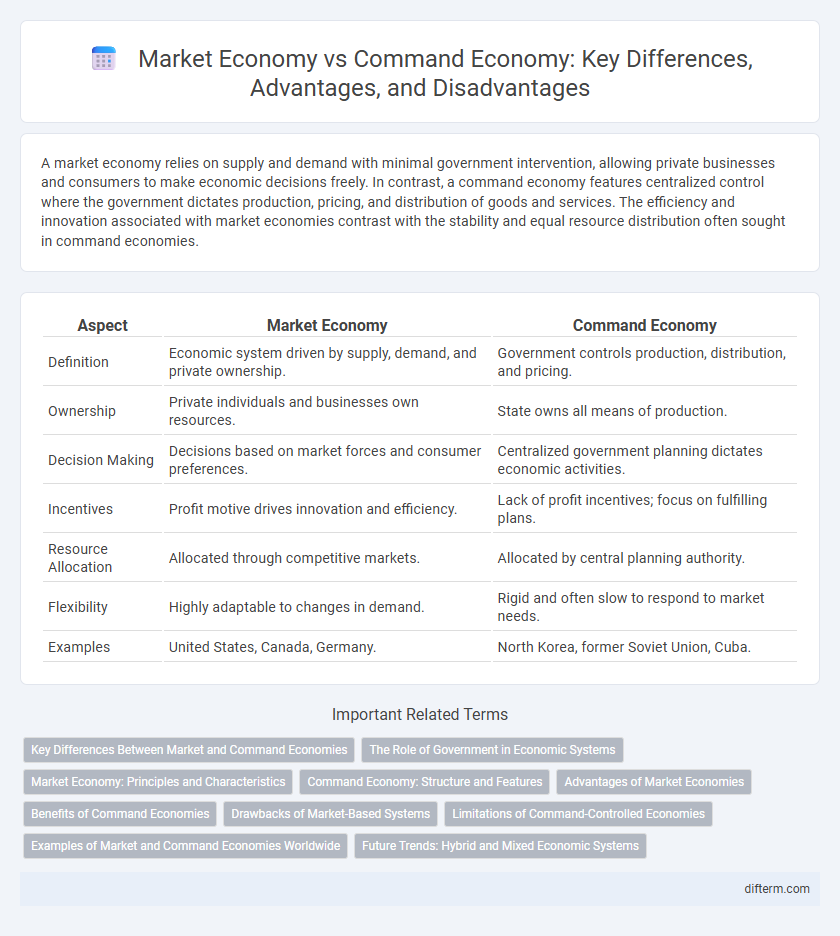
A market economy relies on supply and demand with minimal government intervention, allowing private businesses and consumers to make economic decisions freely. In contrast, a command economy features centralized control where the government dictates production, pricing, and distribution of goods and services. The efficiency and innovation associated with market economies contrast with the stability and equal resource distribution often sought in command economies.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Market Economy | Command Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Economic system driven by supply, demand, and private ownership. | Government controls production, distribution, and pricing. |
| Ownership | Private individuals and businesses own resources. | State owns all means of production. |
| Decision Making | Decisions based on market forces and consumer preferences. | Centralized government planning dictates economic activities. |
| Incentives | Profit motive drives innovation and efficiency. | Lack of profit incentives; focus on fulfilling plans. |
| Resource Allocation | Allocated through competitive markets. | Allocated by central planning authority. |
| Flexibility | Highly adaptable to changes in demand. | Rigid and often slow to respond to market needs. |
| Examples | United States, Canada, Germany. | North Korea, former Soviet Union, Cuba. |
Key Differences Between Market and Command Economies
Market economies rely on supply and demand to allocate resources, promoting competition and consumer choice, while command economies depend on centralized government control to direct production and distribution. In market economies, prices are determined by the interplay of buyers and sellers, whereas in command economies, prices and output levels are set by government planning agencies. The efficiency and innovation driven by market incentives contrast with the stability and equitable resource distribution aimed for in command economic systems.
The Role of Government in Economic Systems
In a market economy, government intervention is limited to enforcing property rights, ensuring competition, and correcting market failures, allowing supply and demand to drive production and pricing. Conversely, a command economy features extensive government control where central planners dictate resource allocation, production targets, and pricing, aiming for equitable distribution and stability. The degree of government involvement defines economic efficiency, innovation incentives, and overall market responsiveness within these distinct systems.
Market Economy: Principles and Characteristics
Market economy operates on the principles of supply and demand, where prices are determined by consumer preferences and competition among businesses. It emphasizes private ownership of resources, decentralized decision-making, and minimal government intervention, fostering innovation and efficiency. Key characteristics include voluntary exchange, profit motive, and the allocation of resources through market mechanisms.
Command Economy: Structure and Features
A command economy is characterized by centralized government control over production, resource allocation, and pricing decisions, with the state dictating economic priorities to achieve specific social or political goals. Key features include a lack of competition, government ownership of major industries, and planned production targets that replace market-driven supply and demand mechanisms. This structure often results in limited consumer choice and reduced incentives for innovation due to the absence of market signals.
Advantages of Market Economies
Market economies foster efficient resource allocation through supply and demand mechanisms, promoting innovation and consumer choice. Entrepreneurs in market economies are incentivized to improve products and services, driving economic growth and competitiveness. This system also adapts quickly to changing market conditions, enhancing flexibility and resilience in the economy.
Benefits of Command Economies
Command economies offer centralized control that enables efficient allocation of resources toward national priorities, such as infrastructure and defense. This system reduces market uncertainties by eliminating supply and demand fluctuations, leading to price stability and predictable production outputs. Government planning can mobilize labor and capital swiftly during crises, ensuring rapid responses to economic challenges.
Drawbacks of Market-Based Systems
Market-based systems often face drawbacks such as income inequality, resource misallocation, and market failures like monopolies or externalities. These issues can result in uneven wealth distribution and under-provision of essential public goods. The absence of centralized control may also lead to economic instability and cyclical fluctuations.
Limitations of Command-Controlled Economies
Command-controlled economies often suffer from inefficiencies due to centralized decision-making, which limits responsiveness to consumer demands and market signals. Resource allocation is typically rigid, causing persistent shortages or surpluses and stifling innovation and productivity growth. The lack of competition reduces incentives for efficiency, resulting in slower economic progress compared to market economies.
Examples of Market and Command Economies Worldwide
Market economies like the United States, Canada, and Australia rely on supply and demand principles with minimal government intervention, promoting innovation and consumer choice. Command economies such as North Korea, Cuba, and the former Soviet Union feature centralized government control over production and distribution, often leading to inefficiencies and resource misallocation. Mixed economies like China and Russia incorporate elements of both, balancing market forces with strategic state planning to drive economic growth.
Future Trends: Hybrid and Mixed Economic Systems
Future economic models increasingly blend characteristics of market and command economies, forming hybrid or mixed systems that leverage both government regulation and market-driven innovation. These mixed economies aim to balance efficient resource allocation with social welfare objectives, adapting to technological advancements and global economic shifts. Emerging trends emphasize dynamic policy frameworks and public-private partnerships to foster sustainable growth and economic resilience.
market economy vs command economy Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com