Foreclosure occurs when a lender takes legal action to repossess a property due to the owner's failure to meet mortgage payments, often resulting in a lengthy, credit-damaging process. A deed in lieu of foreclosure involves the homeowner voluntarily transferring the property deed to the lender to avoid the foreclosure process, which can be less damaging to credit and faster to complete. Understanding the distinctions between these two options is crucial for homeowners seeking alternatives to foreclosure and minimizing financial impact.
Table of Comparison
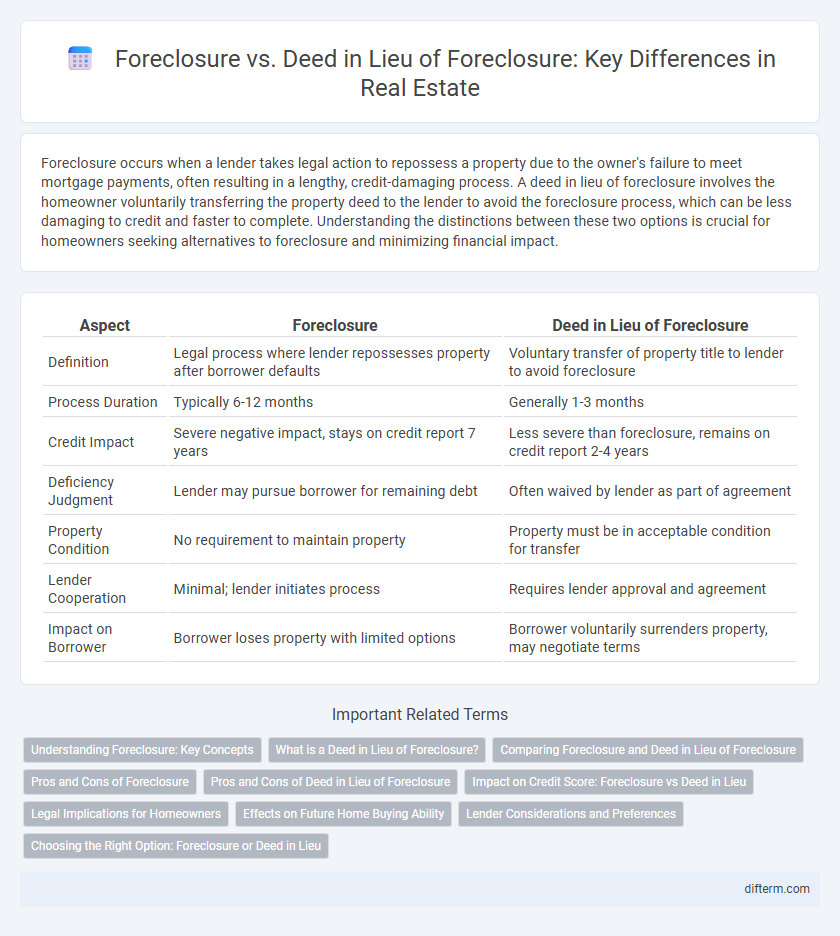
| Aspect | Foreclosure | Deed in Lieu of Foreclosure |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal process where lender repossesses property after borrower defaults | Voluntary transfer of property title to lender to avoid foreclosure |
| Process Duration | Typically 6-12 months | Generally 1-3 months |
| Credit Impact | Severe negative impact, stays on credit report 7 years | Less severe than foreclosure, remains on credit report 2-4 years |
| Deficiency Judgment | Lender may pursue borrower for remaining debt | Often waived by lender as part of agreement |
| Property Condition | No requirement to maintain property | Property must be in acceptable condition for transfer |
| Lender Cooperation | Minimal; lender initiates process | Requires lender approval and agreement |
| Impact on Borrower | Borrower loses property with limited options | Borrower voluntarily surrenders property, may negotiate terms |
Understanding Foreclosure: Key Concepts
Foreclosure occurs when a lender seizes a property due to the borrower's failure to make mortgage payments, often leading to a public auction. A deed in lieu of foreclosure allows the borrower to voluntarily transfer the property title to the lender to avoid foreclosure proceedings and protect credit rating. Understanding these processes helps homeowners evaluate financial risks and explore alternatives to mitigate losses in default situations.
What is a Deed in Lieu of Foreclosure?
A Deed in Lieu of Foreclosure is a legal agreement where a homeowner voluntarily transfers property ownership to the lender to avoid foreclosure proceedings. This option helps borrowers prevent the public stigma of foreclosure and potentially reduces damage to their credit score compared to a full foreclosure. Lenders accept this deed to recover their losses more quickly and minimize legal expenses associated with foreclosure.
Comparing Foreclosure and Deed in Lieu of Foreclosure
Foreclosure is a legal process where a lender forces the sale of a property due to the borrower's default on mortgage payments, often resulting in a public auction and a significant credit score impact. A deed in lieu of foreclosure allows the borrower to voluntarily transfer the property title to the lender to avoid the foreclosure process, which can minimize credit damage and reduce legal expenses. While foreclosure is typically more time-consuming and costly, a deed in lieu offers a faster resolution but requires lender approval and may not eliminate all outstanding debts.
Pros and Cons of Foreclosure
Foreclosure allows lenders to recover the loan balance by selling the property, but it severely impacts the homeowner's credit score for up to seven years and can lead to a lengthy, public legal process. The process can cause significant financial and emotional strain, often resulting in deficiency judgments if the sale proceeds do not cover the mortgage balance. Despite these drawbacks, foreclosure helps lenders enforce mortgage agreements and recoup losses, though it typically results in longer recovery times and higher costs compared to alternatives like a deed in lieu of foreclosure.
Pros and Cons of Deed in Lieu of Foreclosure
A deed in lieu of foreclosure allows homeowners to transfer ownership of their property to the lender, avoiding the lengthy foreclosure process and reducing credit damage compared to foreclosure, with a typical impact lasting around 2-4 years on credit reports. This option can expedite debt resolution and reduce legal fees but may not eliminate all deficiency judgments, and not all lenders accept deed in lieu agreements. Borrowers should consider potential tax implications and the loss of housing before choosing this alternative to traditional foreclosure.
Impact on Credit Score: Foreclosure vs Deed in Lieu
A foreclosure can cause a significant drop in your credit score, often ranging from 85 to 160 points, and remains on your credit report for up to seven years. In contrast, a deed in lieu of foreclosure generally results in a less severe impact, typically lowering your credit score by 50 to 100 points, and it may be reported more favorably by lenders. Both options negatively affect creditworthiness, but a deed in lieu often provides a softer credit impact and may facilitate quicker recovery for future mortgage approvals.
Legal Implications for Homeowners
Foreclosure initiates a legal process where lenders repossess the property through court action, often severely impacting homeowners' credit scores and resulting in potential deficiency judgments. A deed in lieu of foreclosure allows homeowners to voluntarily transfer property ownership to the lender, usually minimizing legal fees and avoiding the public court process, but may still affect credit and eligibility for future loans. Homeowners must carefully evaluate state laws and lender policies, as some jurisdictions have specific regulations regarding deficiency judgments and redemption periods linked to both foreclosure and deed in lieu transactions.
Effects on Future Home Buying Ability
Foreclosure severely damages credit scores, often leading to a waiting period of seven years before qualifying for a new mortgage, whereas a deed in lieu of foreclosure typically results in a shorter recovery time and less negative impact on credit. Both options impact future home buying ability, but lenders tend to view deed in lieu more favorably, improving chances of approval sooner. Understanding these effects can help homeowners make informed decisions to preserve long-term financial stability and homeownership opportunities.
Lender Considerations and Preferences
Lenders often prefer deeds in lieu of foreclosure because they allow for a quicker resolution and reduce legal costs associated with foreclosure proceedings. Foreclosure can be lengthy and costly, involving court processes that may delay recovery of loan amounts. Deeds in lieu provide lenders with clear title to the property, minimizing risks of liens or additional claims.
Choosing the Right Option: Foreclosure or Deed in Lieu
Choosing between foreclosure and deed in lieu of foreclosure depends on the homeowner's financial situation and credit impact. A deed in lieu of foreclosure typically results in less damage to credit scores and faster resolution but requires lender approval and surrender of the property voluntarily. Foreclosure is a legal process that can lead to longer credit recovery times and additional fees, making deed in lieu a preferable option for avoiding extended financial hardship.
foreclosure vs deed in lieu of foreclosure Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com