A honeypot is a decoy system designed to attract and analyze cyber attackers, providing valuable insight into attack methods and malware behavior. In contrast, a honeynet is a network of interconnected honeypots that simulates a real environment, increasing the scope and detail of threat detection and research. Both tools are essential in proactive cybersecurity strategies to identify vulnerabilities and improve defensive measures.
Table of Comparison
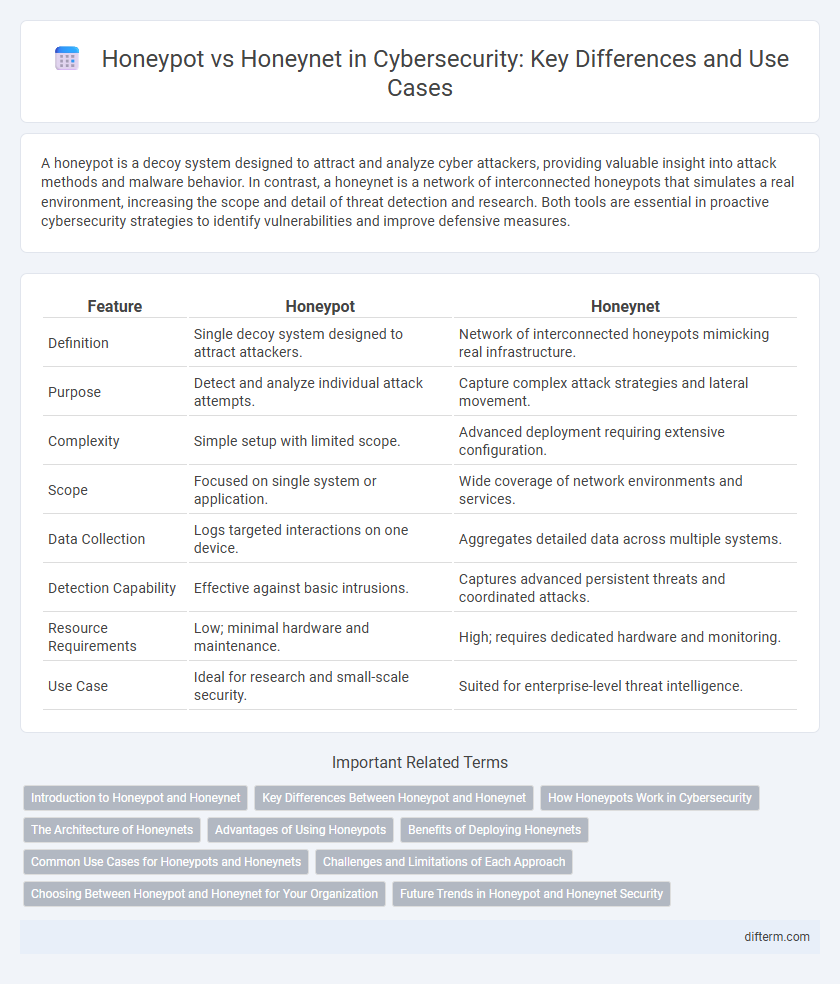
| Feature | Honeypot | Honeynet |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Single decoy system designed to attract attackers. | Network of interconnected honeypots mimicking real infrastructure. |
| Purpose | Detect and analyze individual attack attempts. | Capture complex attack strategies and lateral movement. |
| Complexity | Simple setup with limited scope. | Advanced deployment requiring extensive configuration. |
| Scope | Focused on single system or application. | Wide coverage of network environments and services. |
| Data Collection | Logs targeted interactions on one device. | Aggregates detailed data across multiple systems. |
| Detection Capability | Effective against basic intrusions. | Captures advanced persistent threats and coordinated attacks. |
| Resource Requirements | Low; minimal hardware and maintenance. | High; requires dedicated hardware and monitoring. |
| Use Case | Ideal for research and small-scale security. | Suited for enterprise-level threat intelligence. |
Introduction to Honeypot and Honeynet
A honeypot is a cybersecurity mechanism designed to attract and trap potential attackers, simulating vulnerable systems to gather data on intrusion methods. A honeynet extends this concept by deploying an entire network of interconnected honeypots, providing a broader environment to monitor attacker behavior and techniques. Both tools serve as proactive defense measures, enhancing threat intelligence and improving system security protocols.
Key Differences Between Honeypot and Honeynet
Honeypots are singular decoy systems designed to attract and analyze cyberattack attempts, while honeynets consist of interconnected honeypots simulating an entire network environment. Honeynets provide a broader scope for detecting complex attack patterns and lateral movement within a simulated network compared to isolated honeypots. The main differences lie in scale, complexity, and the depth of threat intelligence gathered from monitoring individual systems versus multiple systems interacting in real-time.
How Honeypots Work in Cybersecurity
Honeypots in cybersecurity function by simulating vulnerable systems or services to attract and detect malicious activities, allowing security teams to monitor attacker behavior without risking real assets. These decoy systems gather intelligence on attack methods, tools, and patterns, enhancing threat analysis and improving defensive measures. Deployed individually or as part of a larger honeynet, honeypots provide valuable insights by isolating and studying cyber threats in a controlled environment.
The Architecture of Honeynets
Honeynets consist of multiple interconnected honeypots designed to simulate an entire network environment, enabling comprehensive analysis of attacker behavior across various systems and services. The architecture includes virtualized or physical machines segmented by firewalls and monitoring tools, which capture and log malicious activities in controlled settings. This layered and scalable design enhances threat intelligence by providing deep insights into sophisticated multi-vector attacks and lateral movement within a network.
Advantages of Using Honeypots
Honeypots provide a strategic advantage in cybersecurity by serving as decoy systems that attract and analyze malicious activity without risking critical assets. Their simplicity, low cost, and ease of deployment allow organizations to quickly identify attack vectors and gather intelligence on threat actor behavior. Unlike honeynets, honeypots require fewer resources but still offer valuable insights for improving network defenses and incident response strategies.
Benefits of Deploying Honeynets
Honeynets provide enhanced security by simulating an entire network environment, capturing sophisticated cyberattack tactics and techniques for comprehensive threat analysis. Deploying honeynets allows organizations to detect lateral movement, pinpoint intruder behavior, and gather detailed intelligence on advanced persistent threats (APTs). These benefits lead to improved incident response strategies and stronger network defense mechanisms.
Common Use Cases for Honeypots and Honeynets
Honeypots are commonly deployed to detect and analyze individual attacker behavior by mimicking a single vulnerable system, making them ideal for identifying specific exploits and malware targeting isolated services. Honeynets, consisting of interconnected honeypots, provide comprehensive network-level insights by simulating an entire infrastructure, enabling organizations to study complex attack patterns and lateral movement techniques used by advanced persistent threats (APTs). Security teams leverage honeypots for focused threat intelligence on specific attack vectors, while honeynets facilitate broader defensive strategies through detailed reconnaissance of coordinated multi-stage cyberattacks.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Honeypots face challenges such as limited visibility and potential detection by sophisticated attackers, which can reduce their effectiveness in capturing comprehensive threat intelligence. Honeynets, while offering broader network emulation to attract and analyze complex attack patterns, encounter limitations related to increased deployment complexity, higher maintenance costs, and the risk of inadvertently facilitating attacker lateral movement. Both approaches require careful configuration and monitoring to mitigate risks and maximize security benefits.
Choosing Between Honeypot and Honeynet for Your Organization
Choosing between a honeypot and a honeynet depends on your organization's security goals and resource availability. Honeypots simulate individual devices or services to attract attackers, making them ideal for targeted threat detection and analysis with lower operational complexity. Honeynets provide a network of interconnected honeypots for comprehensive monitoring of attacker behaviors and tactics across multiple nodes, requiring more extensive deployment and management efforts.
Future Trends in Honeypot and Honeynet Security
Emerging trends in honeypot and honeynet security emphasize the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance threat detection and response capabilities. Advances in cloud-based deployment and virtualization technologies enable scalable and adaptive honeynet architectures that mimic complex network environments for more effective cyberattack analysis. Future honeypot solutions will leverage behavioral analytics and real-time data sharing across distributed systems to improve proactive defense mechanisms against evolving cyber threats.
Honeypot vs Honeynet Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com