A free market economy thrives on supply and demand with minimal government intervention, encouraging innovation and consumer choice. In contrast, a command economy relies on centralized planning where the government controls production and distribution, aiming to achieve equality and stability. Each system presents distinct advantages and challenges in resource allocation and economic growth.
Table of Comparison
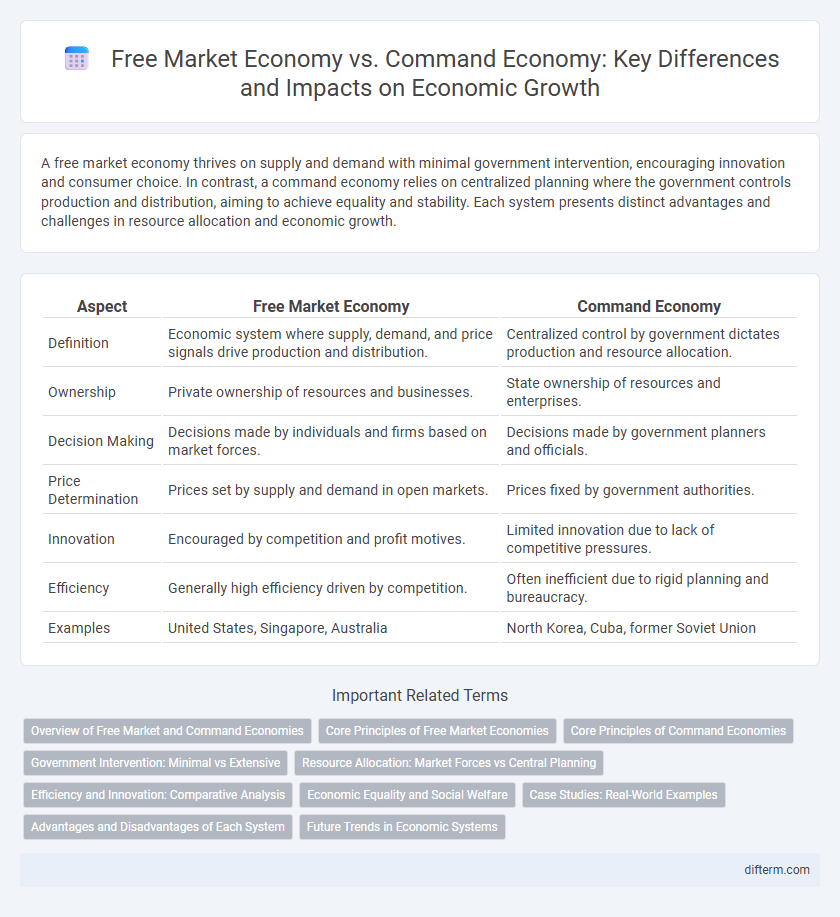
| Aspect | Free Market Economy | Command Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Economic system where supply, demand, and price signals drive production and distribution. | Centralized control by government dictates production and resource allocation. |
| Ownership | Private ownership of resources and businesses. | State ownership of resources and enterprises. |
| Decision Making | Decisions made by individuals and firms based on market forces. | Decisions made by government planners and officials. |
| Price Determination | Prices set by supply and demand in open markets. | Prices fixed by government authorities. |
| Innovation | Encouraged by competition and profit motives. | Limited innovation due to lack of competitive pressures. |
| Efficiency | Generally high efficiency driven by competition. | Often inefficient due to rigid planning and bureaucracy. |
| Examples | United States, Singapore, Australia | North Korea, Cuba, former Soviet Union |
Overview of Free Market and Command Economies
Free market economies rely on supply and demand to determine prices and production, allowing private individuals and businesses to operate with minimal government intervention. Command economies are characterized by centralized control where the government plans and regulates production, distribution, and pricing of goods and services. The efficiency of resource allocation and innovation tends to be higher in free market systems, while command economies prioritize specific national goals and equitable distribution.
Core Principles of Free Market Economies
Free market economies operate on the core principles of supply and demand, private property rights, and minimal government intervention, enabling consumers and producers to make autonomous decisions. Prices in a free market are determined by competition and consumer preferences, which promote efficiency and innovation. This decentralized decision-making contrasts sharply with command economies, where central authorities control production, pricing, and resource allocation.
Core Principles of Command Economies
Command economies operate on centralized control, where government agencies determine production, distribution, and prices, ensuring resource allocation aligns with national objectives. This system often emphasizes collective ownership of property and prioritizes social welfare over individual profit, reducing competition and market-driven incentives. Central planning aims to stabilize the economy through quotas and fixed targets, minimizing economic fluctuations common in free market systems.
Government Intervention: Minimal vs Extensive
Free market economies feature minimal government intervention, allowing supply and demand to dictate production, pricing, and distribution, which promotes competition and innovation. Command economies rely on extensive government control, where central authorities make key economic decisions, allocate resources, and set prices to achieve specific social or political goals. The degree of government involvement fundamentally impacts economic efficiency, market responsiveness, and individual freedoms within these systems.
Resource Allocation: Market Forces vs Central Planning
Resource allocation in a free market economy is driven by market forces, where supply and demand determine the distribution of goods and services, leading to efficient use of resources through competition and innovation. In contrast, a command economy relies on central planning, with government authorities making decisions about production, investment, and distribution, which can result in resource misallocation and inefficiencies due to lack of market signals. The divergence in these approaches critically impacts economic flexibility, responsiveness, and overall productivity.
Efficiency and Innovation: Comparative Analysis
Free market economies drive higher efficiency by allowing supply and demand to dictate resource allocation, fostering competitive environments that encourage cost reduction and productivity improvements. Innovation thrives in free market systems as businesses seek to gain competitive advantages through new technologies and creative solutions. In contrast, command economies often suffer from inefficiencies due to centralized planning and lack of profit incentives, which can stifle innovation and slow economic growth.
Economic Equality and Social Welfare
Free market economies prioritize individual choice and competition, often leading to wealth disparities and limited social welfare programs due to minimal government intervention. Command economies emphasize economic equality by centralizing control over resources and redistributing wealth through comprehensive social welfare systems. The trade-off between efficiency and equity is central, with command economies achieving greater social welfare at the expense of market flexibility.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples
Free market economies like the United States highlight innovation and consumer choice driven by competition and minimal government intervention, exemplified by Silicon Valley's tech industry growth. In contrast, command economies such as North Korea demonstrate centralized control with state-owned enterprises dominating production and distribution, often leading to inefficiencies and limited consumer goods availability. Case studies reveal how China's mixed economic model integrates state planning with market mechanisms, fostering rapid industrialization and export-led growth.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each System
Free market economies promote innovation and efficiency through competition and consumer choice but can lead to income inequality and market failures without regulation. Command economies ensure resource distribution and social welfare but often suffer from inefficiency, lack of innovation, and bureaucratic delays. Balancing the strengths of both systems remains a key challenge in economic policy design.
Future Trends in Economic Systems
Future trends in economic systems indicate a hybridization of free market economy and command economy elements, leveraging advances in technology and data analytics to optimize resource allocation and social welfare. Integration of artificial intelligence and blockchain technology is expected to enhance transparency, efficiency, and decision-making in mixed economies. Policymakers increasingly focus on adaptive regulatory frameworks that balance market freedom with strategic state intervention to address global challenges such as climate change and income inequality.
Free market economy vs Command economy Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com