Rent-to-own agreements allow tenants to apply a portion of their monthly rent toward purchasing the property, providing a pathway to homeownership without immediate full commitment. Lease options give tenants the right, but not the obligation, to buy the property at a predetermined price within a specific timeframe, offering flexibility and potential price advantages. Both strategies can benefit buyers with limited upfront capital, but understanding the financial terms and legal implications is crucial before deciding.
Table of Comparison
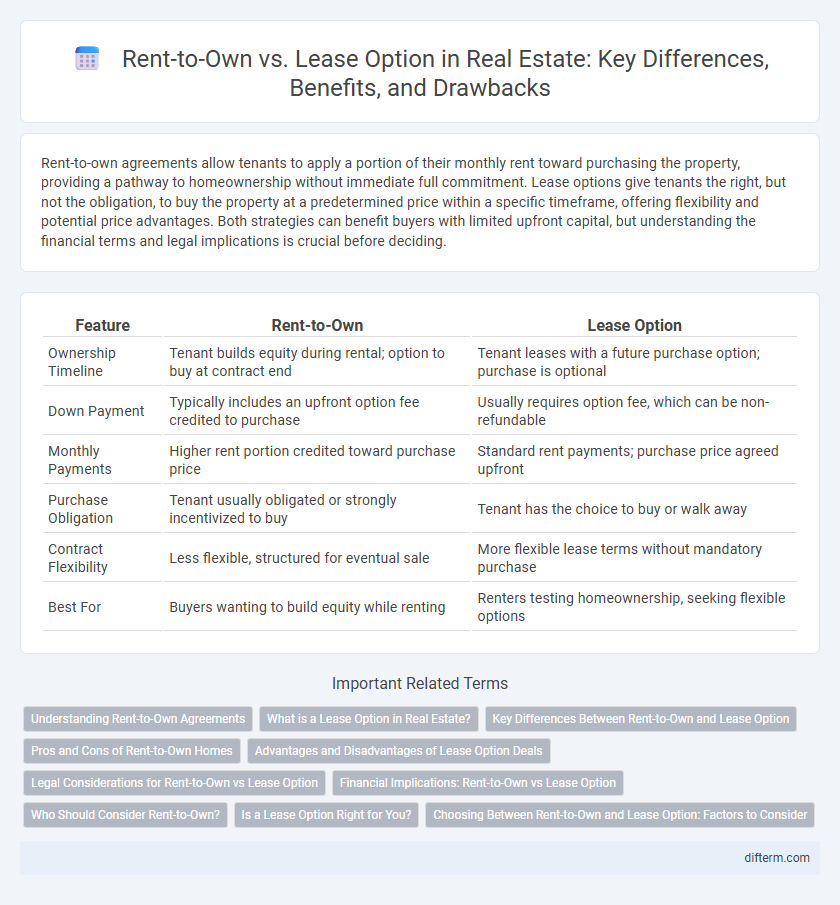
| Feature | Rent-to-Own | Lease Option |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership Timeline | Tenant builds equity during rental; option to buy at contract end | Tenant leases with a future purchase option; purchase is optional |
| Down Payment | Typically includes an upfront option fee credited to purchase | Usually requires option fee, which can be non-refundable |
| Monthly Payments | Higher rent portion credited toward purchase price | Standard rent payments; purchase price agreed upfront |
| Purchase Obligation | Tenant usually obligated or strongly incentivized to buy | Tenant has the choice to buy or walk away |
| Contract Flexibility | Less flexible, structured for eventual sale | More flexible lease terms without mandatory purchase |
| Best For | Buyers wanting to build equity while renting | Renters testing homeownership, seeking flexible options |
Understanding Rent-to-Own Agreements
Rent-to-own agreements allow tenants to rent a property with the option to purchase it later, with a portion of the rent applied toward the home's purchase price, creating a pathway to homeownership. Lease option agreements give tenants the right, but not the obligation, to buy the property at a predetermined price within the lease term, offering flexibility but typically less commitment than rent-to-own contracts. Understanding the financial obligations, purchase price terms, and contract duration is essential for both landlords and tenants to assess the benefits and risks of these alternative home-buying arrangements.
What is a Lease Option in Real Estate?
A lease option in real estate is a contract that combines a traditional lease agreement with an exclusive option to purchase the property at a predetermined price within a specified time frame. This arrangement allows tenants to rent the home while building equity and deciding whether to buy without committing upfront to a mortgage. Lease options provide flexibility for both buyers seeking time to improve credit scores and sellers aiming for steady rental income with potential future sale benefits.
Key Differences Between Rent-to-Own and Lease Option
Rent-to-own agreements typically involve a portion of the monthly rent applied toward the eventual purchase price, providing tenants an opportunity to build equity over time. Lease options grant tenants the right, but not the obligation, to buy the property at a predetermined price within a specified timeframe, often requiring an upfront option fee. While rent-to-own blends renting with a gradual path to ownership, lease options primarily offer flexibility without mandatory purchase commitment.
Pros and Cons of Rent-to-Own Homes
Rent-to-own homes offer the advantage of building equity while renting, providing a pathway to homeownership without immediate mortgage qualification. This option allows renters to lock in the purchase price and apply a portion of rent toward the down payment, fostering financial discipline and credit improvement. However, rent-to-own agreements often require higher monthly payments and non-refundable option fees, with the risk of forfeiting these if the buyer chooses not to purchase.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Lease Option Deals
Lease option deals offer tenants the advantage of locking in a purchase price while renting, providing the opportunity to build equity and test the property before full commitment. Disadvantages include higher monthly payments due to option fees, and the risk of losing the option fee if the buyer decides not to purchase. This arrangement benefits tenants seeking flexibility but requires careful consideration of contract terms and market conditions.
Legal Considerations for Rent-to-Own vs Lease Option
Rent-to-own agreements often create a hybrid legal status, combining elements of both rental and purchase contracts, which may complicate tenant rights and obligations during the contract term. Lease options typically grant tenants the exclusive right to purchase the property at a predetermined price without obligating them, reducing risk but requiring clear documentation to avoid misunderstandings. Legal considerations for rent-to-own versus lease option agreements include contract enforceability, disclosure requirements, tenant protections under landlord-tenant laws, and state-specific regulations governing purchase price adjustments and option periods.
Financial Implications: Rent-to-Own vs Lease Option
Rent-to-own agreements typically require higher monthly payments, part of which is credited toward the eventual purchase price, benefiting buyers aiming to build equity during the rental period. Lease options usually involve lower upfront costs and option fees but may lack long-term financial benefits if the purchase is not exercised. Evaluating total costs, including option fees, rent premiums, and purchase price adjustments, is essential for understanding the financial implications of each contract type.
Who Should Consider Rent-to-Own?
Rent-to-own agreements are ideal for potential homebuyers with limited credit history or insufficient down payment savings who seek a pathway to homeownership while living in the property. Rent-to-own options suit individuals aiming to build equity and improve financial standing during the rental phase before finalizing the purchase. Tenants looking for flexibility combined with a future purchase plan often find rent-to-own contracts advantageous compared to traditional lease options.
Is a Lease Option Right for You?
A lease option allows tenants to rent a property with the exclusive right to purchase it within a specified timeframe, combining flexibility with future ownership potential. This arrangement benefits individuals who may need time to improve credit or save for a down payment while locking in a purchase price. Evaluating your financial stability, long-term goals, and market conditions can help determine if a lease option aligns with your path to homeownership.
Choosing Between Rent-to-Own and Lease Option: Factors to Consider
Choosing between rent-to-own and lease option agreements depends on factors like upfront costs, contract flexibility, and eventual ownership rights. Rent-to-own typically requires a higher initial option fee but secures a portion of rent toward purchase, ideal for buyers wanting to commit gradually. Lease options offer more flexible terms with lower upfront fees but may not always guarantee purchase, suiting renters seeking optional ownership paths.
rent-to-own vs lease option Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com