Phishing is a broad cyberattack technique that uses deceptive emails or messages to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information. Spear phishing targets specific individuals or organizations with personalized content, increasing the likelihood of success by exploiting detailed knowledge about the victim. Both threats require robust cybersecurity measures, including employee training and advanced email filtering systems.
Table of Comparison
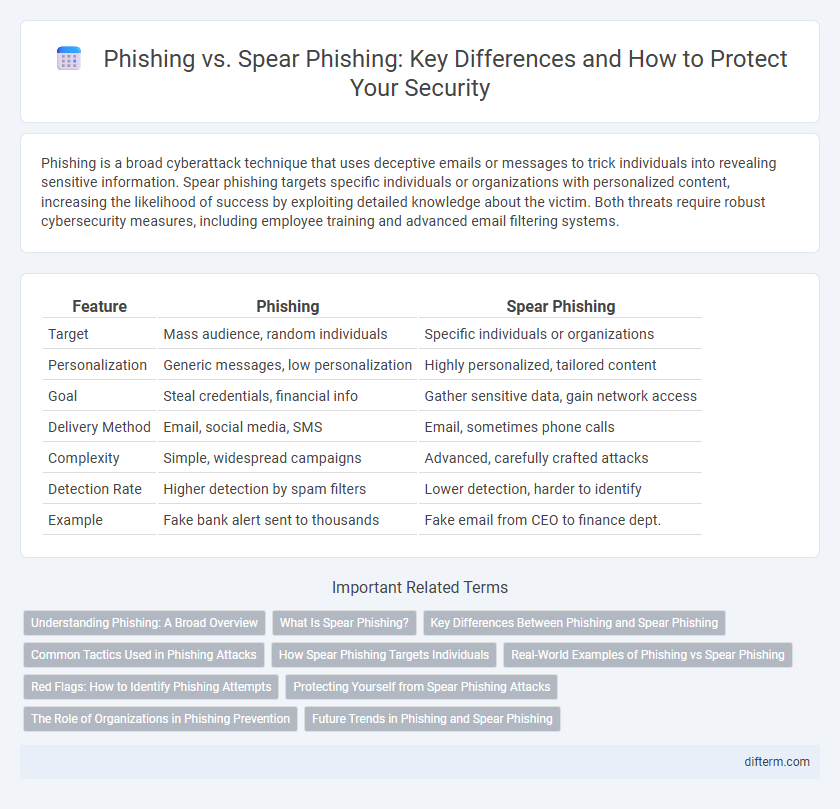
| Feature | Phishing | Spear Phishing |
|---|---|---|
| Target | Mass audience, random individuals | Specific individuals or organizations |
| Personalization | Generic messages, low personalization | Highly personalized, tailored content |
| Goal | Steal credentials, financial info | Gather sensitive data, gain network access |
| Delivery Method | Email, social media, SMS | Email, sometimes phone calls |
| Complexity | Simple, widespread campaigns | Advanced, carefully crafted attacks |
| Detection Rate | Higher detection by spam filters | Lower detection, harder to identify |
| Example | Fake bank alert sent to thousands | Fake email from CEO to finance dept. |
Understanding Phishing: A Broad Overview
Phishing is a cyberattack technique that uses deceptive emails, websites, or messages to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information such as passwords, credit card numbers, or personal data. Spear phishing differs by targeting specific individuals or organizations with personalized messages crafted using gathered information to increase credibility and likelihood of success. Understanding the broad spectrum of phishing helps organizations develop effective cybersecurity strategies and deploy targeted defenses against both general and highly tailored attacks.
What Is Spear Phishing?
Spear phishing is a targeted cyberattack aimed at specific individuals or organizations by using personalized information to make fraudulent emails or messages appear legitimate. Unlike general phishing, spear phishing exploits detailed knowledge of the victim, such as job titles, contacts, or recent activities, increasing the likelihood of deception and data compromise. This type of attack often results in unauthorized access to sensitive information, financial loss, or network breaches.
Key Differences Between Phishing and Spear Phishing
Phishing attacks involve mass-distributed fraudulent emails designed to deceive a broad audience into revealing sensitive information, while spear phishing targets specific individuals or organizations with personalized messages crafted using gathered intelligence. Spear phishing campaigns typically leverage details like the recipient's name, job title, or recent activities to increase credibility and success rates. The primary difference lies in the attack scope and sophistication, where phishing is general and broad, whereas spear phishing is highly focused and tailored.
Common Tactics Used in Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks commonly use deceptive emails, fraudulent websites, and urgent messages to lure victims into revealing sensitive information like passwords and credit card details. Spear phishing employs highly targeted tactics, often researching specific individuals or organizations to craft personalized messages that appear legitimate and trustworthy. Both attack types utilize social engineering techniques such as spoofed sender addresses, fake login pages, and disguised links to manipulate recipients and bypass security measures.
How Spear Phishing Targets Individuals
Spear phishing targets individuals by using personalized information such as their name, job title, or company details to craft convincing and specific messages. Unlike broad phishing attacks, spear phishing exploits social engineering techniques to create trust and increase the likelihood of the victim clicking malicious links or divulging sensitive data. This targeted approach significantly raises the risk of data breaches and financial loss within organizations.
Real-World Examples of Phishing vs Spear Phishing
Phishing attacks often involve mass emails such as the 2016 Twitter Bitcoin scam, where attackers impersonated celebrities to solicit cryptocurrency from thousands globally. In contrast, spear phishing targets specific individuals or organizations, exemplified by the 2011 RSA breach, where attackers sent highly personalized emails to select employees, leading to significant data compromise. Understanding these real-world examples highlights the importance of tailored security training to recognize general phishing attempts versus sophisticated spear phishing tactics.
Red Flags: How to Identify Phishing Attempts
Phishing attempts often exhibit generic greetings, urgent language, and suspicious links or attachments that prompt immediate action, signaling potential threats. Spear phishing targets specific individuals or organizations, using personalized information to appear legitimate and bypass basic detection methods. Recognizing inconsistencies in sender addresses, unsolicited requests for sensitive data, and poor grammar or spelling errors are critical red flags for identifying both phishing and spear phishing attacks.
Protecting Yourself from Spear Phishing Attacks
Spear phishing targets specific individuals or organizations by using personalized information to appear legitimate, making it more dangerous than generic phishing attacks. Protecting yourself requires verifying email senders through multi-factor authentication, scrutinizing unexpected requests for sensitive data, and employing advanced email filtering solutions that detect personalized threats. Regular training on recognizing social engineering tactics and implementing secure password practices are essential defenses against spear phishing attacks.
The Role of Organizations in Phishing Prevention
Organizations play a crucial role in phishing prevention by implementing comprehensive employee training focused on recognizing deceptive email tactics and suspicious links. Deploying advanced email filtering systems and multi-factor authentication significantly reduces the risk of successful phishing and spear phishing attacks. Regular security audits and incident response protocols enhance the organization's resilience against targeted cyber threats.
Future Trends in Phishing and Spear Phishing
Future trends in phishing and spear phishing indicate increasing use of AI-driven personalization, making attacks more convincing and harder to detect. Cybercriminals are leveraging deepfake technology to create authentic-looking communications, escalating the threat landscape. Enhanced machine learning defenses and behavioral analytics will become critical in identifying and mitigating these advanced phishing attempts.
Phishing vs Spear Phishing Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com