Title insurance protects property buyers and lenders from potential defects or disputes in the ownership history of a property, ensuring a secure transfer of ownership. Homeowners insurance provides coverage for damages to the home and personal property caused by events like fires, theft, or natural disasters, as well as liability protection. While title insurance addresses legal ownership risks, homeowners insurance covers physical property damage and personal liability.
Table of Comparison
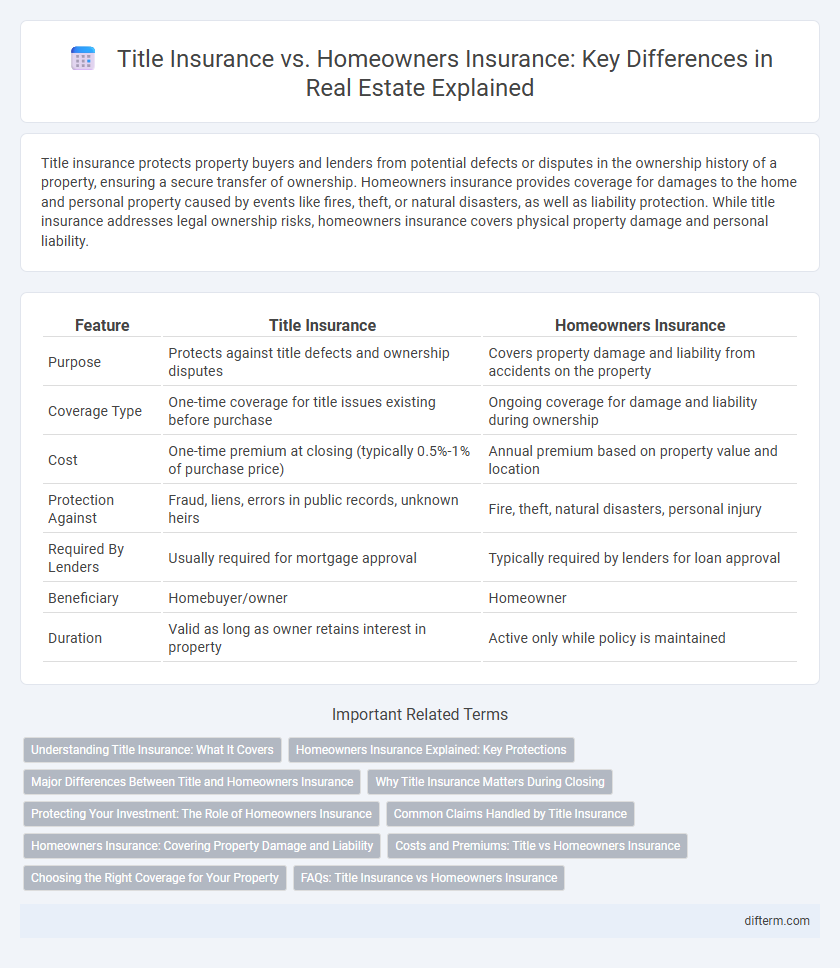
| Feature | Title Insurance | Homeowners Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Protects against title defects and ownership disputes | Covers property damage and liability from accidents on the property |
| Coverage Type | One-time coverage for title issues existing before purchase | Ongoing coverage for damage and liability during ownership |
| Cost | One-time premium at closing (typically 0.5%-1% of purchase price) | Annual premium based on property value and location |
| Protection Against | Fraud, liens, errors in public records, unknown heirs | Fire, theft, natural disasters, personal injury |
| Required By Lenders | Usually required for mortgage approval | Typically required by lenders for loan approval |
| Beneficiary | Homebuyer/owner | Homeowner |
| Duration | Valid as long as owner retains interest in property | Active only while policy is maintained |
Understanding Title Insurance: What It Covers
Title insurance protects property buyers and lenders from financial loss due to defects in the property's title, such as liens, encumbrances, or ownership disputes that were unknown at the time of purchase. Unlike homeowners insurance, which covers damage to the home and personal property, title insurance ensures the legal ownership of the property is clear and marketable. Key coverage includes protection against fraud, undisclosed heirs, errors in public records, and forgery affecting the title's validity.
Homeowners Insurance Explained: Key Protections
Homeowners insurance provides essential protections including coverage for structural damage, personal property loss, and liability for accidents occurring on the property. This insurance typically covers fire, theft, storms, and certain natural disasters, ensuring financial security for homeowners. Title insurance, in contrast, protects against legal disputes over property ownership but does not cover physical damage or liability risks associated with the home.
Major Differences Between Title and Homeowners Insurance
Title insurance protects buyers and lenders from financial loss due to defects in the property's title, such as ownership disputes or liens, while homeowners insurance covers damages to the property and personal belongings caused by events like fire, theft, or natural disasters. Title insurance is a one-time purchase made during the closing process, guaranteeing legal ownership, whereas homeowners insurance requires ongoing premiums and provides liability coverage and property protection throughout homeownership. Understanding these distinctions helps ensure comprehensive risk management when acquiring residential real estate.
Why Title Insurance Matters During Closing
Title insurance protects buyers and lenders from financial loss due to defects in property ownership or liens that may not be discovered during a title search. It ensures clear ownership rights, preventing disputes over claims against the property after closing. This protection is crucial to secure the investment and avoid costly legal battles related to ownership issues.
Protecting Your Investment: The Role of Homeowners Insurance
Homeowners insurance protects your investment by covering damages to your property caused by fire, theft, or natural disasters, ensuring financial recovery for repairs or replacements. Unlike title insurance, which safeguards against ownership disputes and liens, homeowners insurance provides ongoing protection for the physical structure and personal belongings. This coverage is essential for maintaining the value and safety of your real estate asset throughout ownership.
Common Claims Handled by Title Insurance
Title insurance primarily handles claims related to ownership disputes, liens, and encumbrances that arise from defects in the property title prior to purchase. Common claims include unresolved liens, fraud or forgery in the chain of title, undisclosed heirs, and errors in public records that can affect the ownership rights. Unlike homeowners insurance, which covers property damages and liability, title insurance protects buyers and lenders from legal challenges to property ownership.
Homeowners Insurance: Covering Property Damage and Liability
Homeowners insurance primarily protects against property damage caused by events such as fire, theft, or natural disasters, while also providing liability coverage for injuries occurring on the property. This insurance covers the cost of repairs, replacement of personal belongings, and medical expenses related to accidents on the premises. Unlike title insurance, which safeguards against ownership disputes, homeowners insurance focuses on losses and liabilities associated with the physical home and personal property.
Costs and Premiums: Title vs Homeowners Insurance
Title insurance typically involves a one-time premium paid at closing, ranging from 0.5% to 1% of the property's purchase price, while homeowners insurance requires ongoing annual premiums averaging $1,200 to $1,500 depending on location and coverage. Title insurance protects against past ownership disputes and title defects, whereas homeowners insurance covers property damage and liability risks during ownership. Buyers should compare these costs carefully, considering title insurance as a crucial upfront safeguard and homeowners insurance as an essential recurring expense for property protection.
Choosing the Right Coverage for Your Property
Title insurance protects against legal issues related to property ownership, such as liens or title defects, ensuring clear ownership rights. Homeowners insurance covers property damage and personal liability from events like fire, theft, or natural disasters. Selecting the right coverage depends on securing both title protection for ownership disputes and homeowners insurance for physical and liability risks, providing comprehensive property security.
FAQs: Title Insurance vs Homeowners Insurance
Title insurance protects against defects in property ownership, such as liens or encumbrances, discovered after purchase, ensuring clear title transfer. Homeowners insurance covers property damage and liability for incidents like fire, theft, or accidents occurring on the home premises. Buyers often ask if both are necessary, with experts confirming title insurance safeguards ownership rights while homeowners insurance protects the physical property and personal liability.
Title Insurance vs Homeowners Insurance Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com