Zero Trust security eliminates implicit trust by continuously verifying every user and device attempting to access resources, regardless of their location, unlike perimeter-based security that relies on a defined network boundary for protection. Perimeter-based approaches are increasingly vulnerable to sophisticated cyberattacks and insider threats as network perimeters blur with cloud and remote work environments. Zero Trust enhances defense by enforcing strict access controls, micro-segmentation, and continuous monitoring, reducing the risk of breaches and lateral movement within the network.
Table of Comparison
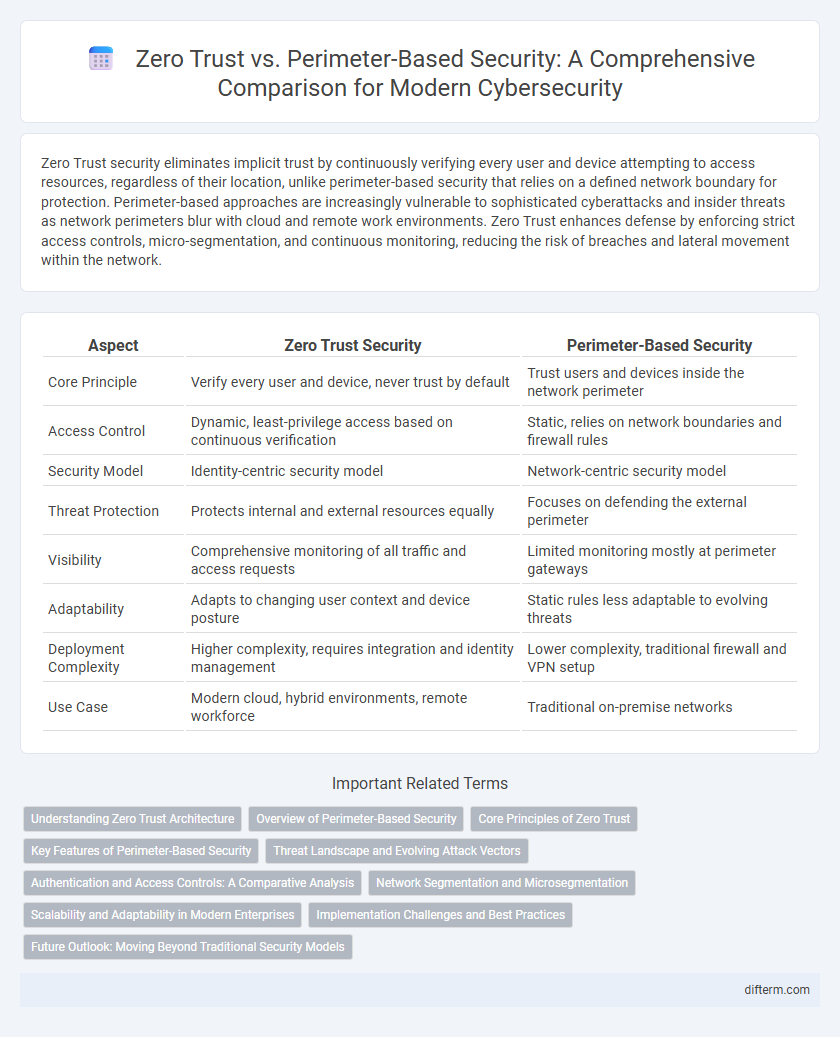
| Aspect | Zero Trust Security | Perimeter-Based Security |
|---|---|---|
| Core Principle | Verify every user and device, never trust by default | Trust users and devices inside the network perimeter |
| Access Control | Dynamic, least-privilege access based on continuous verification | Static, relies on network boundaries and firewall rules |
| Security Model | Identity-centric security model | Network-centric security model |
| Threat Protection | Protects internal and external resources equally | Focuses on defending the external perimeter |
| Visibility | Comprehensive monitoring of all traffic and access requests | Limited monitoring mostly at perimeter gateways |
| Adaptability | Adapts to changing user context and device posture | Static rules less adaptable to evolving threats |
| Deployment Complexity | Higher complexity, requires integration and identity management | Lower complexity, traditional firewall and VPN setup |
| Use Case | Modern cloud, hybrid environments, remote workforce | Traditional on-premise networks |
Understanding Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust Architecture eliminates implicit trust by continuously verifying every user and device attempting to access resources, regardless of their location within or outside the network perimeter. This security model enforces strict identity verification, micro-segmentation, and least-privilege access controls to reduce attack surfaces and prevent lateral movement by threats. Unlike perimeter-based security that relies on fixed boundaries, Zero Trust adapts to dynamic environments and evolving cyber threats through continuous monitoring and risk assessment.
Overview of Perimeter-Based Security
Perimeter-based security relies on establishing a defined boundary around a network where security controls like firewalls and intrusion detection systems monitor and block unauthorized access. This approach assumes that threats originate outside the perimeter and that internal users and devices within the boundary are trustworthy. While effective against external attacks, perimeter-based security often struggles with insider threats and the growing complexity of remote work environments.
Core Principles of Zero Trust
Zero Trust security operates on the core principles of continuous verification, least privilege access, and micro-segmentation, ensuring that no user or device is trusted by default regardless of network location. Unlike perimeter-based security, which relies heavily on defined network boundaries to prevent intrusions, Zero Trust treats every access attempt as potentially hostile and requires strict identity authentication and authorization. This approach minimizes attack surfaces and limits lateral movement within networks, enhancing protection against advanced threats and insider risks.
Key Features of Perimeter-Based Security
Perimeter-based security relies on a clearly defined boundary that protects the internal network from external threats using firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and gateway security measures. It focuses on creating a strong outer defense layer to monitor and control traffic entering and leaving the network. Key features include network segmentation, access control policies, and centralized threat detection at the network edge.
Threat Landscape and Evolving Attack Vectors
Zero Trust security addresses the evolving threat landscape by assuming no user or device is inherently trusted, effectively mitigating risks from insider threats and compromised credentials that perimeter-based security often overlooks. Unlike perimeter-based security, which depends on strong external defenses and can falter once attackers breach the network boundary, Zero Trust continuously verifies and enforces strict access controls based on user identity, device health, and real-time behavior analytics. As attack vectors evolve to exploit cloud environments, remote work setups, and IoT devices, Zero Trust's granular, adaptive approach offers enhanced resilience against sophisticated threats targeting endpoints and lateral network movements.
Authentication and Access Controls: A Comparative Analysis
Zero Trust architecture enforces strict identity verification and granular access controls based on continuous authentication and least privilege principles, minimizing risks from compromised credentials or insider threats. Perimeter-Based Security relies heavily on network boundaries and assumes internal users are trusted, often leading to weaker authentication protocols and broader access permissions within the network. Implementing Zero Trust enhances security posture by requiring multi-factor authentication, contextual access evaluation, and dynamic policy enforcement for every access request.
Network Segmentation and Microsegmentation
Network segmentation divides a network into separate zones to limit access and reduce attack surfaces, while microsegmentation applies granular security controls within those zones by isolating workloads or applications individually. Zero Trust relies heavily on microsegmentation to enforce strict access policies based on identity and context rather than location, contrasting with perimeter-based security that assumes trust within segmented network boundaries. Implementing microsegmentation enhances visibility, limits lateral movement of threats, and strengthens overall network security posture beyond traditional perimeter defense models.
Scalability and Adaptability in Modern Enterprises
Zero Trust architecture offers superior scalability by continuously verifying user identity and device integrity across distributed environments, making it ideal for modern enterprises with dynamic workloads and remote workforces. Unlike perimeter-based security, which relies on fixed network boundaries vulnerable to breaches, Zero Trust adapts seamlessly to cloud, hybrid, and multi-cloud infrastructures, ensuring consistent protection as the organization grows. This adaptability reduces attack surfaces and enhances security posture without compromising operational agility or increasing complexity.
Implementation Challenges and Best Practices
Zero Trust architecture demands continuous verification of users and devices, making implementation complex due to the need for comprehensive identity management and granular access controls. Perimeter-based security struggles as threats bypass network boundaries, but it requires less operational overhaul compared to Zero Trust. Best practices for Zero Trust include adopting multi-factor authentication, micro-segmentation, and automated monitoring to enhance threat detection while minimizing disruptions during transition.
Future Outlook: Moving Beyond Traditional Security Models
Zero Trust architecture eliminates reliance on perimeter-based security by enforcing strict identity verification and continuous monitoring regardless of user location, driving a shift towards more adaptive and resilient cybersecurity frameworks. As cloud adoption and remote work proliferate, Zero Trust's granular access controls and micro-segmentation techniques provide superior protection against increasingly sophisticated threats. Future security models will prioritize context-aware, risk-based access decisions, rendering traditional perimeter defenses insufficient in dynamic, distributed environments.
Zero Trust vs Perimeter-Based Security Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com