EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response) focuses on identifying, investigating, and mitigating threats on individual endpoints such as laptops and servers, providing detailed visibility and rapid response capabilities at the device level. XDR (Extended Detection and Response) expands this approach by integrating data from multiple security layers, including endpoints, networks, servers, and cloud environments, offering a holistic view for more comprehensive threat detection and automated response. Choosing XDR over EDR enables organizations to improve incident correlation, reduce detection gaps, and streamline security operations across diverse infrastructures.
Table of Comparison
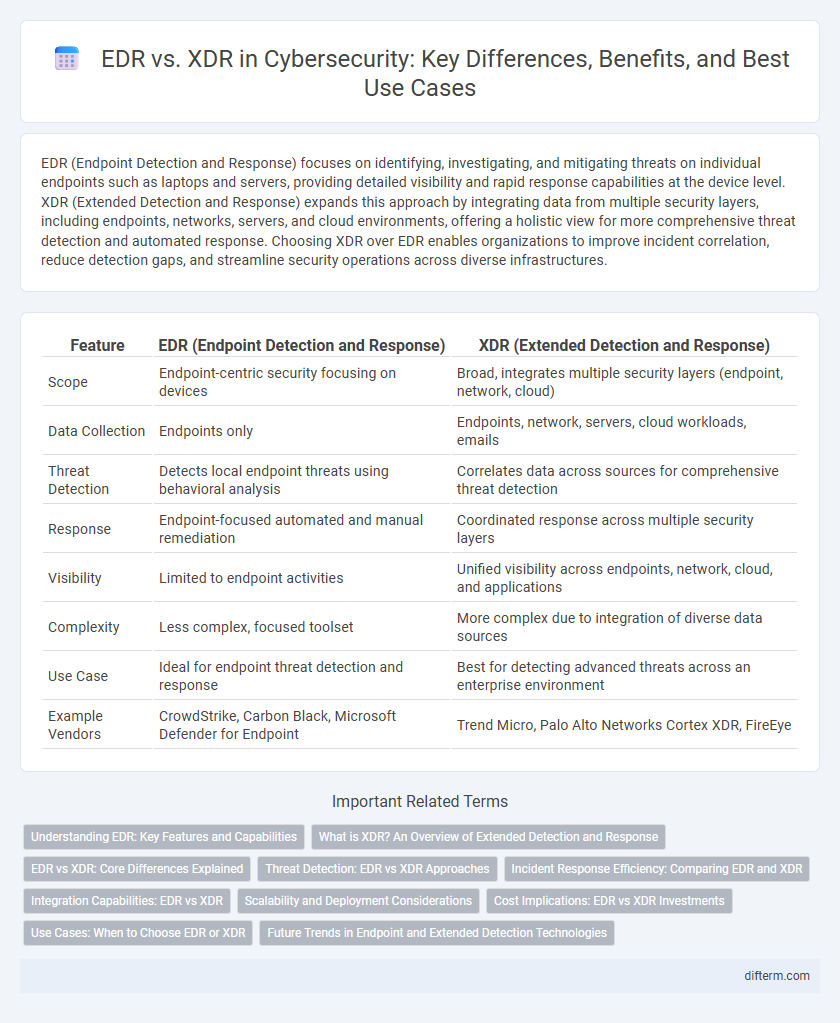
| Feature | EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response) | XDR (Extended Detection and Response) |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Endpoint-centric security focusing on devices | Broad, integrates multiple security layers (endpoint, network, cloud) |
| Data Collection | Endpoints only | Endpoints, network, servers, cloud workloads, emails |
| Threat Detection | Detects local endpoint threats using behavioral analysis | Correlates data across sources for comprehensive threat detection |
| Response | Endpoint-focused automated and manual remediation | Coordinated response across multiple security layers |
| Visibility | Limited to endpoint activities | Unified visibility across endpoints, network, cloud, and applications |
| Complexity | Less complex, focused toolset | More complex due to integration of diverse data sources |
| Use Case | Ideal for endpoint threat detection and response | Best for detecting advanced threats across an enterprise environment |
| Example Vendors | CrowdStrike, Carbon Black, Microsoft Defender for Endpoint | Trend Micro, Palo Alto Networks Cortex XDR, FireEye |
Understanding EDR: Key Features and Capabilities
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions provide continuous monitoring, detection, and response capabilities specifically for endpoints such as desktops, laptops, and servers. Core features include advanced threat detection through behavioral analysis, real-time data collection, and automated response actions to contain and remediate threats. EDR platforms enhance visibility into endpoint activities, enabling security teams to investigate incidents thoroughly and reduce dwell time for sophisticated cyberattacks.
What is XDR? An Overview of Extended Detection and Response
Extended Detection and Response (XDR) is a comprehensive security solution that integrates data from multiple security products, including endpoint detection and response (EDR), network traffic analysis, and cloud security. XDR enhances threat detection and response by correlating data across diverse environments, providing deeper visibility and faster incident investigation. This unified platform enables security teams to identify complex threats more effectively than traditional EDR solutions.
EDR vs XDR: Core Differences Explained
EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response) focuses on monitoring and analyzing endpoint activities to detect and respond to threats specific to individual devices, while XDR (Extended Detection and Response) integrates data across multiple security layers including endpoints, networks, servers, and cloud environments for comprehensive threat detection. EDR solutions provide in-depth visibility and response capabilities limited to endpoints, whereas XDR offers a holistic approach by correlating data from diverse sources to identify sophisticated attacks more effectively. The core difference lies in XDR's ability to unify and automate threat detection and response across the entire security infrastructure, enhancing contextual awareness and reducing response times.
Threat Detection: EDR vs XDR Approaches
EDR solutions focus on endpoint-specific threat detection using behavioral analysis and signature-based techniques to identify and respond to malware, ransomware, and unauthorized activities. XDR extends detection capabilities by integrating data from multiple security layers, including endpoints, networks, servers, and cloud environments, providing a holistic view for faster identification of complex, multi-vector attacks. XDR's correlation of diverse threat intelligence sources enhances detection accuracy and reduces false positives compared to traditional EDR systems.
Incident Response Efficiency: Comparing EDR and XDR
EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response) focuses on identifying and mitigating threats at the endpoint level, enabling rapid incident response through detailed endpoint telemetry and behavioral analysis. XDR (Extended Detection and Response) integrates data across multiple security layers--endpoints, networks, servers, and cloud--offering a holistic view that enhances threat correlation and accelerates incident detection and remediation. XDR's unified approach typically results in higher incident response efficiency by reducing alert fatigue and providing comprehensive context compared to standalone EDR solutions.
Integration Capabilities: EDR vs XDR
XDR (Extended Detection and Response) offers superior integration capabilities by correlating data across multiple security layers, including endpoints, networks, servers, and cloud environments, enhancing threat detection and response. EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response) primarily focuses on endpoint data, limiting its visibility and integration scope to endpoint-specific threats. Organizations seeking comprehensive security visibility benefit from XDR's unified platform that consolidates disparate security tools for streamlined incident management and faster response times.
Scalability and Deployment Considerations
EDR solutions offer focused endpoint visibility and can be rapidly deployed on existing hardware, making them scalable for organizations prioritizing endpoint protection. XDR platforms integrate data across multiple security layers--endpoints, networks, and cloud environments--allowing for scalable analysis and response across complex, hybrid IT infrastructures. Deployment of XDR may require more comprehensive integration efforts but delivers centralized management that improves scalability in enterprise environments with diverse security assets.
Cost Implications: EDR vs XDR Investments
EDR solutions typically involve lower upfront costs, focusing primarily on endpoint protection and detection, which makes them a cost-effective choice for organizations with limited budgets. XDR platforms demand higher investments due to their comprehensive integration of multiple security layers, including endpoints, networks, and cloud environments, providing broader threat visibility and response capabilities. Long-term, XDR can reduce overall security expenses by improving threat detection accuracy and operational efficiency, potentially lowering incident response costs.
Use Cases: When to Choose EDR or XDR
EDR solutions excel in detecting and responding to endpoint-specific threats, making them ideal for organizations prioritizing deep visibility into individual devices and rapid incident investigation. XDR extends beyond endpoints to integrate data from multiple security layers, providing a comprehensive view for advanced threat detection and response across networks, cloud workloads, and email systems. Organizations facing complex, multi-vector attacks or seeking unified security analytics benefit from XDR, while those with a narrower focus on endpoint protection may opt for EDR.
Future Trends in Endpoint and Extended Detection Technologies
Future trends in endpoint and extended detection technologies emphasize AI-driven threat intelligence integration to enhance real-time detection and response capabilities. EDR solutions are evolving to incorporate behavioral analytics for anomaly detection, while XDR platforms focus on unifying data across multiple security layers, including network, cloud, and endpoint environments. The convergence of machine learning and automated response systems is expected to significantly reduce the mean time to detect (MTTD) and mean time to respond (MTTR) in cybersecurity operations.
EDR vs XDR Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com