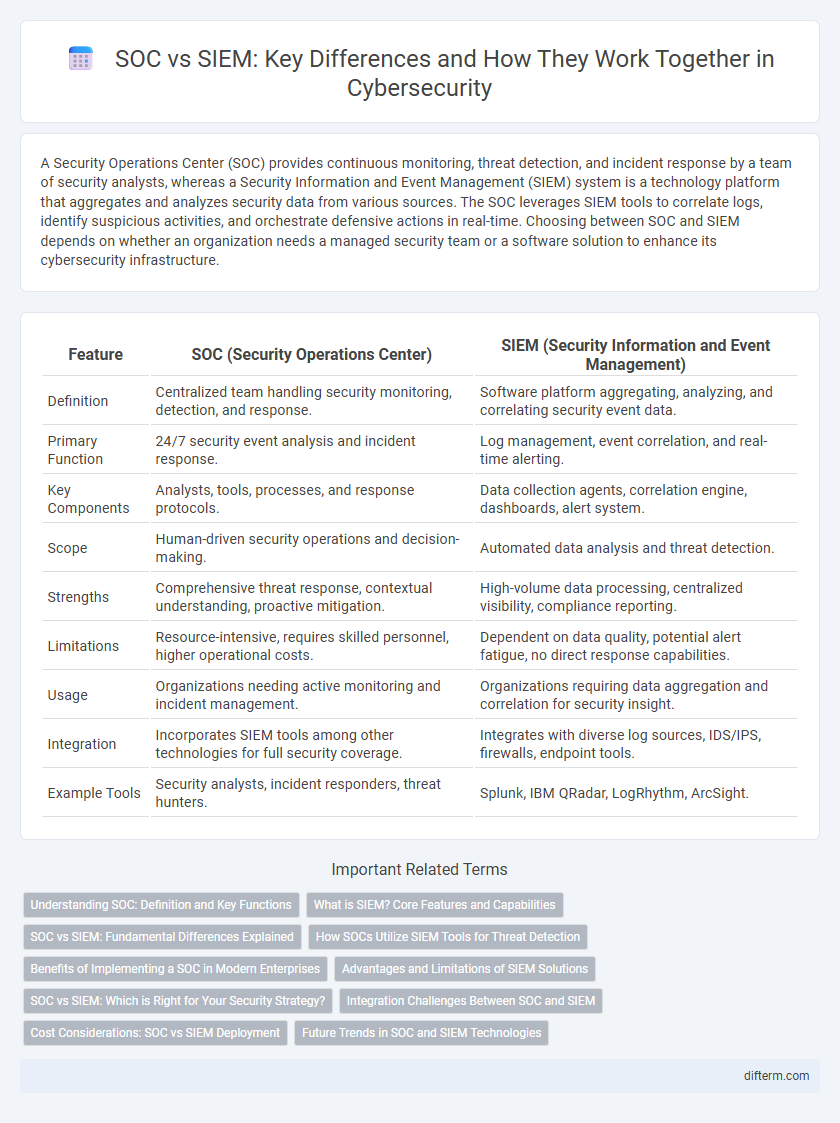
| Feature | SOC (Security Operations Center) | SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Centralized team handling security monitoring, detection, and response. | Software platform aggregating, analyzing, and correlating security event data. |
| Primary Function | 24/7 security event analysis and incident response. | Log management, event correlation, and real-time alerting. |
| Key Components | Analysts, tools, processes, and response protocols. | Data collection agents, correlation engine, dashboards, alert system. |
| Scope | Human-driven security operations and decision-making. | Automated data analysis and threat detection. |
| Strengths | Comprehensive threat response, contextual understanding, proactive mitigation. | High-volume data processing, centralized visibility, compliance reporting. |
| Limitations | Resource-intensive, requires skilled personnel, higher operational costs. | Dependent on data quality, potential alert fatigue, no direct response capabilities. |
| Usage | Organizations needing active monitoring and incident management. | Organizations requiring data aggregation and correlation for security insight. |
| Integration | Incorporates SIEM tools among other technologies for full security coverage. | Integrates with diverse log sources, IDS/IPS, firewalls, endpoint tools. |
| Example Tools | Security analysts, incident responders, threat hunters. | Splunk, IBM QRadar, LogRhythm, ArcSight. |
Understanding SOC: Definition and Key Functions
A Security Operations Center (SOC) is a centralized unit responsible for monitoring, detecting, and responding to cybersecurity threats in real-time through continuous analysis and incident management. SOC teams utilize advanced tools, including Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems, to aggregate and correlate security data from multiple sources, enhancing threat intelligence and situational awareness. Key functions of a SOC include threat detection, incident response, vulnerability management, and compliance monitoring to protect organizational assets effectively.
What is SIEM? Core Features and Capabilities
SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) is a technology that collects, analyzes, and correlates security data from across an organization's IT infrastructure to detect and respond to threats in real time. Core features include log management, event correlation, real-time monitoring, alerting, and compliance reporting, enabling security teams to identify suspicious activities quickly. SIEM capabilities also encompass advanced analytics, threat intelligence integration, and automated incident response to enhance overall security posture.
SOC vs SIEM: Fundamental Differences Explained
SOC (Security Operations Center) is a dedicated team responsible for monitoring, detecting, and responding to cybersecurity threats, whereas SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) is a technology platform that collects, analyzes, and correlates security data from multiple sources. SOC leverages SIEM tools alongside other technologies and human expertise to provide comprehensive threat intelligence and incident response. The fundamental difference lies in SOC being an operational unit focused on active defense, while SIEM serves as a critical tool enabling data-driven security insights within the SOC.
How SOCs Utilize SIEM Tools for Threat Detection
Security Operations Centers (SOCs) leverage Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tools to aggregate and analyze vast amounts of security data in real-time, enabling rapid threat detection and incident response. SIEM platforms provide SOC analysts with centralized visibility into network activities, correlated alerts, and historical logs, which enhances their ability to identify anomalies and potential cyberattacks. By integrating SIEM with threat intelligence feeds and automated workflows, SOCs improve accuracy in detecting sophisticated threats while reducing response time.
Benefits of Implementing a SOC in Modern Enterprises
Implementing a Security Operations Center (SOC) enhances threat detection and response capabilities by providing 24/7 monitoring from skilled cybersecurity analysts, which surpasses the alert generation focus of traditional Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems. SOC integration centralizes incident management and automates threat intelligence sharing, reducing response times and minimizing potential damages from cyberattacks. Modern enterprises benefit from a SOC's proactive approach to continuous risk assessment, compliance management, and advanced analytics that together strengthen their overall security posture.
Advantages and Limitations of SIEM Solutions
SIEM solutions offer real-time event correlation, log management, and centralized monitoring, enabling faster threat detection and compliance reporting for enterprises. Their limitations include high complexity, significant resource requirements, and potential false positives that can overwhelm security teams. Effective SIEM deployment demands skilled personnel and integration with other security tools to maximize its benefits and reduce operational challenges.
SOC vs SIEM: Which is Right for Your Security Strategy?
A Security Operations Center (SOC) provides a comprehensive approach with a dedicated team monitoring, analyzing, and responding to threats in real time, ensuring proactive incident management. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems collect and analyze security data to identify potential threats but require expert interpretation and integration within a SOC for effective response. Choosing between SOC and SIEM depends on organizational size, resources, and the need for hands-on threat detection versus automated data aggregation and alerting.
Integration Challenges Between SOC and SIEM
Integration challenges between Security Operations Centers (SOC) and Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems often stem from data overload and alert fatigue, complicating effective threat detection. Disparate data formats and lack of seamless API connectivity hinder real-time correlation and incident response, reducing overall security posture efficiency. Organizations must address these issues by enhancing interoperability, standardizing logging practices, and investing in advanced analytics to bridge the SOC-SIEM integration gap.
Cost Considerations: SOC vs SIEM Deployment
Deploying a Security Operations Center (SOC) involves substantial upfront and ongoing expenses, including staffing skilled cybersecurity analysts, investing in infrastructure, and maintaining 24/7 monitoring capabilities. In contrast, Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) solutions often require lower initial costs but entail continuous licensing fees, integration complexities, and potential scalability expenses as data volumes grow. Evaluating total cost of ownership (TCO) for SOC versus SIEM deployment must consider factors such as hardware investments, software subscriptions, personnel salaries, and operational overhead to align security capabilities with budget constraints.
Future Trends in SOC and SIEM Technologies
Future trends in Security Operations Centers (SOC) emphasize the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance real-time threat detection and automate incident response, improving overall efficiency. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) technologies are evolving to include advanced analytics, behavior-based anomaly detection, and cloud-native architectures, enabling scalable and adaptive security monitoring. The convergence of SOC and SIEM with Extended Detection and Response (XDR) platforms is driving comprehensive threat intelligence sharing, fostering proactive cybersecurity defense strategies.
SOC vs SIEM Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com