A sovereign wealth fund manages state-owned assets and invests globally to stabilize the economy and generate long-term returns, often derived from natural resource revenues or budget surpluses. Pension funds pool contributions from workers and employers to provide retirement income, focusing on steady, long-term growth with lower risk tolerance. Both funds play critical roles in economic stability and wealth management but differ fundamentally in their sources of capital and investment objectives.
Table of Comparison
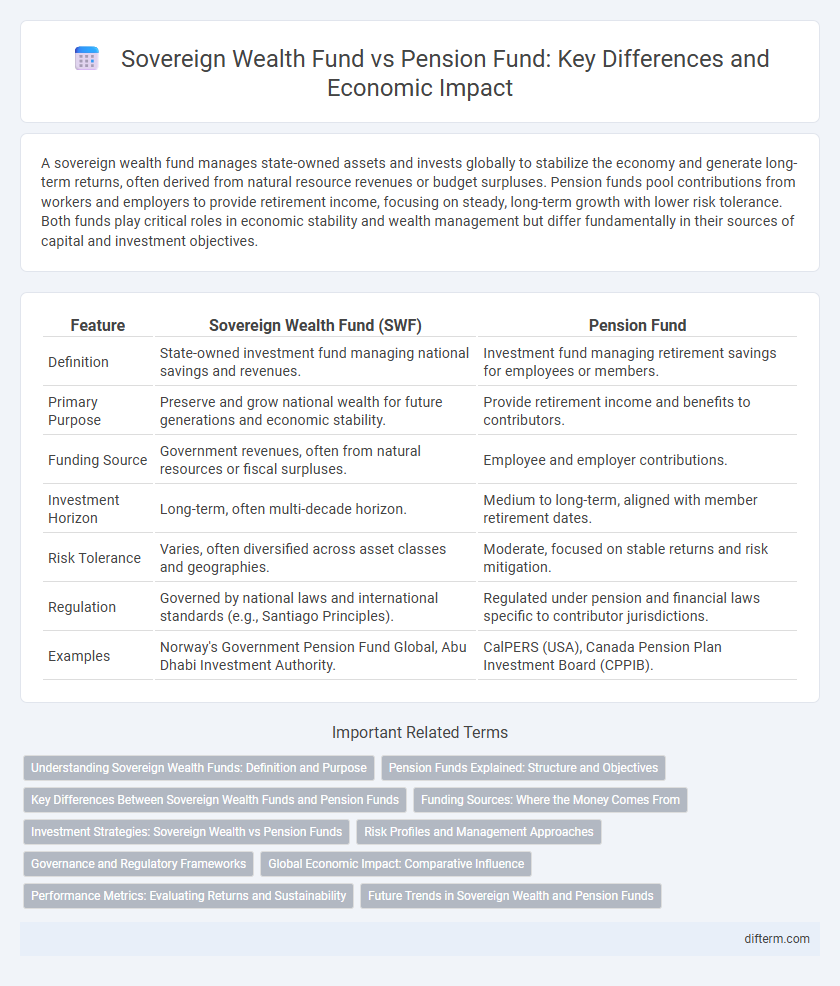
| Feature | Sovereign Wealth Fund (SWF) | Pension Fund |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | State-owned investment fund managing national savings and revenues. | Investment fund managing retirement savings for employees or members. |
| Primary Purpose | Preserve and grow national wealth for future generations and economic stability. | Provide retirement income and benefits to contributors. |
| Funding Source | Government revenues, often from natural resources or fiscal surpluses. | Employee and employer contributions. |
| Investment Horizon | Long-term, often multi-decade horizon. | Medium to long-term, aligned with member retirement dates. |
| Risk Tolerance | Varies, often diversified across asset classes and geographies. | Moderate, focused on stable returns and risk mitigation. |
| Regulation | Governed by national laws and international standards (e.g., Santiago Principles). | Regulated under pension and financial laws specific to contributor jurisdictions. |
| Examples | Norway's Government Pension Fund Global, Abu Dhabi Investment Authority. | CalPERS (USA), Canada Pension Plan Investment Board (CPPIB). |
Understanding Sovereign Wealth Funds: Definition and Purpose
Sovereign wealth funds (SWFs) are state-owned investment pools established to manage national wealth, typically derived from budget surpluses, commodity exports, or foreign exchange reserves. Their primary purpose is to achieve long-term returns that stabilize the economy, support fiscal policies, and fund future generations. Unlike pension funds, which specifically aim to meet retirement liabilities for public or private sector employees, SWFs serve broader economic stabilization and development goals.
Pension Funds Explained: Structure and Objectives
Pension funds are investment pools that manage retirement savings for employees, structured to provide long-term income security through diversified asset allocation including equities, bonds, and real estate. Their primary objective is to ensure stable, inflation-adjusted pension payouts by optimizing risk and return over extended periods, often spanning several decades. Compared to sovereign wealth funds, pension funds are more focused on fulfilling specific beneficiary obligations rather than strategic national wealth management.
Key Differences Between Sovereign Wealth Funds and Pension Funds
Sovereign wealth funds are state-owned investment vehicles primarily funded by national revenues, such as oil exports or trade surpluses, whereas pension funds are managed on behalf of individual contributors to provide retirement benefits. Sovereign wealth funds typically have broader mandates to stabilize the economy and generate long-term wealth, while pension funds focus on meeting future pension liabilities and ensuring retirees' financial security. Risk tolerance and investment horizons also differ significantly, with sovereign wealth funds often pursuing more diversified, global portfolios compared to the relatively conservative strategies of pension funds.
Funding Sources: Where the Money Comes From
Sovereign wealth funds primarily receive their funding from national revenues such as surplus fiscal budgets, commodity exports like oil and gas, and foreign exchange reserves accumulated by governments. Pension funds are mainly financed through mandatory contributions from employees and employers, along with investment returns on those contributions over time. Both fund types rely on distinct sources reflecting their roles: sovereign wealth funds serve national fiscal stability and investment, while pension funds focus on securing retirement benefits.
Investment Strategies: Sovereign Wealth vs Pension Funds
Sovereign wealth funds typically pursue long-term, diversified investment strategies across global equities, real estate, and alternative assets to maximize national wealth while managing macroeconomic risks. Pension funds focus on balancing growth and liability matching by investing in fixed income, equities, and inflation-protected securities to ensure stable payouts for retirees. Sovereign wealth funds often have higher risk tolerance due to their large capital base and longer investment horizons compared to pension funds' relatively conservative, liability-driven approaches.
Risk Profiles and Management Approaches
Sovereign wealth funds (SWFs) typically manage national savings with a focus on long-term economic stability, often adopting diversified, conservative investment strategies to mitigate geopolitical and market risks. Pension funds prioritize steady, predictable returns to meet future liabilities for retirees, emphasizing fixed-income securities and liability-driven investment approaches to minimize shortfall risk. Risk management in SWFs involves balancing national economic objectives and intergenerational wealth preservation, while pension funds apply actuarial models and stress testing to ensure long-term solvency and cash flow adequacy.
Governance and Regulatory Frameworks
Sovereign wealth funds are typically governed by state-level regulations emphasizing national economic stability and strategic investments, often operating under strict transparency and accountability standards mandated by government statutes. Pension funds, managed primarily under labor and fiduciary laws, prioritize beneficiary interests with governance frameworks designed to ensure long-term retirement income security and compliance with pension-specific regulatory authorities. Differences in regulatory oversight reflect their distinct objectives, risk profiles, and stakeholder obligations within the broader economic environment.
Global Economic Impact: Comparative Influence
Sovereign wealth funds, often backed by state revenues from natural resources or fiscal surpluses, wield significant influence in stabilizing global financial markets and funding large-scale infrastructure projects. Pension funds, driven by long-term retirement savings, provide substantial capital for private sector growth and corporate governance improvements worldwide. Together, these funds shape capital allocation patterns, risk management strategies, and economic development trajectories on an international scale.
Performance Metrics: Evaluating Returns and Sustainability
Sovereign wealth funds (SWFs) typically prioritize long-term national economic stability and often measure performance through aggregate returns and impact on fiscal balance, while pension funds emphasize consistent, risk-adjusted returns aligned with beneficiaries' retirement timelines. Performance metrics for SWFs include total asset growth, contribution to sovereign wealth, and intergenerational equity, whereas pension funds focus on funded status, actuarial soundness, and funding ratios. Sustainability assessment in SWFs involves environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors integrated with macroeconomic resilience, contrasted by pension funds' focus on demographic trends, cash flow stability, and solvency over the retirement horizon.
Future Trends in Sovereign Wealth and Pension Funds
Sovereign wealth funds are increasingly diversifying portfolios with a strong emphasis on sustainable and technology-driven investments, while pension funds prioritize long-term liability matching and inflation protection strategies. Digital transformation and ESG integration are key trends shaping the future, with both fund types adopting advanced data analytics and climate risk assessments to enhance decision-making. Collaboration between sovereign wealth funds and pension funds is expected to grow, leveraging scale to access alternative assets and co-investment opportunities.
Sovereign wealth fund vs pension fund Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com