Functional obsolescence occurs when a property's design, layout, or features become outdated, reducing its utility and market value compared to newer buildings. Economic obsolescence results from external factors such as changes in neighborhood conditions, zoning laws, or economic shifts that negatively impact property value regardless of its physical condition. Understanding the distinction between these types of obsolescence is crucial for accurate property valuation and investment decisions.
Table of Comparison
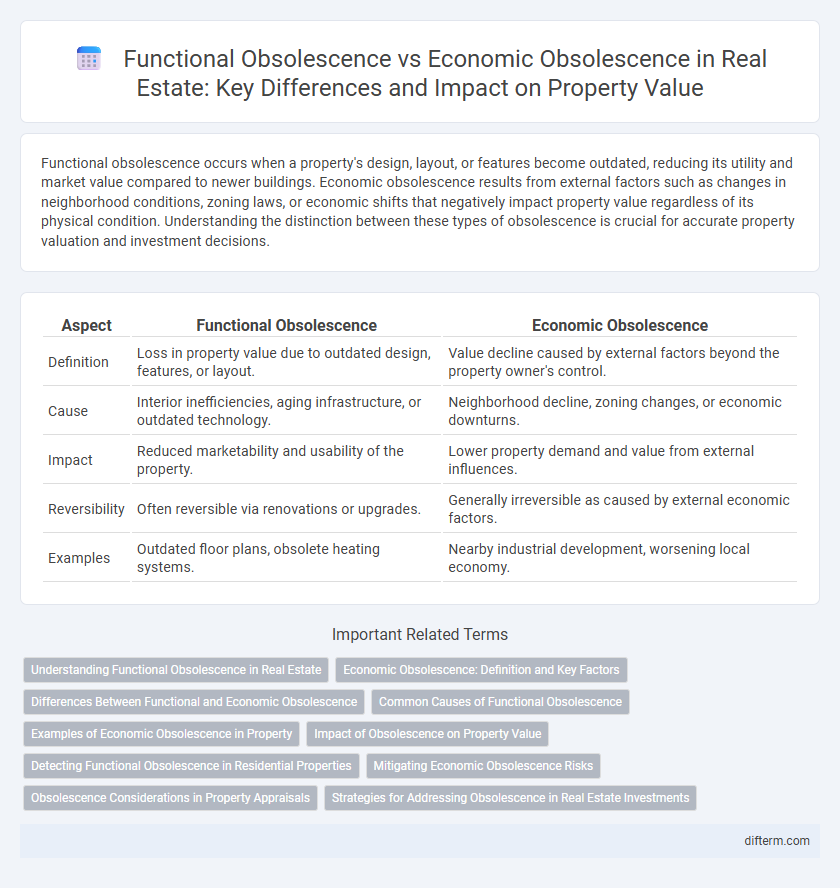
| Aspect | Functional Obsolescence | Economic Obsolescence |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Loss in property value due to outdated design, features, or layout. | Value decline caused by external factors beyond the property owner's control. |
| Cause | Interior inefficiencies, aging infrastructure, or outdated technology. | Neighborhood decline, zoning changes, or economic downturns. |
| Impact | Reduced marketability and usability of the property. | Lower property demand and value from external influences. |
| Reversibility | Often reversible via renovations or upgrades. | Generally irreversible as caused by external economic factors. |
| Examples | Outdated floor plans, obsolete heating systems. | Nearby industrial development, worsening local economy. |
Understanding Functional Obsolescence in Real Estate
Functional obsolescence in real estate refers to a loss in property value due to outdated design, features, or layout that no longer meet current market demands, such as inefficient floor plans or insufficient electrical wiring. This differs from economic obsolescence, which stems from external factors like neighborhood decline or zoning changes affecting property desirability. Accurately assessing functional obsolescence helps investors and appraisers determine necessary renovations or adjustments to improve a property's market competitiveness and value.
Economic Obsolescence: Definition and Key Factors
Economic obsolescence refers to the loss of property value caused by external factors beyond the property's control, such as changes in zoning laws, increased crime rates, or shifts in neighborhood demographics. Key factors include proximity to undesirable land uses, environmental hazards, and broader economic downturns impacting market demand. Unlike functional obsolescence, economic obsolescence cannot be remedied by property improvements or renovations.
Differences Between Functional and Economic Obsolescence
Functional obsolescence in real estate refers to the loss in property value due to outdated design features, poor layout, or inadequacies that affect the building's utility or appeal. Economic obsolescence occurs from external factors, such as neighborhood decline, zoning changes, or environmental issues, which negatively impact the property's market value. The primary difference lies in functional obsolescence being an internal issue related to the property's physical characteristics, while economic obsolescence stems from external economic or environmental influences beyond the owner's control.
Common Causes of Functional Obsolescence
Common causes of functional obsolescence in real estate include outdated architectural designs, inadequate room layouts, and obsolete mechanical systems such as heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC). Properties with insufficient electrical wiring capacity or lack of modern amenities often experience reduced market value due to diminished functionality. These issues impact the property's utility and desirability, leading to decreased investment appeal despite the physical conditions remaining intact.
Examples of Economic Obsolescence in Property
Economic obsolescence in real estate refers to the loss of property value due to external or environmental factors beyond the property's control, such as proximity to industrial sites, declining neighborhood quality, or changes in zoning laws. Examples include a residential property losing value because of nearby high-traffic highways causing noise and pollution or commercial buildings affected by shifts in local economic conditions, like the closure of a major employer. Unlike functional obsolescence, which relates to internal design or layout issues, economic obsolescence impacts the property's marketability due to external influences.
Impact of Obsolescence on Property Value
Functional obsolescence reduces property value by diminishing utility or appeal due to outdated design, features, or layout, such as inefficient floor plans or obsolete building systems. Economic obsolescence impacts property value through external factors beyond the property's control, including changes in neighborhood demographics, zoning laws, or nearby developments that decrease desirability. Both forms of obsolescence cause depreciation but economic obsolescence typically results in more significant and irreversible value loss.
Detecting Functional Obsolescence in Residential Properties
Detecting functional obsolescence in residential properties involves identifying outdated design features that reduce usability, such as inadequate room layouts, insufficient bathrooms, or obsolete electrical systems. This type of depreciation often arises from changes in homeowner preferences and modern living standards, impacting property value more directly than economic obsolescence. Professional inspections and market comparisons are essential tools for assessing functional deficiencies relative to current real estate trends.
Mitigating Economic Obsolescence Risks
Mitigating economic obsolescence risks requires strategic property location analysis and market trend monitoring to avoid depreciation from external factors like neighborhood decline or zoning changes. Investing in adaptive reuse and sustainable upgrades can enhance asset resilience, preserving value despite adverse economic shifts. Effective risk management also involves diversifying real estate portfolios to minimize exposure to area-specific market downturns.
Obsolescence Considerations in Property Appraisals
Functional obsolescence in property appraisals refers to the loss in value due to outdated design, layout, or features that no longer meet current market standards, such as insufficient electrical capacity or obsolete floor plans. Economic obsolescence arises from external factors affecting property value, like declining neighborhood conditions or zoning changes that reduce desirability. Accurate appraisal requires distinguishing these obsolescence types to assess depreciation effects and provide a realistic market value estimate.
Strategies for Addressing Obsolescence in Real Estate Investments
Implementing renovation and modernization plans helps counter functional obsolescence by updating property features to meet current market standards and tenant expectations. Economic obsolescence can be mitigated by conducting thorough market analysis and selecting locations with stable economic indicators, reducing exposure to external factors like neighborhood decline or zoning changes. Investors often leverage adaptive reuse strategies and negotiate favorable lease terms to maintain asset value despite obsolescence challenges.
functional obsolescence vs economic obsolescence Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com