Digital certificates authenticate the identity of entities by linking public keys to verified information, establishing trust in online communications. Digital signatures ensure data integrity and non-repudiation by cryptographically signing electronic documents with a private key. While digital certificates validate identity, digital signatures verify the authenticity and integrity of the signed content.
Table of Comparison
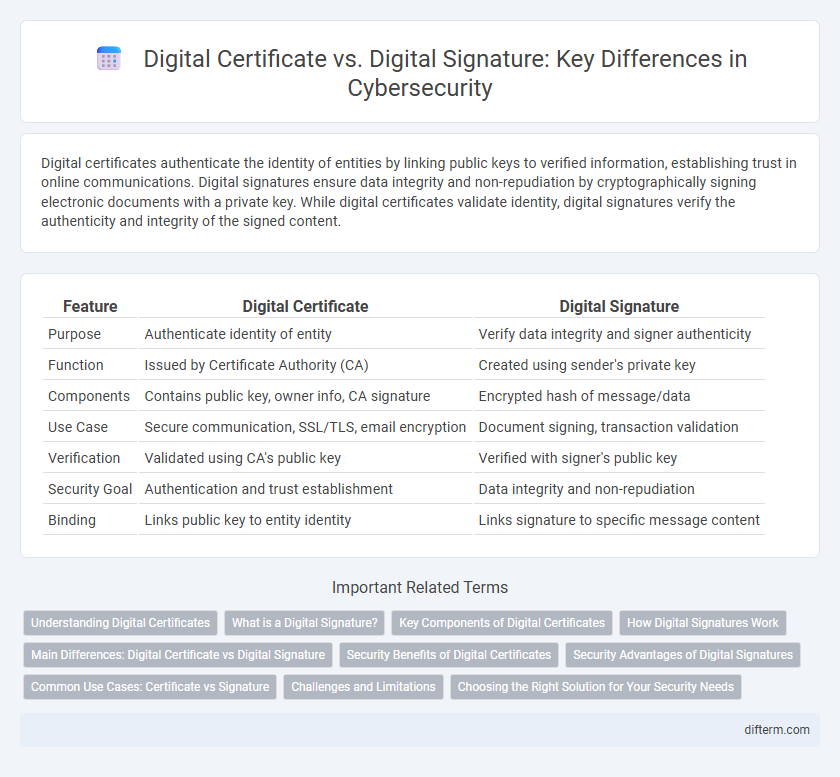
| Feature | Digital Certificate | Digital Signature |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Authenticate identity of entity | Verify data integrity and signer authenticity |
| Function | Issued by Certificate Authority (CA) | Created using sender's private key |
| Components | Contains public key, owner info, CA signature | Encrypted hash of message/data |
| Use Case | Secure communication, SSL/TLS, email encryption | Document signing, transaction validation |
| Verification | Validated using CA's public key | Verified with signer's public key |
| Security Goal | Authentication and trust establishment | Data integrity and non-repudiation |
| Binding | Links public key to entity identity | Links signature to specific message content |
Understanding Digital Certificates
Digital certificates serve as electronic credentials issued by trusted Certificate Authorities (CAs) to verify the identity of entities and secure online communications through Public Key Infrastructure (PKI). They contain a public key, the certificate holder's identity, expiration date, and the CA's digital signature, ensuring authenticity and integrity. Unlike digital signatures that authenticate individual documents, digital certificates establish trust by confirming the legitimacy of websites, users, or devices in encrypted transactions.
What is a Digital Signature?
A digital signature is a cryptographic mechanism that ensures the authenticity, integrity, and non-repudiation of digital documents or messages by using asymmetric encryption, typically involving a private key to sign and a public key for verification. It provides a unique identifier linked to the signer, confirming that the content has not been altered since signing and that it originates from the claimed sender. Digital signatures play a crucial role in secure communications, legal transactions, and software distribution by safeguarding against forgery and tampering.
Key Components of Digital Certificates
Digital certificates rely on key components such as the public key, information about the certificate holder, the certificate authority's (CA) digital signature, and the certificate's validity period. These elements work together to authenticate the identity of entities and secure communications over networks. The CA's digital signature ensures the integrity and trustworthiness of the certificate, enabling encrypted data exchange and verification processes.
How Digital Signatures Work
Digital signatures use cryptographic algorithms to verify the authenticity and integrity of digital messages or documents by generating a unique hash value that is encrypted with the sender's private key. When the recipient receives the signed data, they decrypt the hash with the sender's public key and compare it to a newly generated hash of the received content, ensuring it has not been tampered with. This process guarantees non-repudiation, confirming the origin of the message while protecting against forgery and alteration.
Main Differences: Digital Certificate vs Digital Signature
Digital certificates are electronic credentials issued by Certificate Authorities (CAs) that verify the identity of entities and enable secure communication through encryption protocols like SSL/TLS. Digital signatures are cryptographic mechanisms that provide message integrity, authenticity, and non-repudiation by using private keys to sign data and public keys to verify signatures. Unlike digital certificates, which establish trust by binding a public key to an entity, digital signatures ensure the signed data has not been altered and confirm the signer's identity.
Security Benefits of Digital Certificates
Digital certificates enhance security by providing a trusted third-party authentication that verifies the identity of websites and users, preventing phishing and man-in-the-middle attacks. They enable encrypted communication through SSL/TLS protocols, ensuring data integrity and confidentiality during transmission. By binding public keys to verified identities, digital certificates establish a secure foundation for digital signatures and secure transactions.
Security Advantages of Digital Signatures
Digital signatures provide enhanced security by ensuring data integrity, authentication, and non-repudiation through cryptographic algorithms that link the signer to the document uniquely. Unlike digital certificates, which primarily serve as digital IDs issued by trusted certificate authorities, digital signatures actively verify that the content has not been altered after signing. This robust verification process prevents tampering and unauthorized modifications, making digital signatures critical for secure electronic transactions and communications.
Common Use Cases: Certificate vs Signature
Digital certificates primarily serve to authenticate the identity of entities in online transactions, enabling secure communication through SSL/TLS protocols and establishing trust in websites and software. Digital signatures provide proof of data integrity and non-repudiation by allowing recipients to verify the origin and verify that content has not been altered in documents, emails, and contracts. While certificates validate identity and enable encryption, digital signatures ensure message authenticity and protect against tampering in electronic exchanges.
Challenges and Limitations
Digital certificates face challenges such as susceptibility to certificate authority (CA) compromise and issues with certificate revocation, which can undermine trust in secure communications. Digital signatures, while providing data integrity and authentication, are limited by key management complexities and potential vulnerabilities to cryptographic attacks if weak algorithms are used. Both mechanisms also struggle with scalability in large networks and require robust infrastructure to maintain security and trustworthiness.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Security Needs
Digital certificates authenticate the identity of entities in online communications, establishing trust through a trusted Certificate Authority (CA), while digital signatures ensure data integrity and non-repudiation by verifying that a message or document has not been altered. Selecting the right security solution depends on your specific needs; choose digital certificates to secure website connections via SSL/TLS and validate identities, and opt for digital signatures to protect document authenticity and confirm signer identity. Combining both technologies provides robust protection for transactions requiring identity verification and data integrity.
Digital Certificate vs Digital Signature Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com